Embed presentation


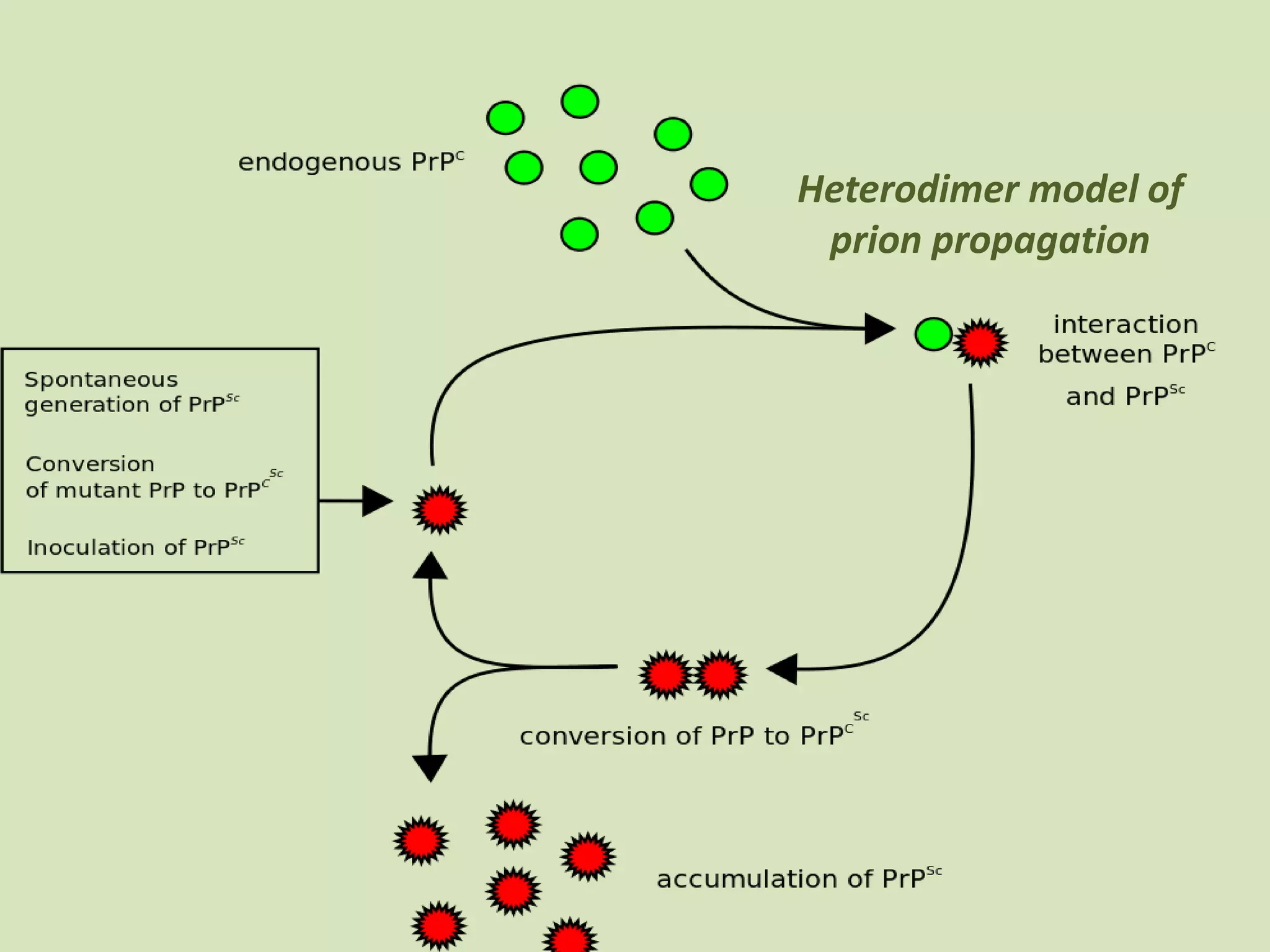
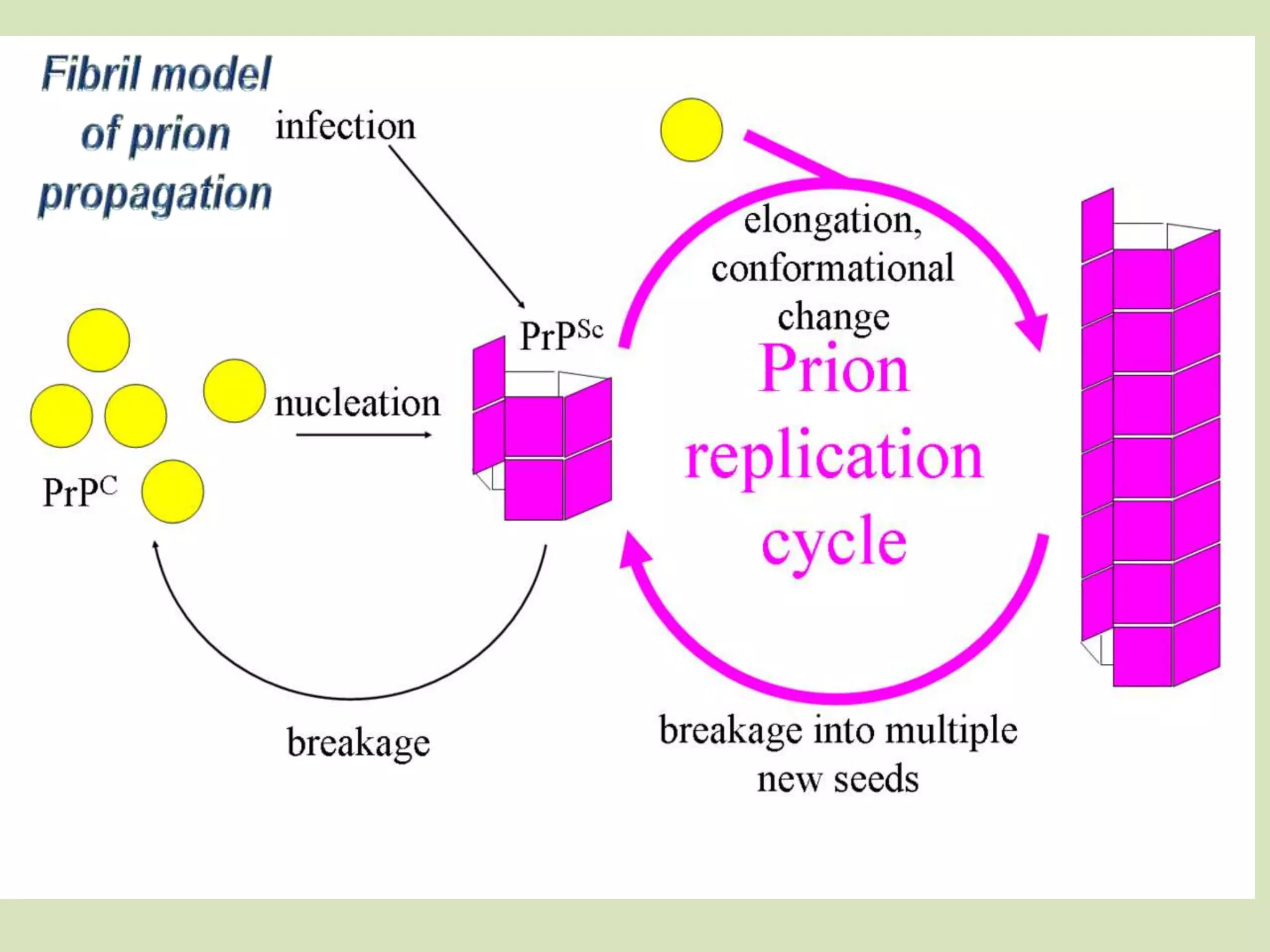


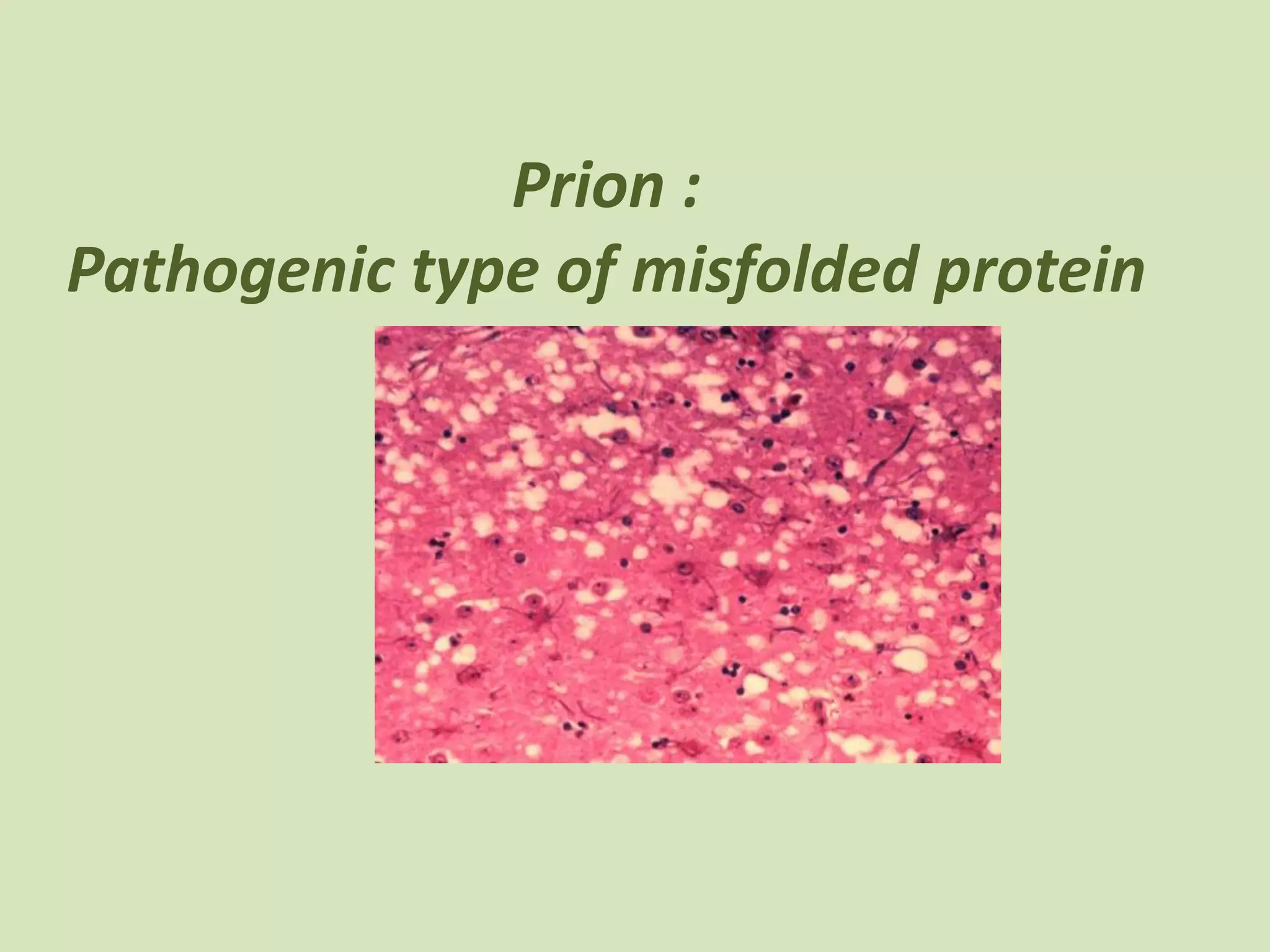

Prions are misfolded proteins that can transmit their misfolded shape to normal variants of the same protein. They are the smallest known infectious agents, contain no genetic material, and have been implicated in diseases like mad cow disease. Prions multiply by converting normal proteins into additional misfolded versions, causing them to accumulate in neurons and not break down. This progressive neuron destruction leaves the brain tissue filled with holes in a spongelike pattern.







