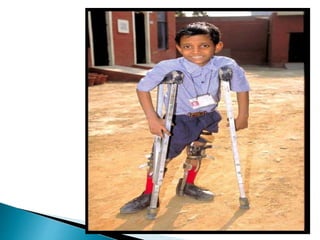
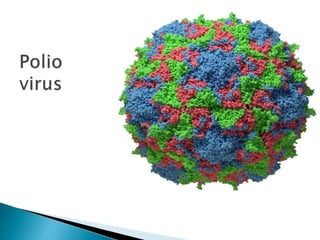
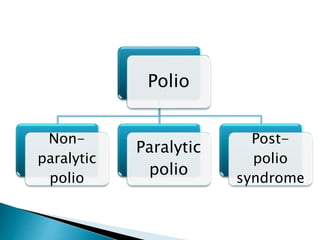
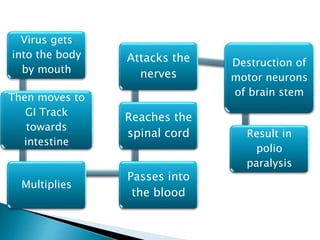
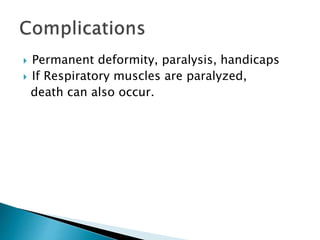
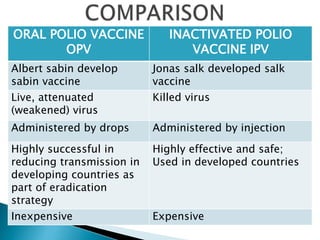
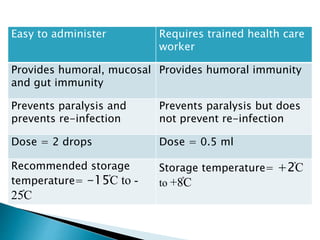
Polio is a highly infectious disease caused by three strains of the poliovirus. It mainly affects children under 5 years old and is transmitted through fecal-oral contamination or droplets from infected individuals. While most infections cause mild symptoms, in some cases it can cause paralysis by destroying motor neurons in the spinal cord. There is no cure, but vaccination is the primary prevention method and has been very effective in reducing cases globally through initiatives like the Expanded Programme on Immunization in India.