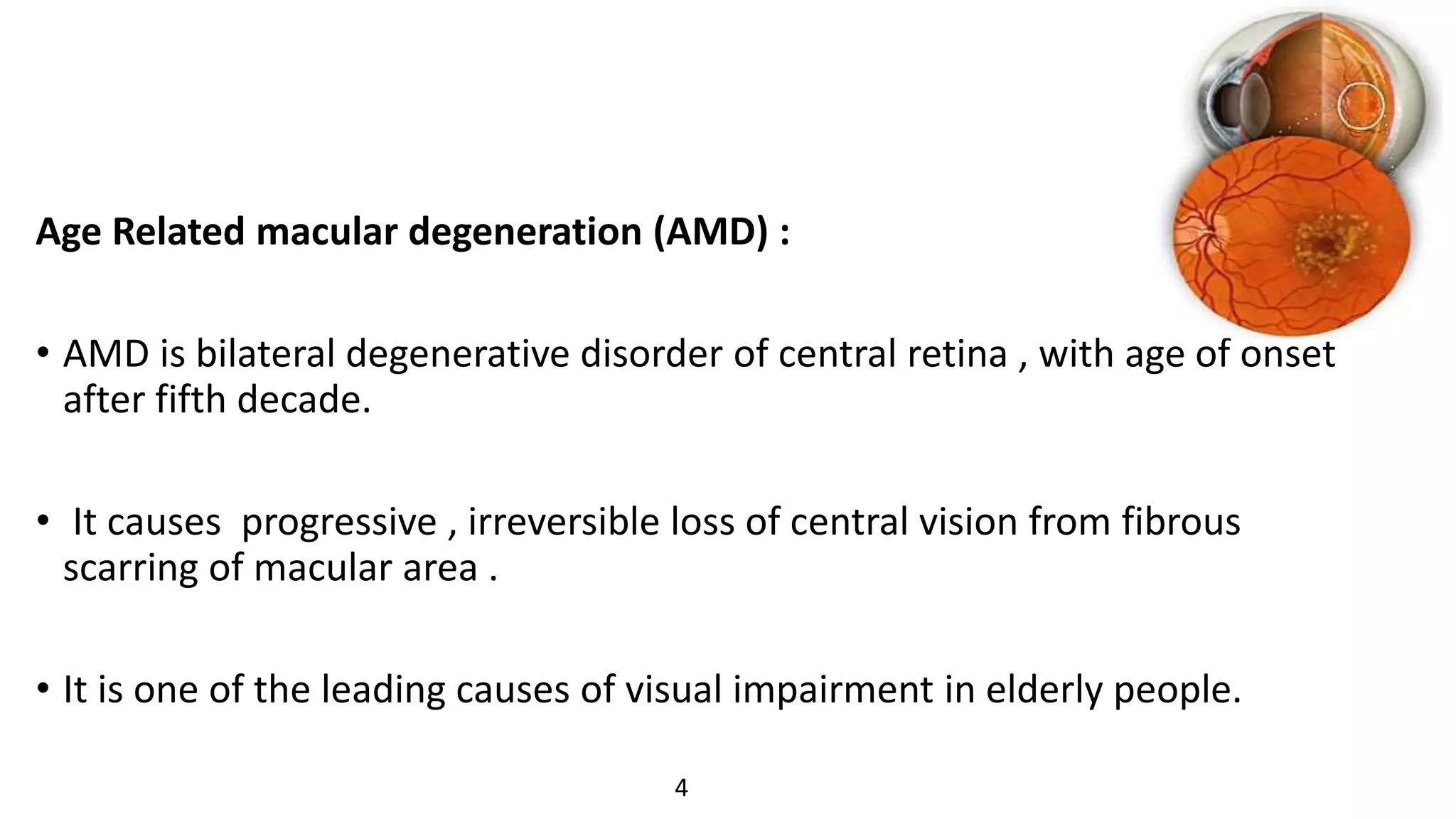
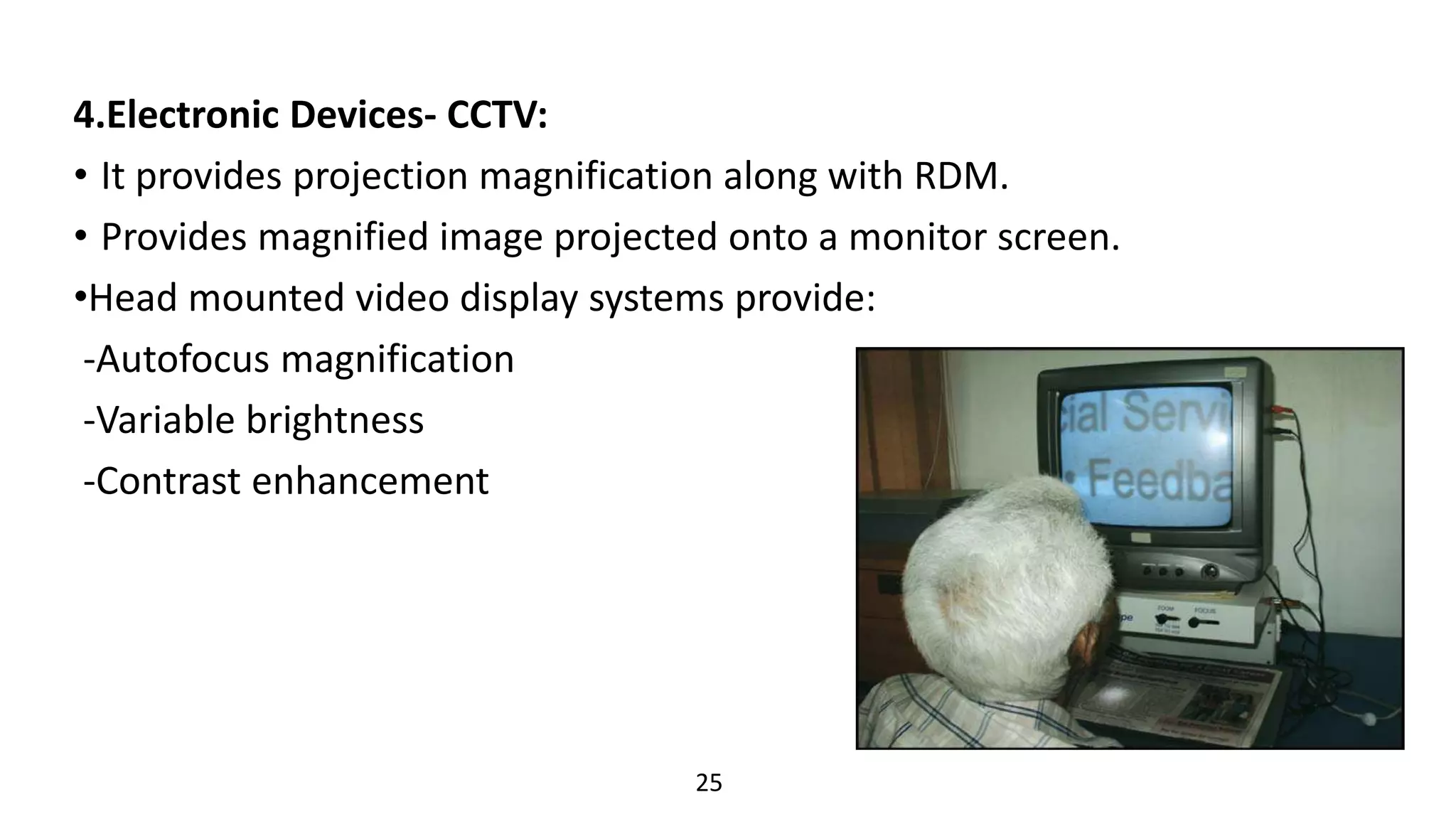
This document provides an overview of low vision management for patients with age-related macular degeneration (AMD). It discusses AMD and the visual deformities it causes. Management includes optical aids like magnifying glasses, telescopes, and electronic devices to enhance residual vision. Non-optical aids and visual rehabilitation help patients utilize their remaining sight and maintain independence. The goal is optimizing function through a combination of refractive correction, magnification, and training to perform daily living tasks.