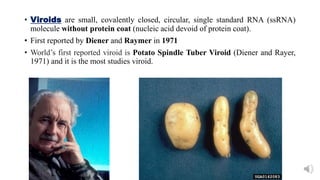
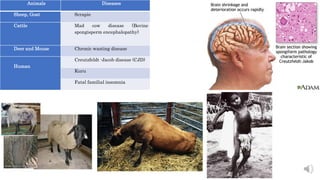
This document discusses viroids, virusoids, and prions. It defines viroids as small, circular, single-stranded RNA molecules without a protein coat that can infect plants. Viroids were first reported in 1971 and the most studied is the Potato Spindle Tuber Viroid. Virusoids are also circular single-stranded RNAs that depend on plant viruses for replication and encapsidation. Prions are small infectious particles composed of abnormally folded protein that can transmit their misfolded shape to normal variants of the same protein.