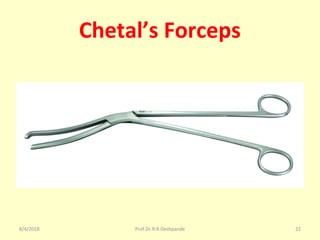
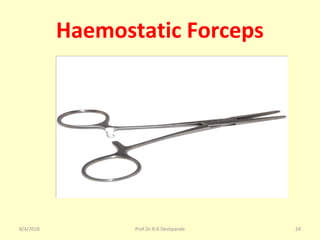
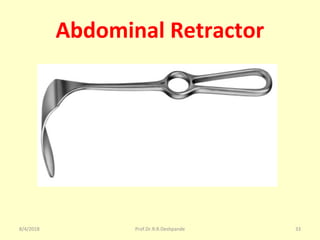
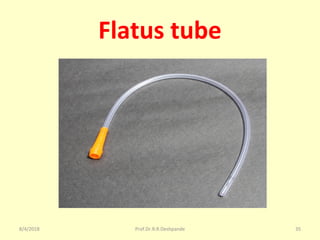
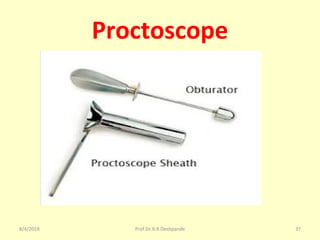
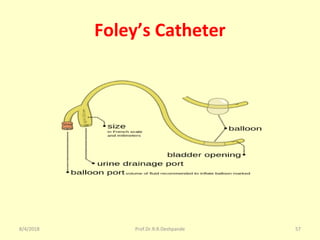
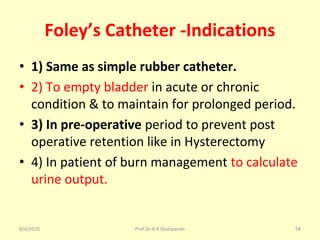
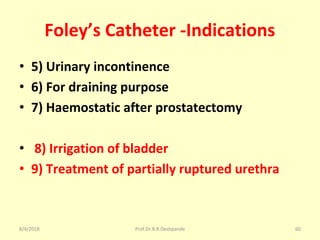
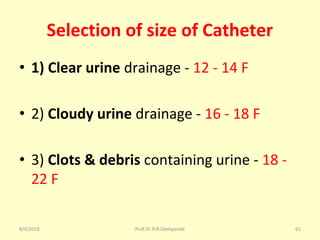
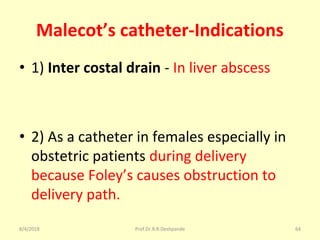
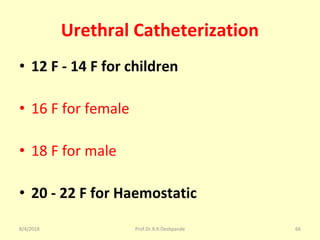
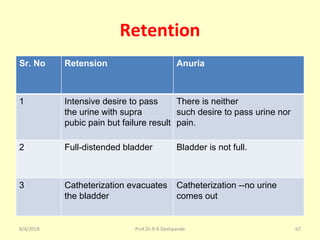
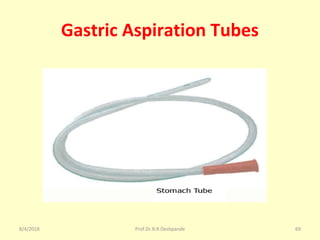
The document is a presentation on Shalya Tantra (surgery) by Prof. Dr. R. R. Deshpande, covering various historical points, abnormalities at birth, and surgical instruments. It details the evolution of surgical practices and specific instruments such as scalpels, forceps, and catheters, along with their uses and types. The document serves as an educational overview of surgical techniques and equipment in the field of Ayurveda.