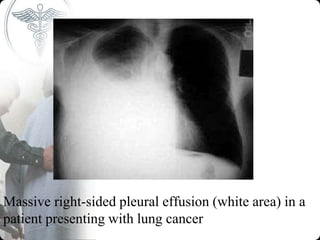
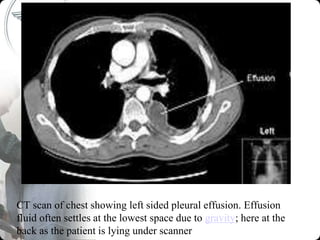
This document provides information on pleural effusion, including its definition, causes, classification, pathogenesis, clinical features, investigations, and management. A pleural effusion occurs when there is excess fluid in the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall. Effusions are classified as transudative or exudative based on the fluid characteristics. Common causes include infections, malignancies, heart failure, and kidney or liver diseases. Investigations include chest x-rays, thoracentesis, and biochemistry of pleural fluid. Management involves treating the underlying cause, relieving symptoms, and procedures like chest tube drainage or pleurodesis for recurrent effusions.