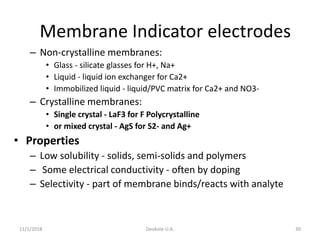
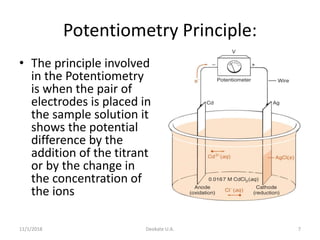
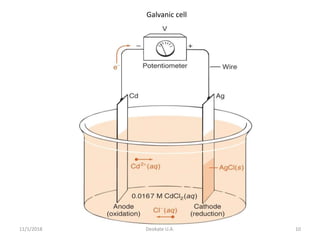
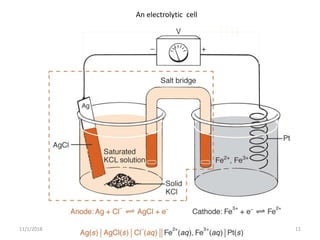
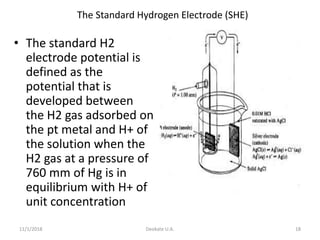
The document discusses potentiometry and electroanalytical chemistry, focusing on electrochemical cells and various types of electrodes, including reference and indicator electrodes. It outlines methods for potentiometric titration, including the use of the standard hydrogen electrode, silver/silver chloride, and calomel electrodes. Additionally, the document highlights applications of potentiometric techniques in clinical chemistry, environmental analysis, agriculture, and food processing.













![11/1/2018 Deokate U.A. 20
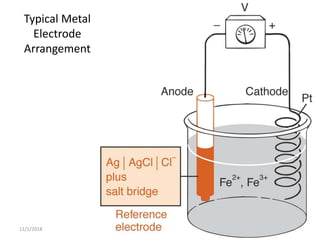
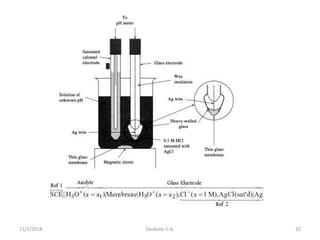
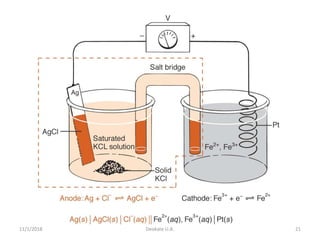
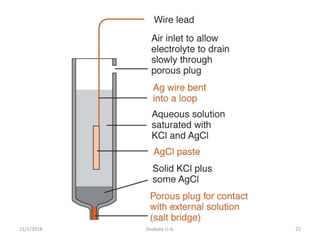
Ag/AgCl
• Constructed of a silver wire, coated with silver chloride, in a
solution containing silver chloride
– Sometimes AgCl is in solution saturated with KCl
– Saturated KCl keeps the chloride activity constant and
helps keep the electrode stable
log!tenbasewithlnreplaceweIF
C25@0.05916
nF
RT
][Clln
nF
RT
EE
S.H.E)to(relativemV197KCl)(sat.E
S.H.E)to(relativemV222E
ClAgeAgCl
-o
o
(aq)
-
(s)
-
(s)
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/potentiometry-181101041159/85/Potentiometry-20-320.jpg)
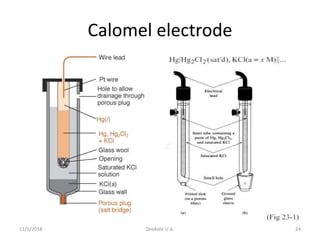
![11/1/2018 Deokate U.A. 23
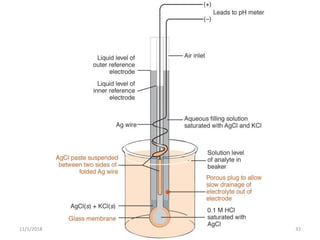
Calomel (S.C.E)
• Calomel is mercury (I) chloride
• One of the most common reference
electrodes
2-0
o
(aq)
-
(l)
-
(s)22
][Clln
nF
RT
EE
S.H.E)to(relativemV241KCl)(sat.E
S.H.E)to(relativemV268E
Cl2Hg2e2ClHg
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/potentiometry-181101041159/85/Potentiometry-23-320.jpg)