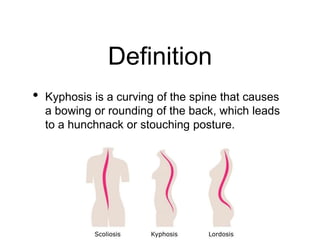
This document discusses three main types of kyphosis (curvature of the spine): postural, Scheuemann's, and congenital. Postural kyphosis is the most common type and results from poor posture. Scheuemann's kyphosis develops during adolescence due to structural vertebral deformities. Congenital kyphosis is the rarest type and caused by abnormal vertebral development before birth. The document also covers lordosis (inward curvature), its causes including poor posture and hip problems, clinical features like back pain, and treatments depending on the underlying condition.