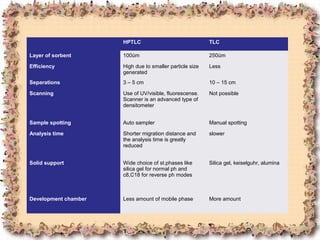
This document discusses high performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC), which is an automated form of thin layer chromatography that allows for efficient separation of samples in a short time. HPTLC has several advantages over other chromatographic methods, including its ability to simultaneously process multiple samples, lower analysis times and costs, simple sample preparation, and use of a scanner for detection and documentation of results. The document outlines the basic principles and steps of HPTLC, including sample preparation, selecting the chromatographic layer, pre-washing and conditioning plates, applying samples, mobile phase selection and development, and detection of spots using scanning.