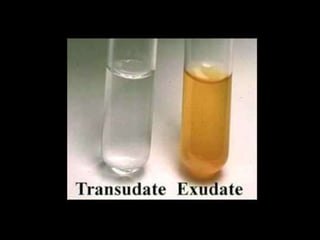
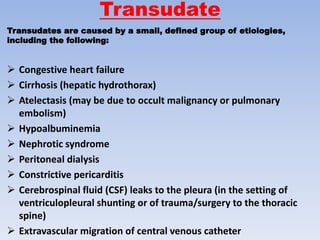
This document discusses pleural effusions, which are collections of fluid in the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall. It covers the etiology, mechanisms, classification as transudates or exudates, clinical presentation, diagnostic evaluation including thoracentesis, and treatment approaches for pleural effusions. Common causes include congestive heart failure, pneumonia, malignancy, and pulmonary embolism. Diagnostic thoracentesis is performed to analyze pleural fluid characteristics and determine the underlying condition. Treatment depends on the cause but may involve drainage procedures, chemotherapy, or sclerosing agents.







![ The more common causes of exudates include the following:
Parapneumonic causes
Malignancy (most commonly lung or breast cancer, lymphoma, and leukemia; less
commonly ovarian carcinoma, stomach cancer, sarcomas, melanoma) [9]
Pulmonary embolism
Collagen-vascular conditions (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus
Tuberculosis (TB)
Pancreatitis
Trauma
Esophageal perforation
Sarcoidosis
Pericardial disease
Uremia
Chylothorax (acute illness with elevated triglycerides in pleural fluid)
Fistula (ventriculopleural, biliopleural, gastropleural)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/siminarpleuraleffusiion-210212143503/85/Pleural-Effusiion-10-320.jpg)