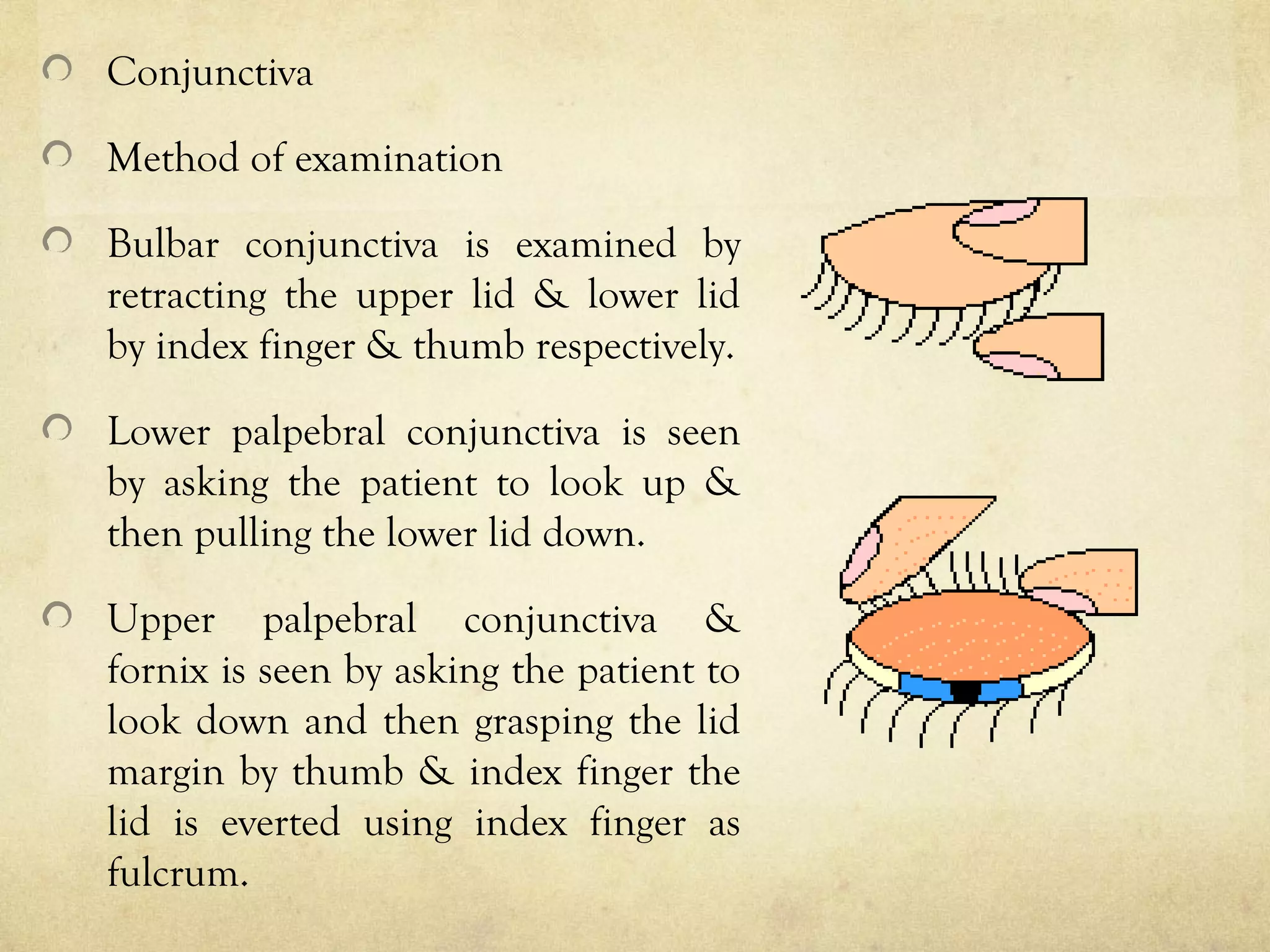
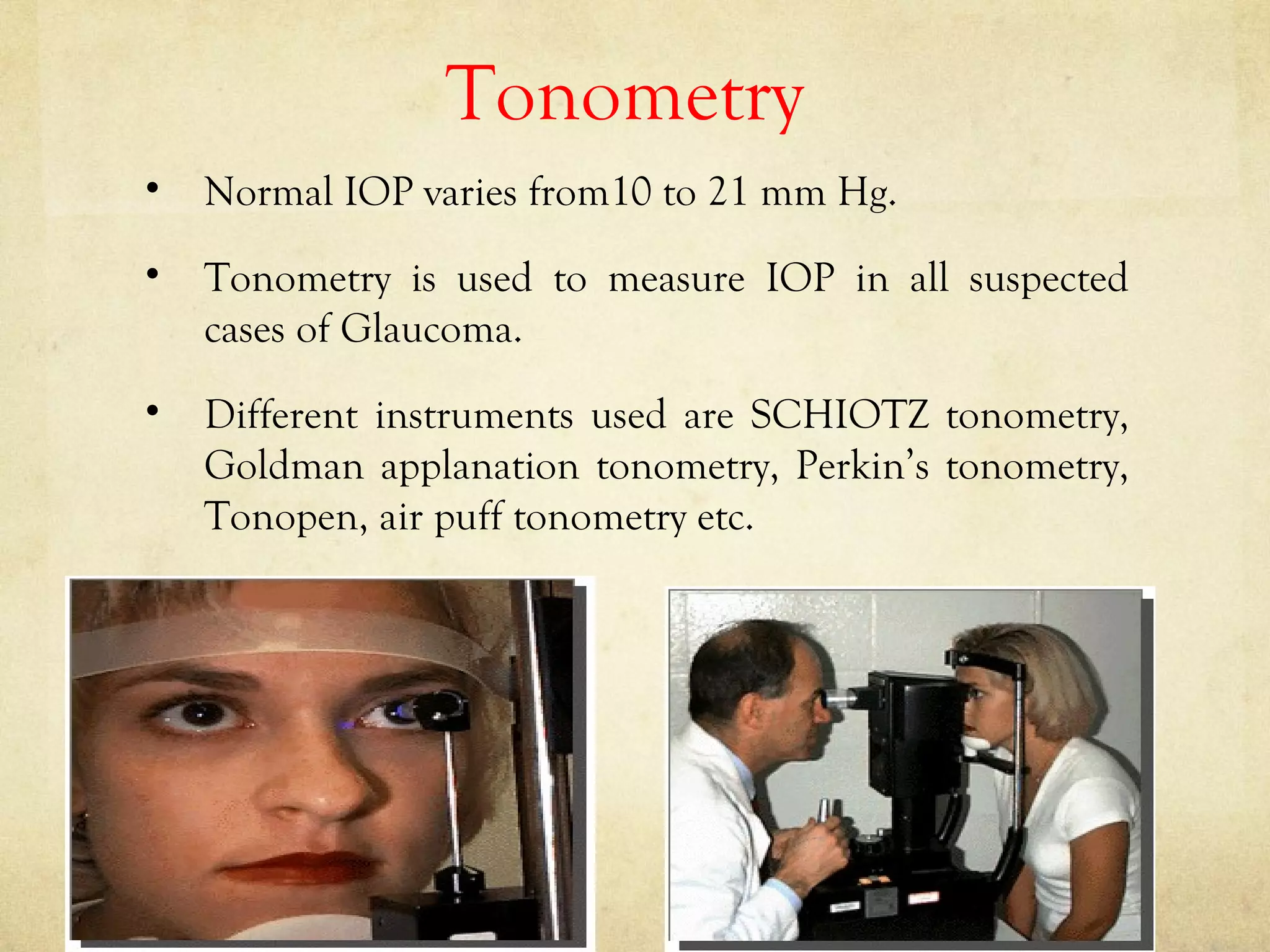
The purpose of a preliminary examination is to detect any gross anomalies and make a tentative diagnosis. It involves assessing visual acuity, ocular motility, binocular vision, color vision, visual fields, tonometry, blood pressure, and external and internal eye examination. The external exam evaluates lids, conjunctiva, sclera, cornea, iris, pupil, anterior chamber, and lens, while the internal exam assesses the posterior segment including the optic disc, retina, and macula using techniques like slit lamp biomicroscopy and fundoscopy. Special tests evaluate aspects like tear production, intraocular pressure, and the lacrimal system. Careful general observation of the patient is important before beginning specific examinations.