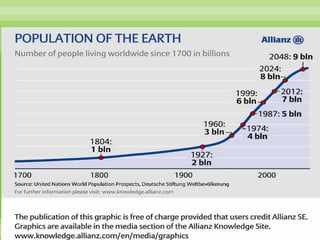
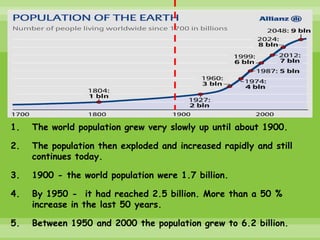
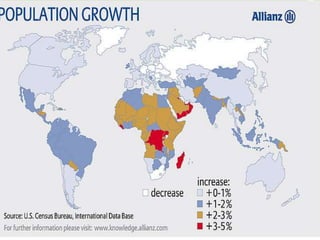
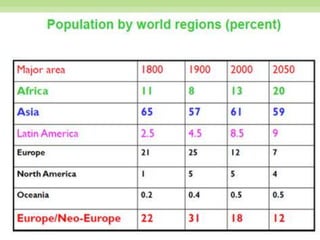
The world population grew slowly until 1900 but then increased rapidly, reaching 1 billion in 1900, 2.5 billion in 1950, and 7 billion in 2011. Most population growth occurs in developing countries with high birth rates, like India and China. While populations in developed countries are stable or declining, populations in developing countries continue to rise due to historically high birth rates and increasing lifespans. Rapid population growth creates challenges for governments to provide resources and threatens the environment, food security, and political stability.