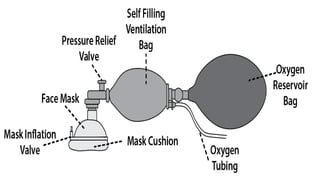
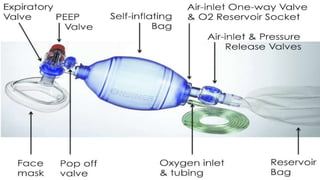
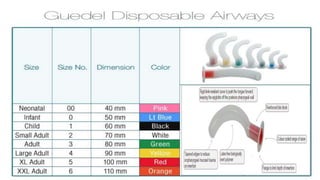
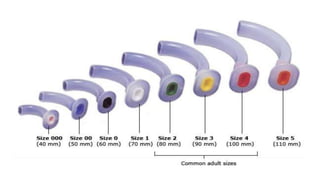
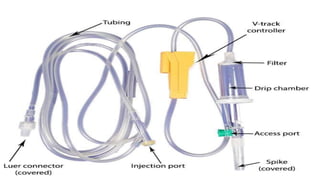
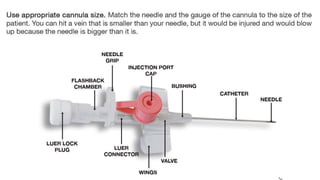
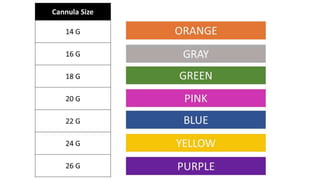
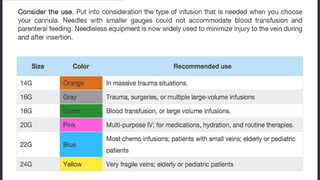
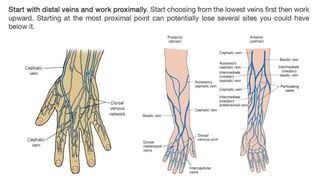
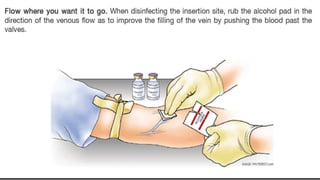
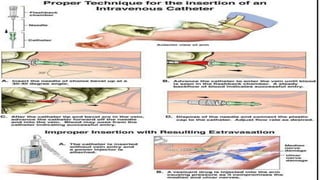
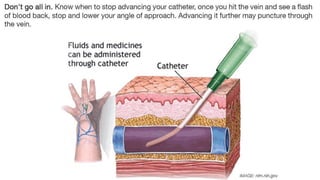
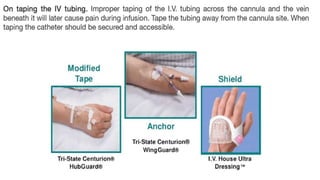
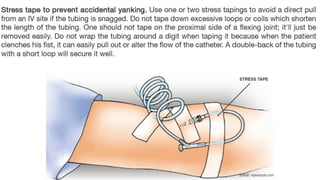
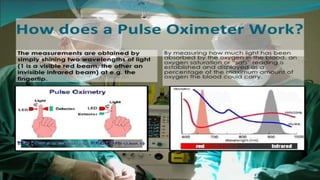
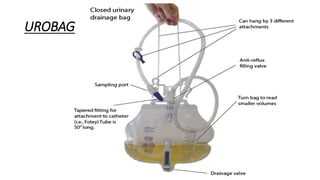
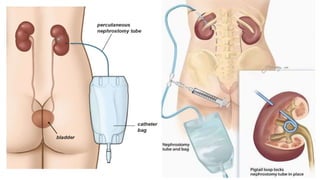
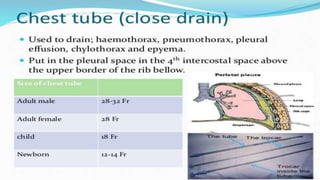
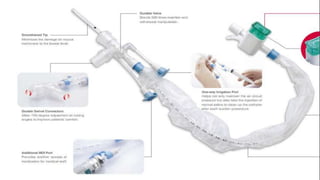
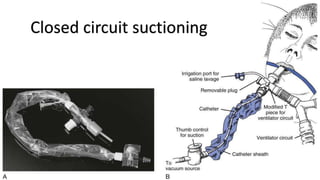
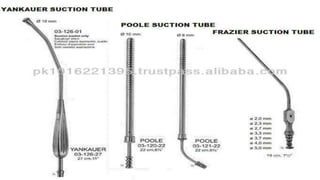
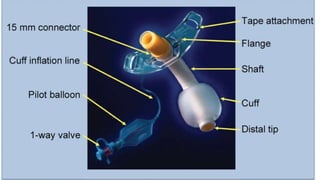
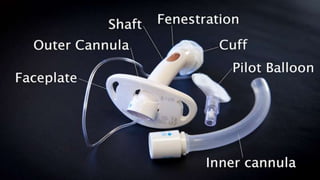
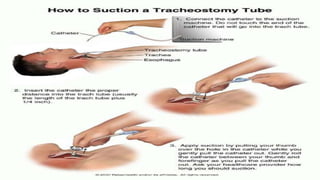
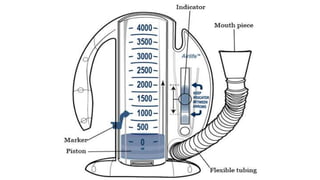
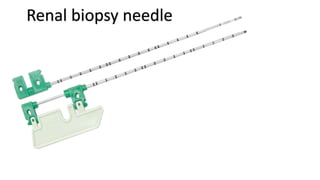
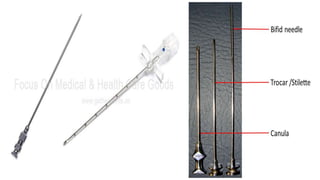
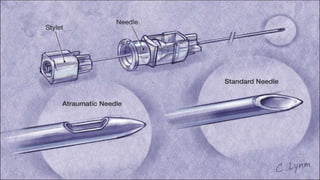
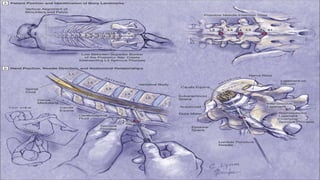
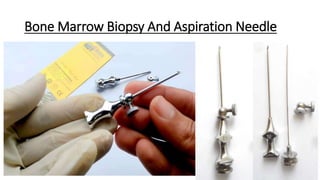
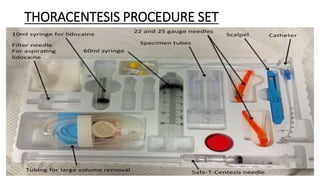
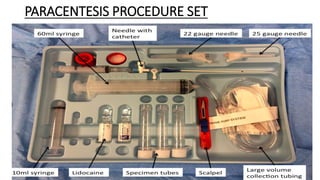
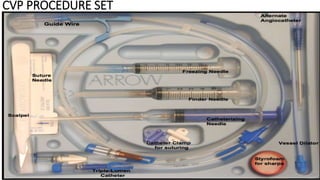
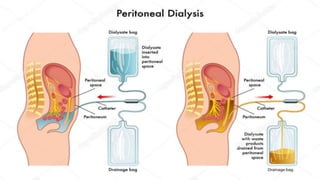
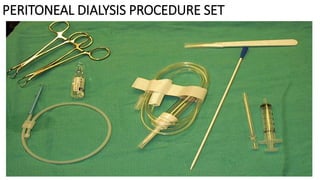
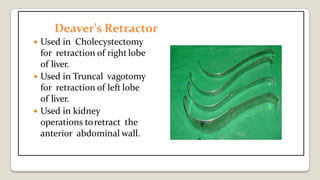
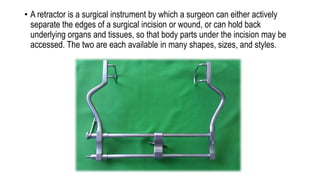
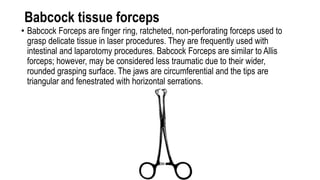
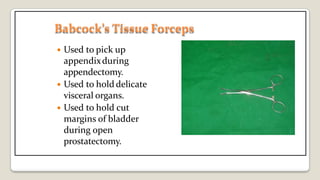
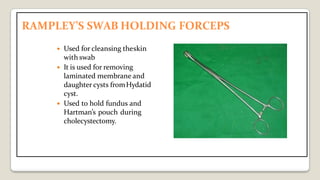
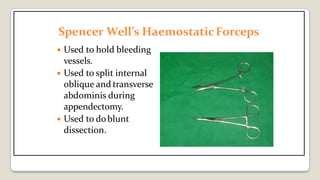
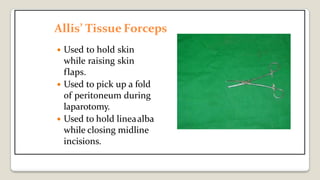
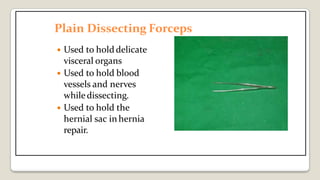
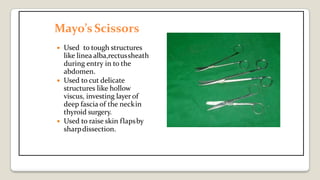
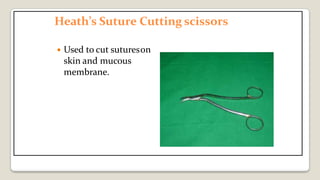
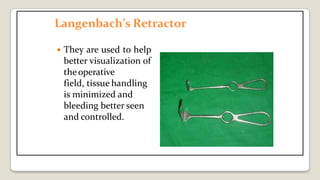
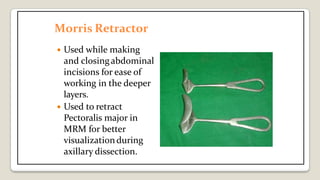
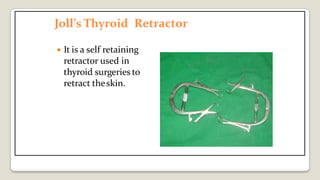
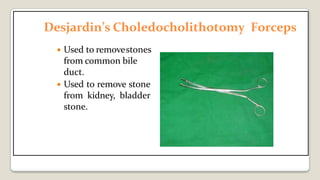
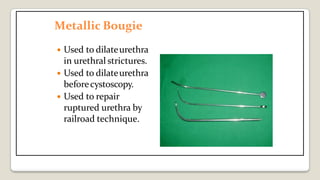
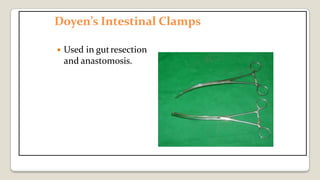
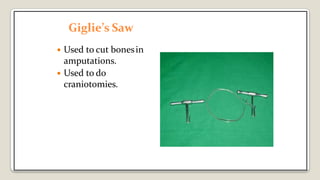
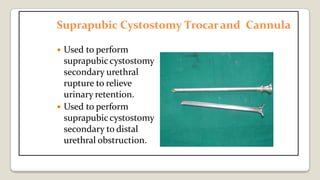
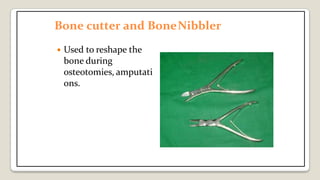
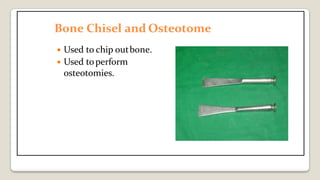
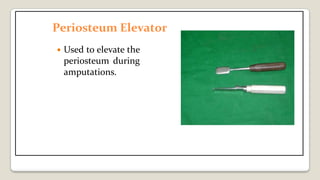
The document provides a comprehensive overview of various medical topics relevant to nursing students, emphasizing renal failure, urine analysis, and surgical instruments used in various procedures. It details urine volume and characteristics during different phases of renal failure, renal function indicators such as creatinine clearance, and the implications of lab findings. Additionally, it describes various surgical instruments, their uses, and applications in procedures, enhancing the practical knowledge necessary for nursing students.