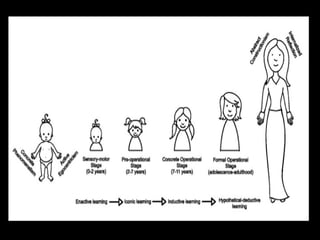
Piaget's theory of cognitive development consists of 4 main stages:
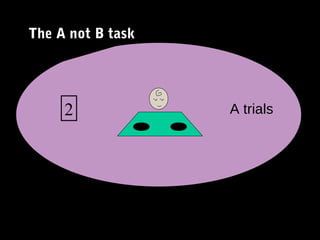
1) Sensory-motor stage (0-2 years): Children understand the world through senses and physical actions. Object permanence emerges around age 2.
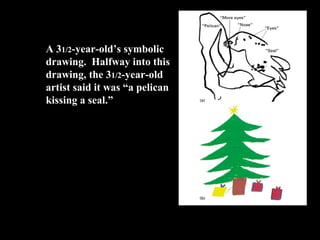
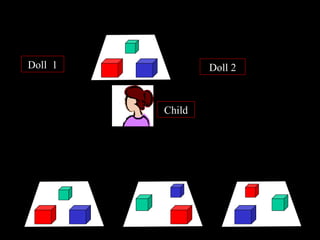
2) Pre-operational stage (2-7 years): Symbolic thought and language develop but logical operations have not emerged. Thinking is egocentric and based on perception.
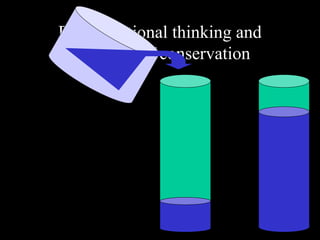
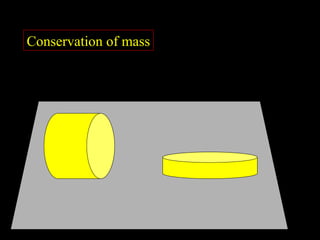
3) Concrete operational stage (7-11 years): Children can think logically and conserve quantities for concrete objects and events.
4) Formal operational stage (11-15+ years): Abstract and hypothetical thinking emerges allowing for planning, propositional thought, and scientific reasoning. Development occurs through processes of assimilation