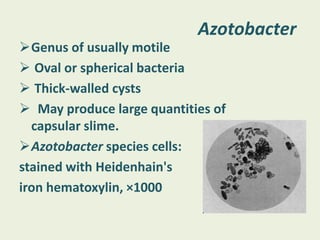
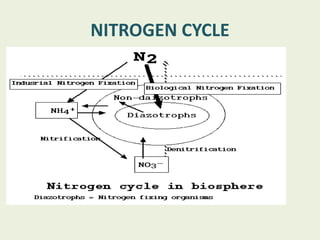
Azotobacter is a genus of free-living, motile bacteria known for its ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, primarily found in neutral to alkaline soils and aquatic environments. These microorganisms possess a unique system of nitrogenase enzymes, enabling their significant metabolic capabilities and making them of interest in agricultural research. Azotobacter also competes for nutrients in the soil and produces growth and fungistatic substances, although nitrogen fixation is inhibited in the presence of available nitrogen sources.