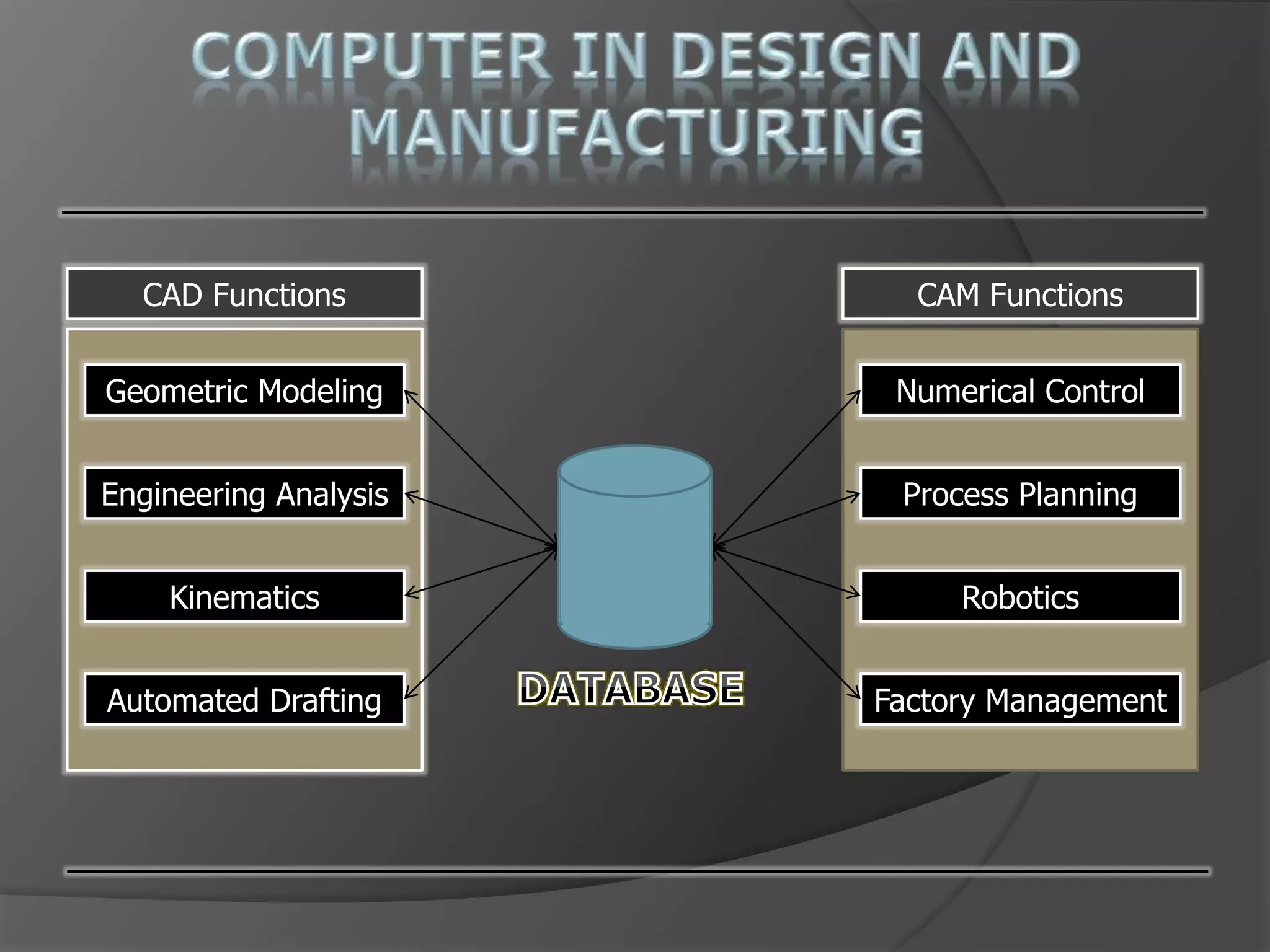
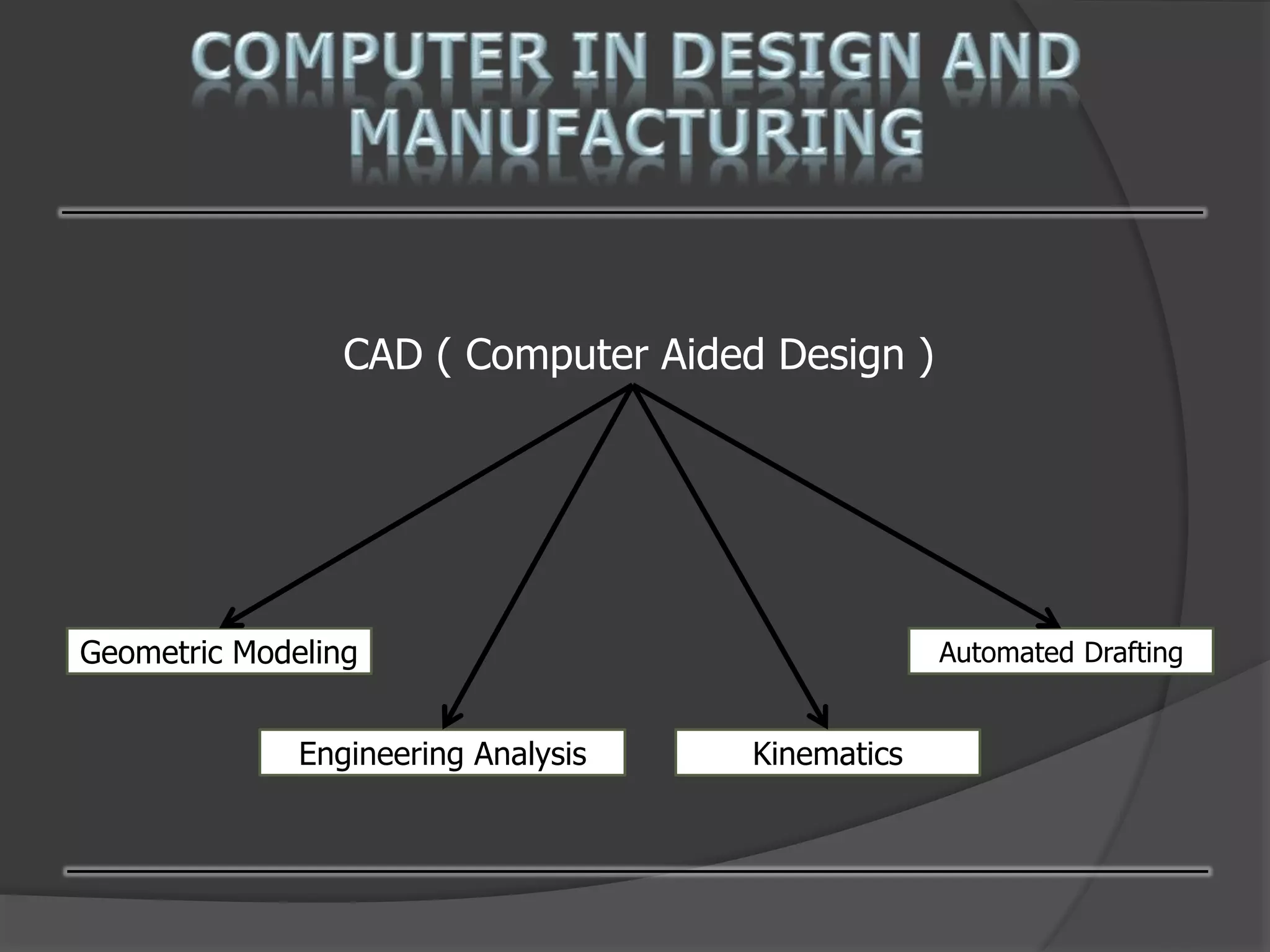
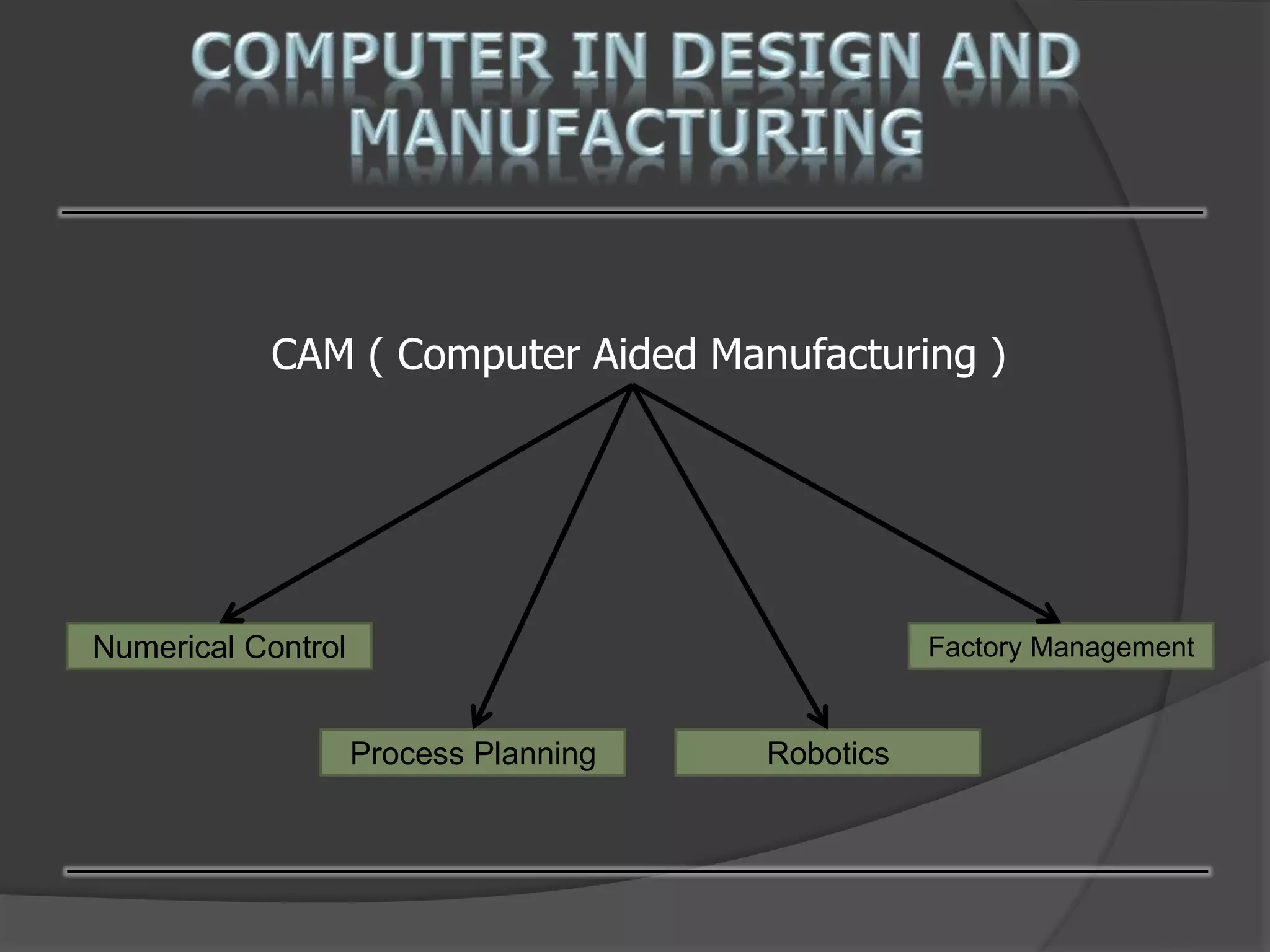
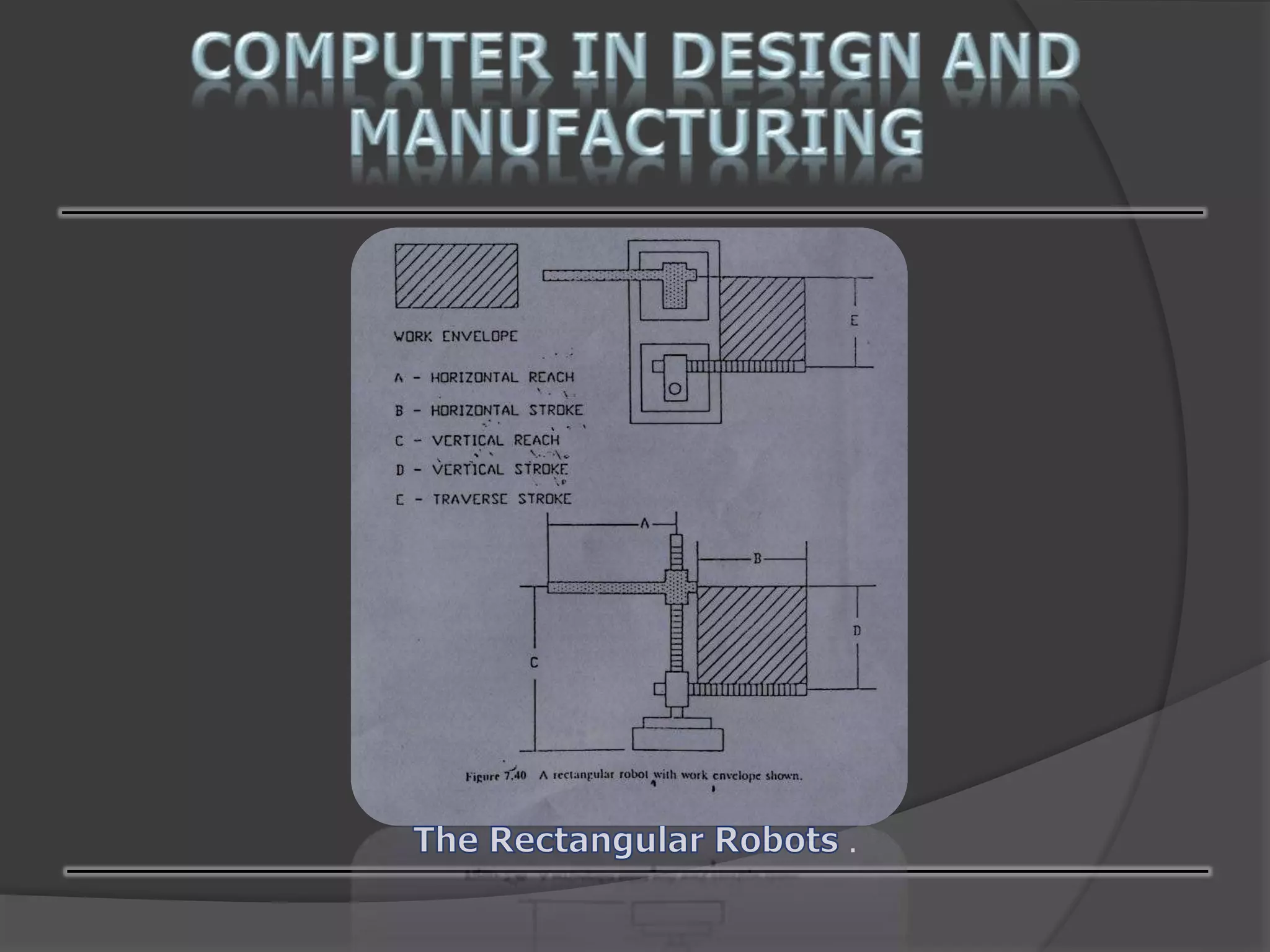
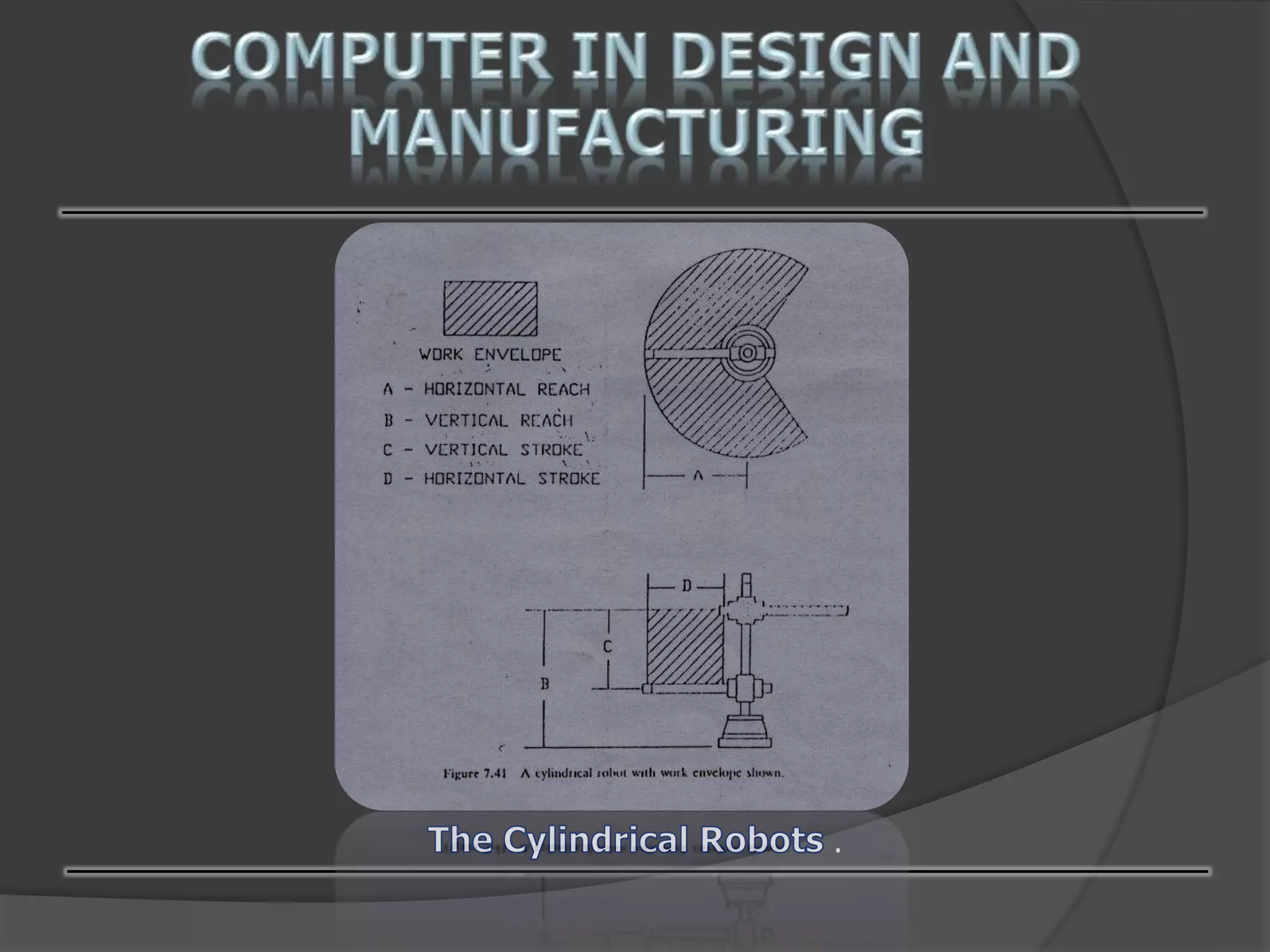
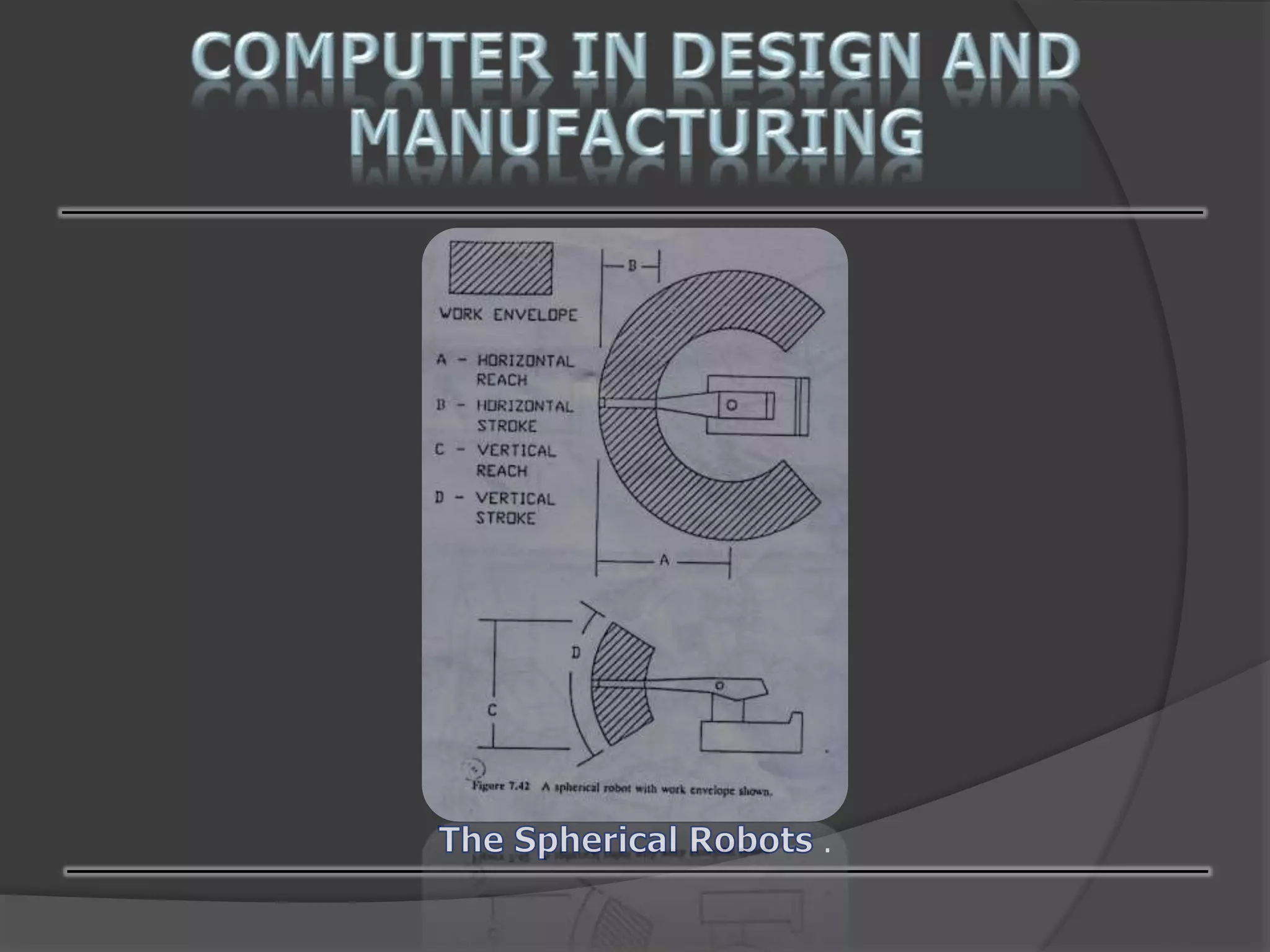
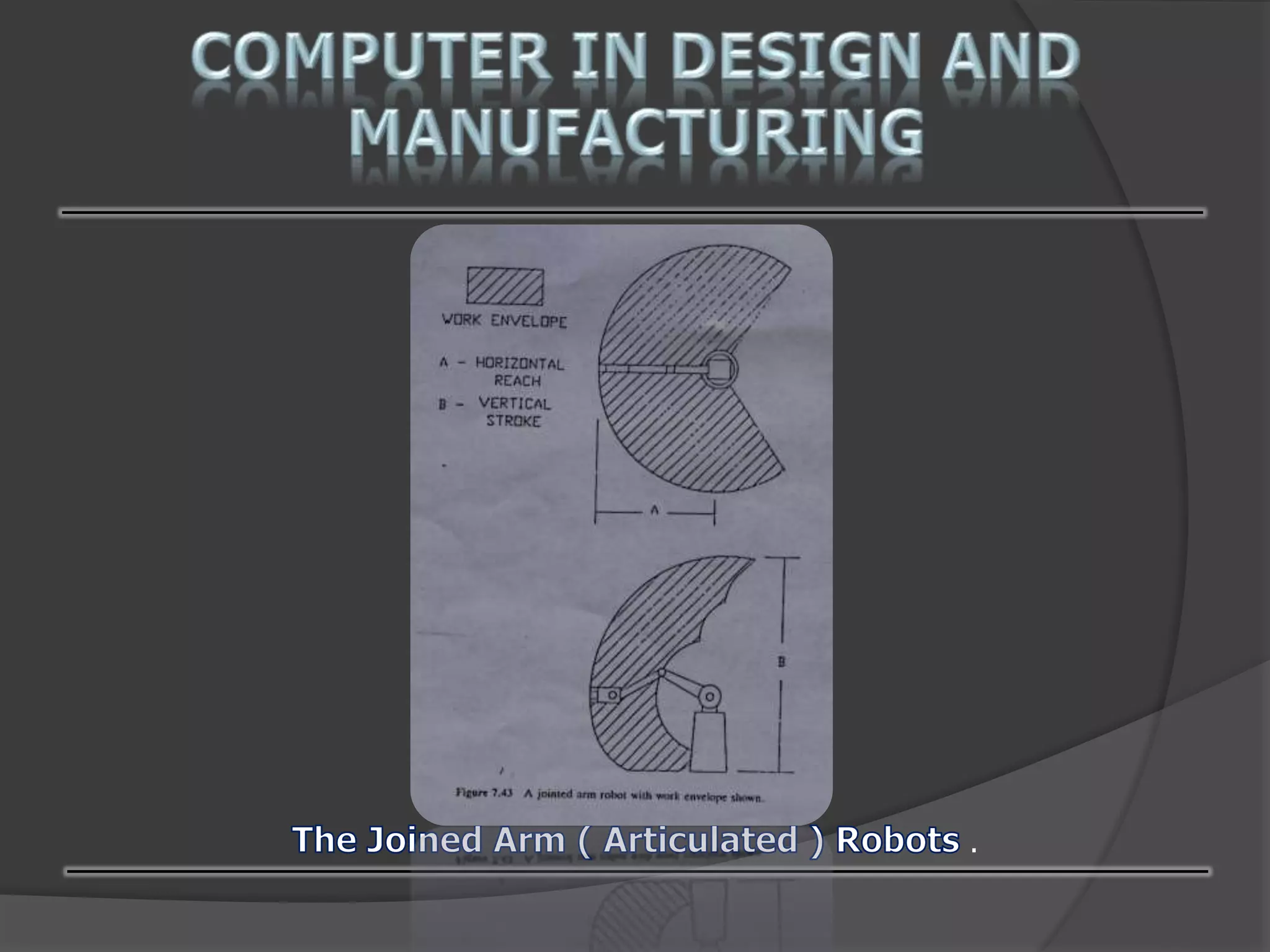
This document discusses computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) technologies. It explains that CAD is used for geometric modeling, engineering analysis, and automated drafting to construct digital designs. CAM then uses numerical control, process planning, robotics, and factory management to efficiently manufacture physical products based on the CAD files. The document provides details on various CAD and CAM applications, functions, and systems to illustrate how computers enhance and optimize industrial design and production processes.