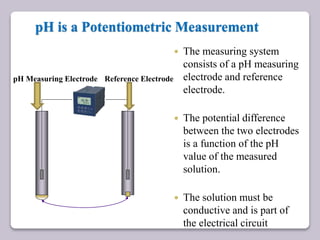
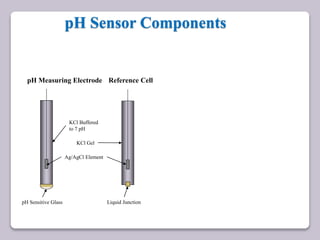
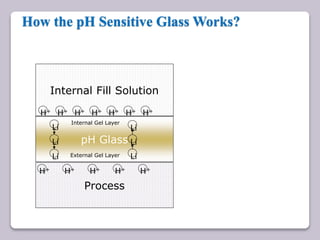
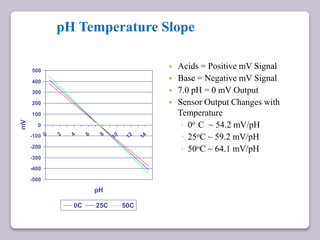
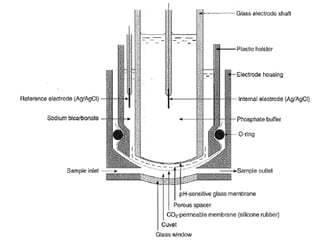
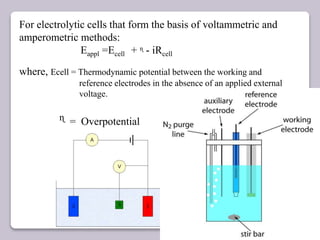
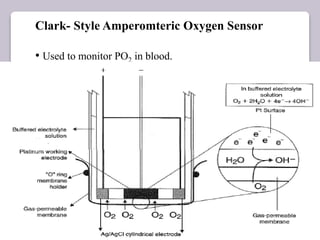
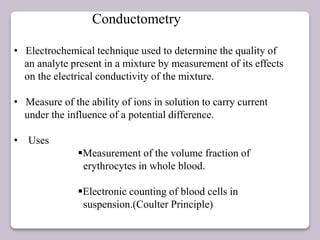
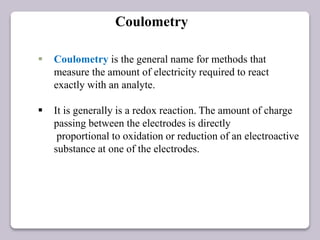
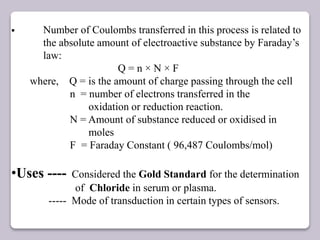
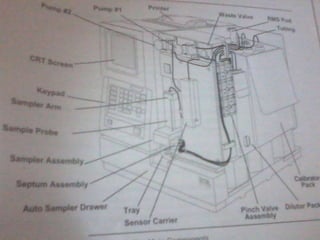
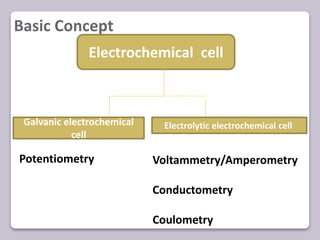
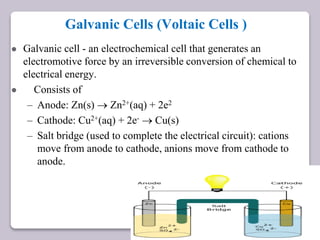
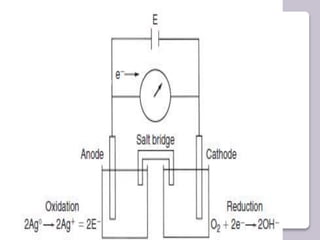
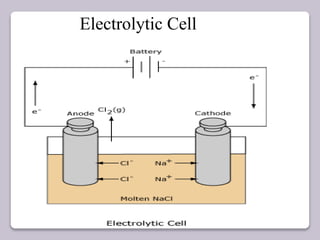
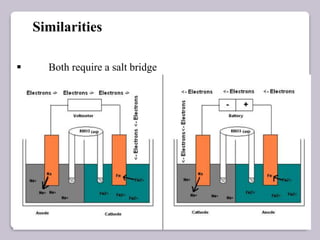
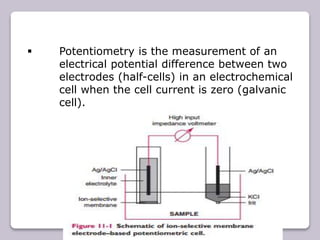
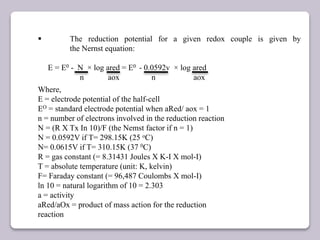
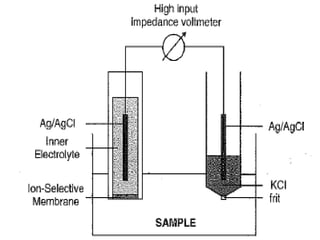
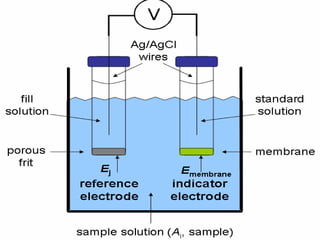
This document discusses various electroanalytical techniques used in clinical laboratories including potentiometry, voltammetry, conductometry, and coulometry. Potentiometry measures electrical potential differences using ion-selective electrodes or redox electrodes. Voltammetry and amperometry are sensitive techniques that apply a voltage to induce an electrochemical reaction and measure the resulting current. Conductometry measures how well ions conduct electricity. Coulometry determines the amount of an electroactive substance by measuring the charge required for its oxidation or reduction reaction. The NOVA-8 analyzer is highlighted as an example that can test for electrolytes, pH, hematocrit, and other clinical analytes using these electroanalytical methods.






![The Nicolsky-Eisenman equation describes the selectivity
of an ISE for the ion of interest over interfering ions:
E= E0 + [ 2.303RT ] log ( ai + Ʃ ki/j aj zi/zj )
zi F
where
ai = activity of the ion of interest
aj = activity of the interfering ion
Ki/j = selectivity coefficient for the primary ion over the
interfering ion. Low values indicate good selectivity for
the analyte "i" over the interfering ion "t.
Zi = charge of primary ion
Zj = charge of interfering ion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/potentiometryvoltamemtryandconductometry-200130090722/85/Potentiometry-voltamemtry-and-conductometry-19-320.jpg)