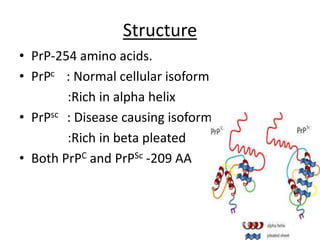
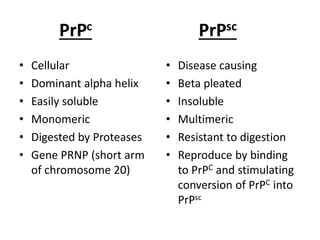
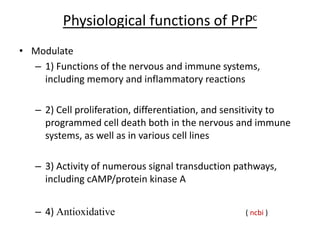
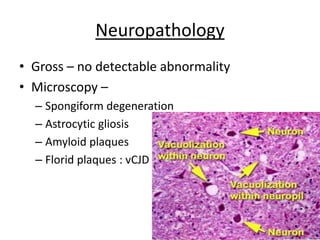
Prions are proteinaceous infectious particles that lack nucleic acid and cause fatal neurodegenerative diseases. They exist in two forms - a normal cellular form (PrPc) and an abnormal disease-causing form (PrPsc). PrPsc has a different structure than PrPc which allows it to accumulate and convert PrPc into more PrPsc, ultimately causing neuropathology. Prion diseases affect both humans and animals and manifest as infectious, genetic, and sporadic disorders with varied clinical presentations. Common features include neurological deficits, dementia, and spongiform changes in the brain. Prions are extremely resistant to decomposition and differ from bacteria and viruses by being protein-only entities that propagate through conversion of