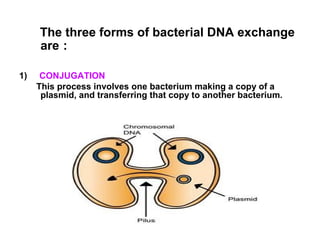
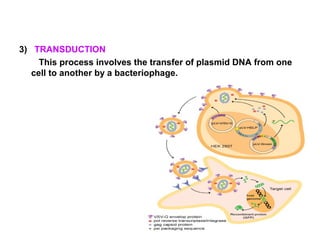
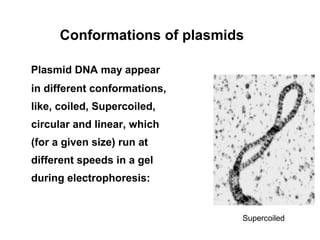
Plasmids are extra-chromosomal DNA molecules found in bacteria that can replicate independently of chromosomal DNA. They vary in size but are usually between 1,000 to 25,000 base pairs. Plasmids are not essential for bacterial survival but can contain genes that allow bacteria to survive better in adverse environments or compete with other microbes. There are several classes of plasmids including F-plasmids for conjugation, R-plasmids for antibiotic resistance, Col-plasmids for bacteriocin production, and virulence plasmids that make bacteria pathogenic. Bacteria can exchange plasmids through conjugation, transformation, or transduction. Plasmids are useful tools in molecular biology and