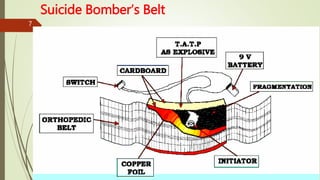
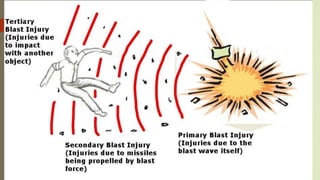
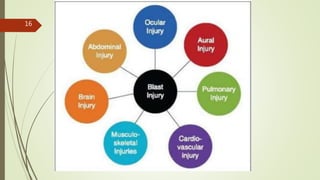
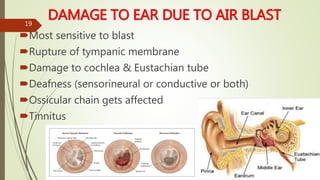
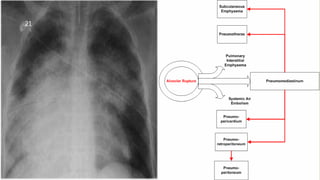
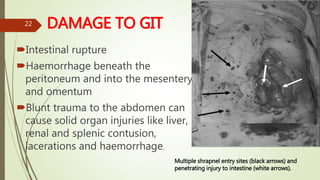
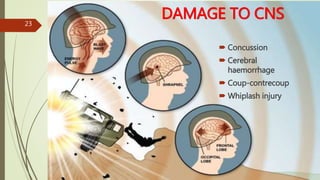
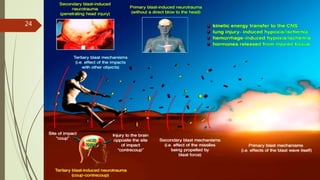
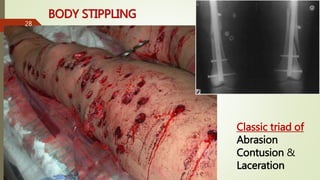
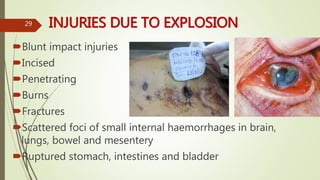
The document provides an in-depth overview of explosion injuries and their forensic aspects, detailing the types of explosive devices, the physics of explosions, and classifications of blast injuries. It highlights the mechanisms of harm caused by explosions, including primary, secondary, and tertiary injuries, as well as the impact on various organs such as the lungs, ears, and gastrointestinal tract. Additionally, it discusses investigative procedures and the medicolegal implications surrounding explosion-related incidents.