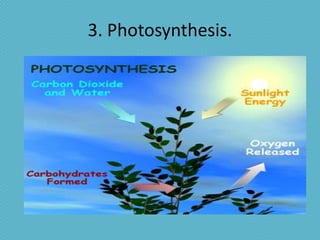
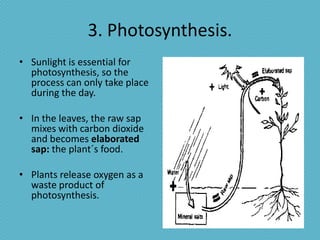
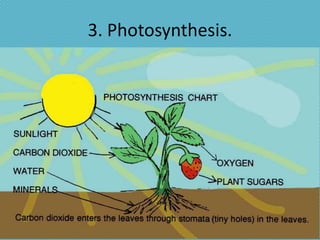
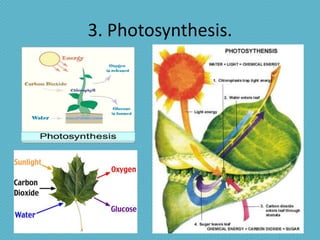
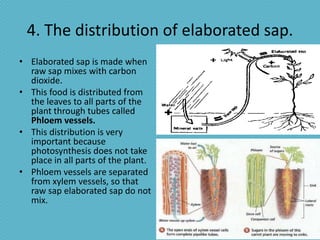
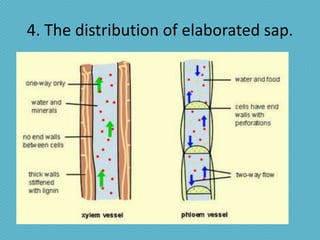
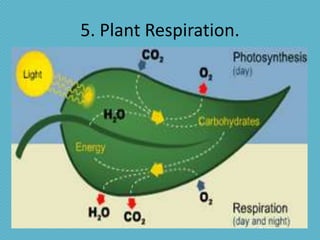
This document discusses plant nutrition and how plants obtain nutrients. It covers how plants make their own food through photosynthesis, using sunlight, carbon dioxide, water and minerals from the soil. Photosynthesis occurs in the leaves and uses chlorophyll to produce oxygen and "elaborated sap", the plant's food. This food is distributed throughout the plant via phloem vessels. The document also discusses plant respiration, growth, movement and perception of time.