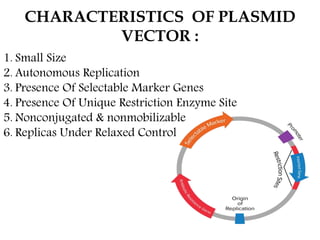
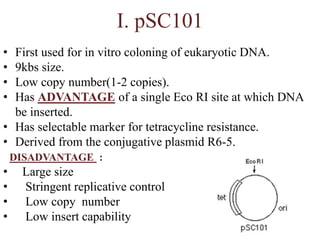
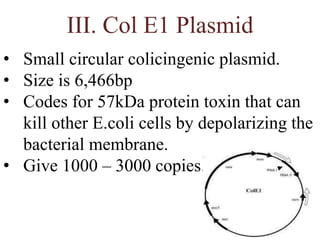
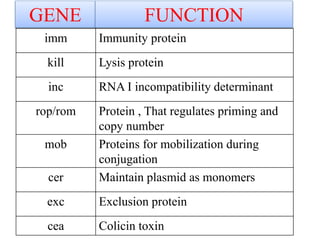
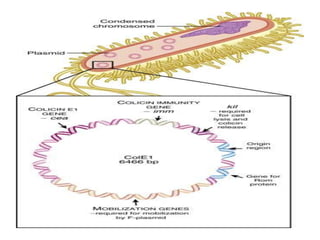
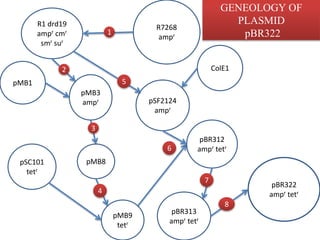
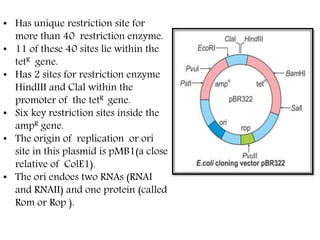
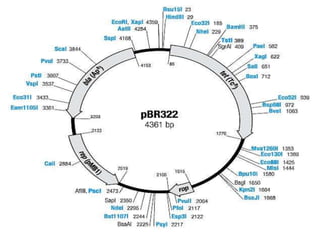
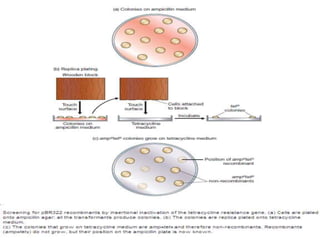
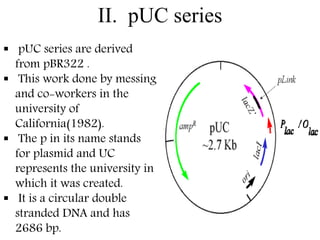
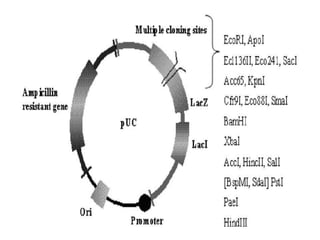
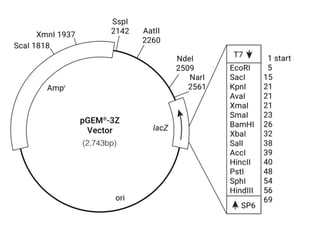
Plasmids are small, autonomous DNA molecules that can replicate independently of the bacterial chromosome. They are useful as vectors in genetic engineering due to their ability to replicate autonomously and contain selectable marker genes. This document discusses the characteristics and functions of various natural and artificial plasmid vectors used in E. coli, including pSC101, pBR322, pUC series, and pGEMR. Key features of these vectors like size, copy number, restriction sites, resistance genes, and applications are described.