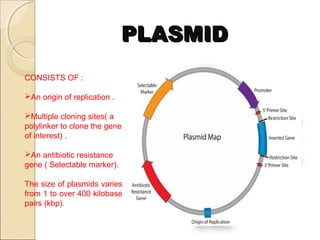
The document discusses plasmids, which are small DNA molecules found in bacteria that can replicate independently of the bacterial chromosome. Plasmids contain genes and can be transferred between bacteria. They have various functions like carrying antibiotic resistance genes or virulence genes. Plasmids are commonly used as cloning vectors in genetic engineering to make copies of genes and produce proteins of interest.