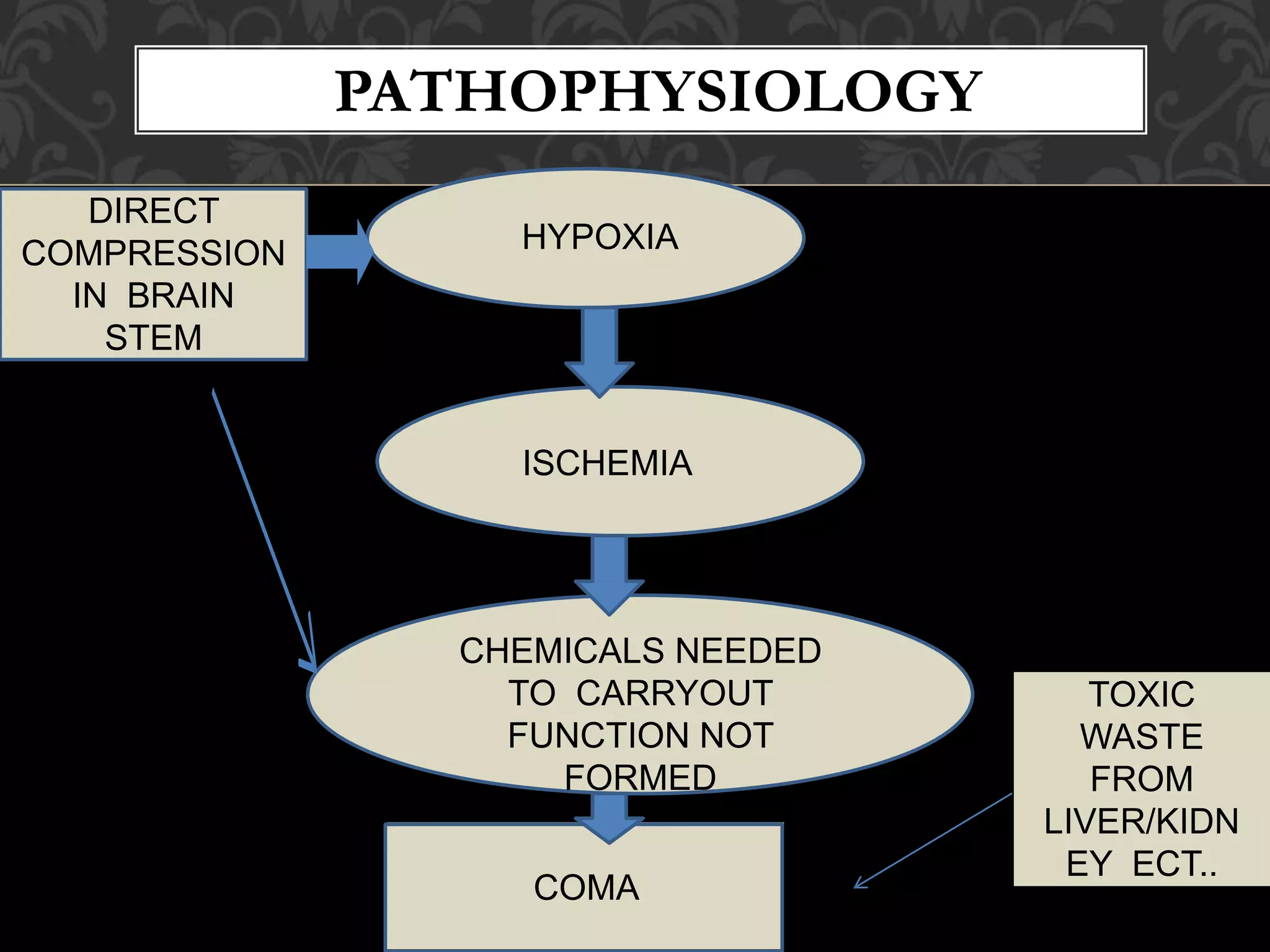
Unconsciousness is an abnormal state where a patient is unaware of their surroundings. It can be momentary or last for months. Common causes include head injuries, low blood sugar, drug overdoses, or lack of oxygen. The first steps in treatment are the ABCs - maintaining airway, breathing, and circulation. A brief examination and history should be done to investigate the cause and plan further treatment. Potential complications include coma, brain damage, broken ribs from CPR, or choking.