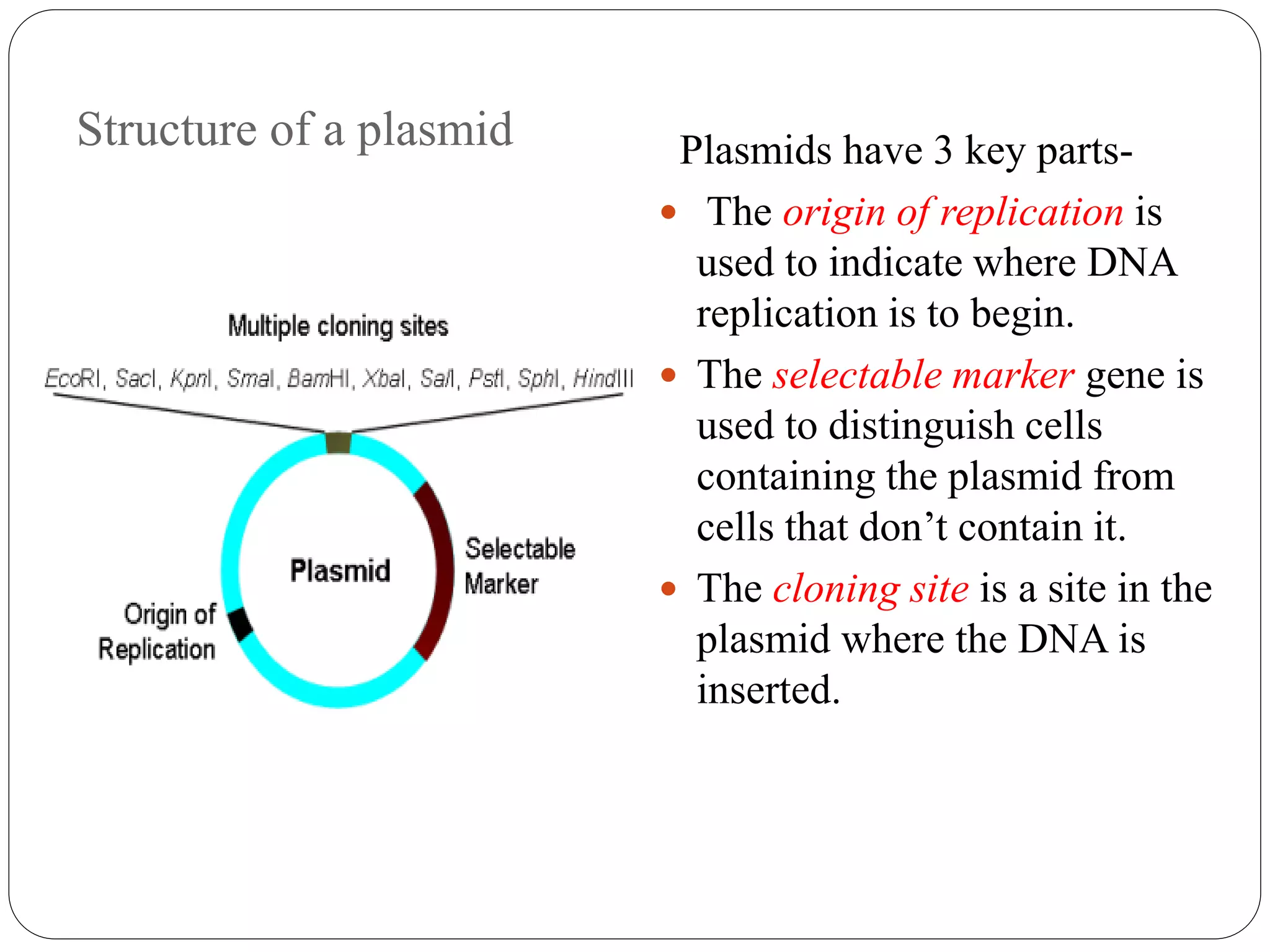
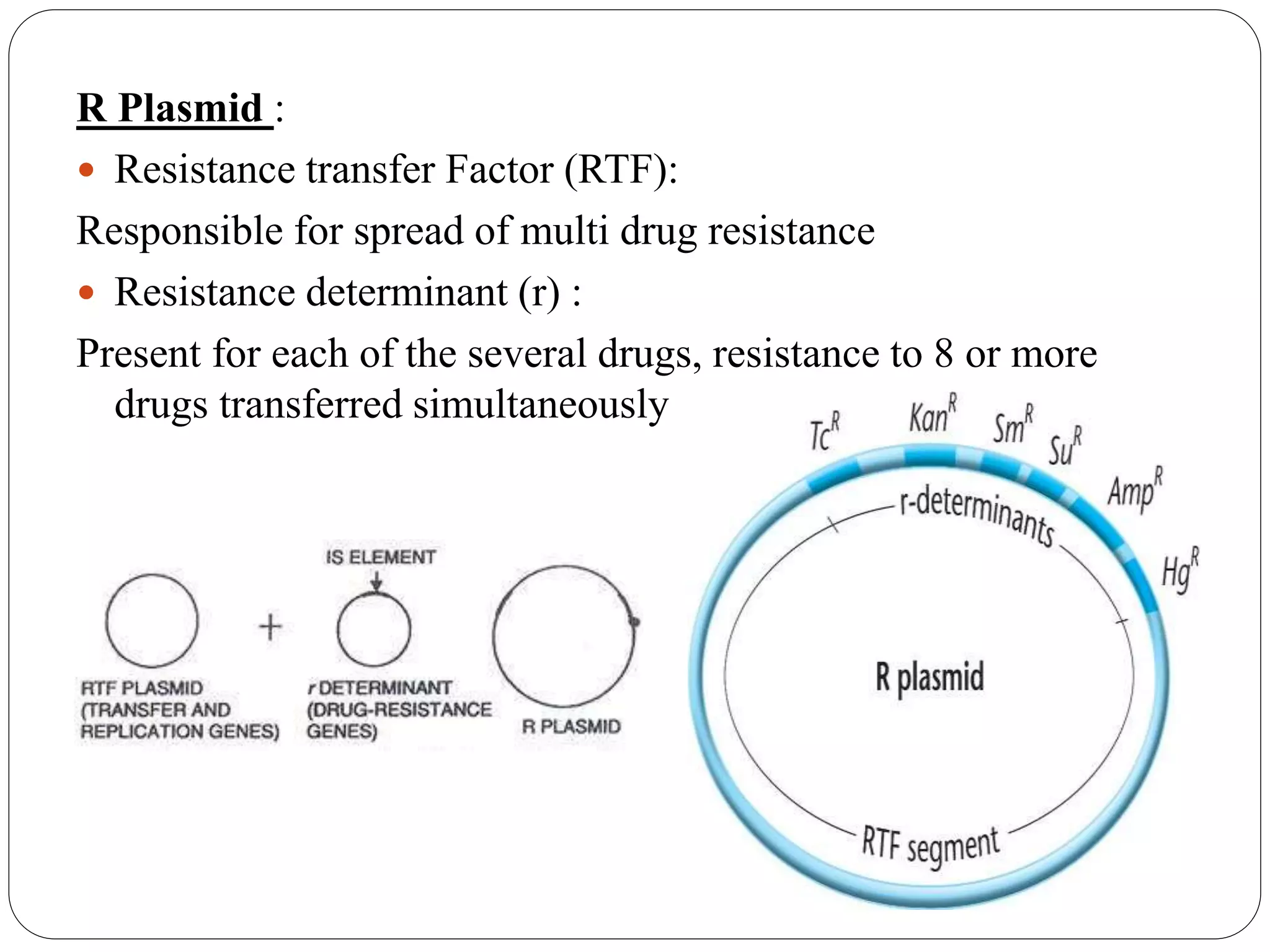
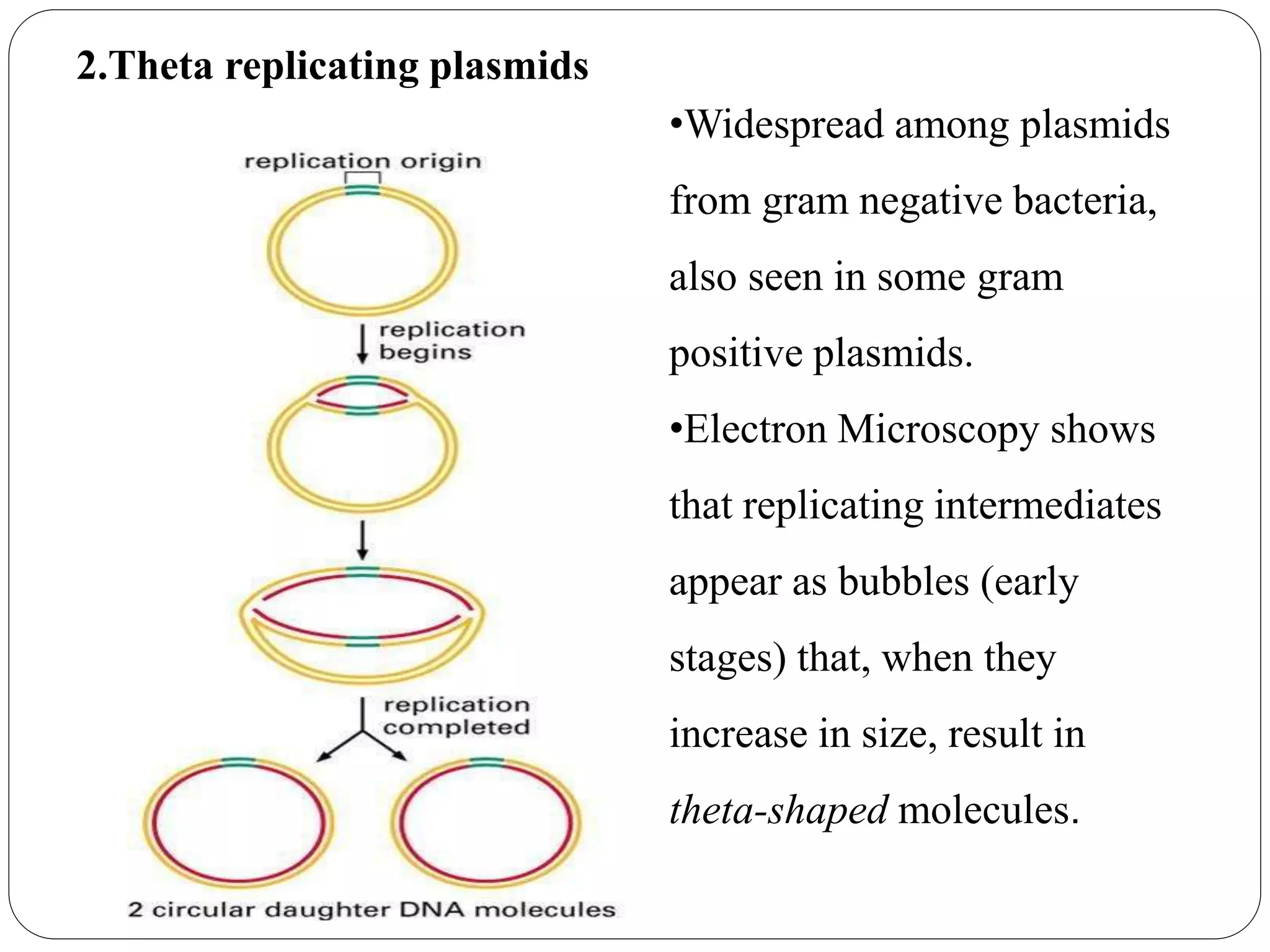
Plasmids are extrachromosomal DNA elements found in bacteria that can replicate independently of the bacterial chromosome. They play an important role in horizontal gene transfer between bacteria by allowing bacterial populations to acquire beneficial traits. Plasmids are also useful genetic engineering tools as they can be used to clone DNA fragments and produce recombinant proteins. Plasmid DNA vaccines utilize purified plasmid vectors encoding antigen genes to induce immune responses against the encoded antigen.