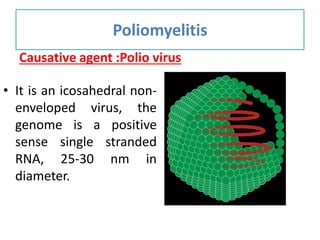
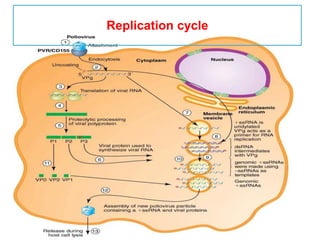
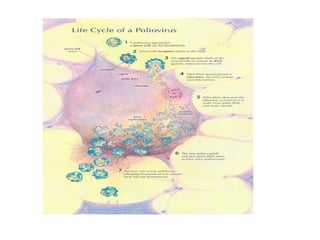
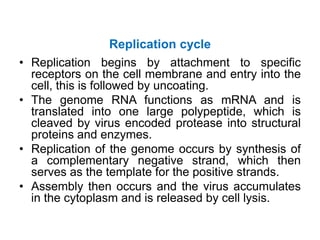
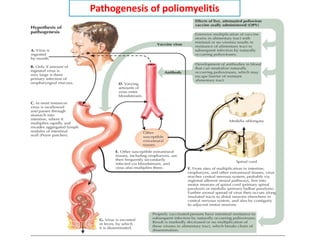
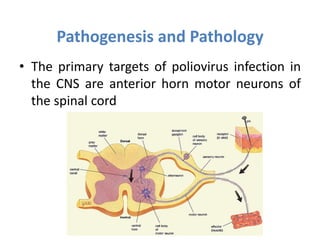
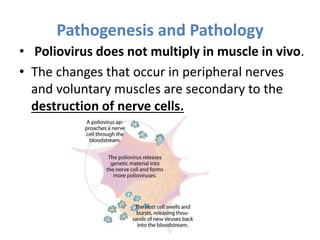
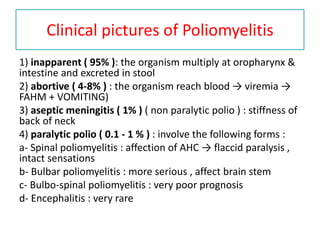
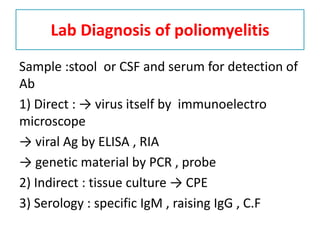
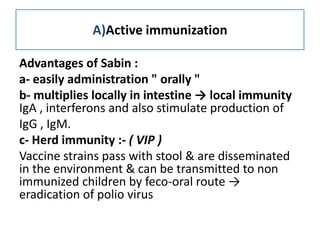
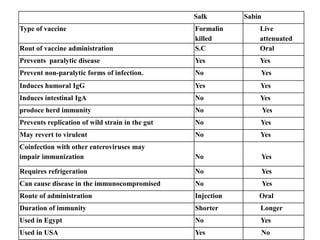
This document discusses polioviruses, including their properties, transmission, replication cycle, pathogenesis, clinical presentations, diagnosis, and prophylaxis. It focuses on the causative agent of poliomyelitis, poliovirus, describing it as a non-enveloped RNA virus that infects the gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system. The document compares the Salk inactivated polio vaccine and Sabin live attenuated oral polio vaccine, explaining their differences in inducing immunity and preventing transmission.