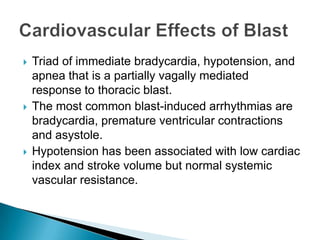
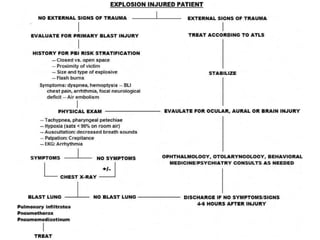
The document provides an update on primary blast injuries, including their classification into various types and their pathophysiology. Key injuries discussed include tympanic membrane rupture, blast lung injury, and gastrointestinal injuries, emphasizing the importance of prompt diagnosis and management strategies. Additionally, the document highlights the complexities in evaluating and treating blast victims due to potential internal injuries and the need for immediate resuscitation efforts.
![Primary Blast Injury: Update on diagnosis and treatmentCrit Care Med 2008; 36:[Suppl.]:S311–S317](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primaryblastinjury-110425113712-phpapp02/85/Primary-Blast-Injury-1-320.jpg)