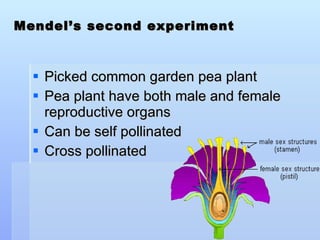
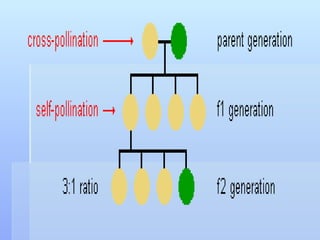
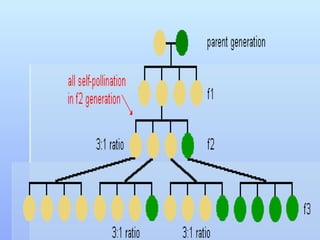
The document discusses basic biological concepts and genetics. It defines cells as the basic unit of life and describes prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell structures. It also summarizes Mendel's experiments with pea plants which demonstrated that traits are passed from parents to offspring through discrete units now called genes, and that genes assort independently during reproduction.