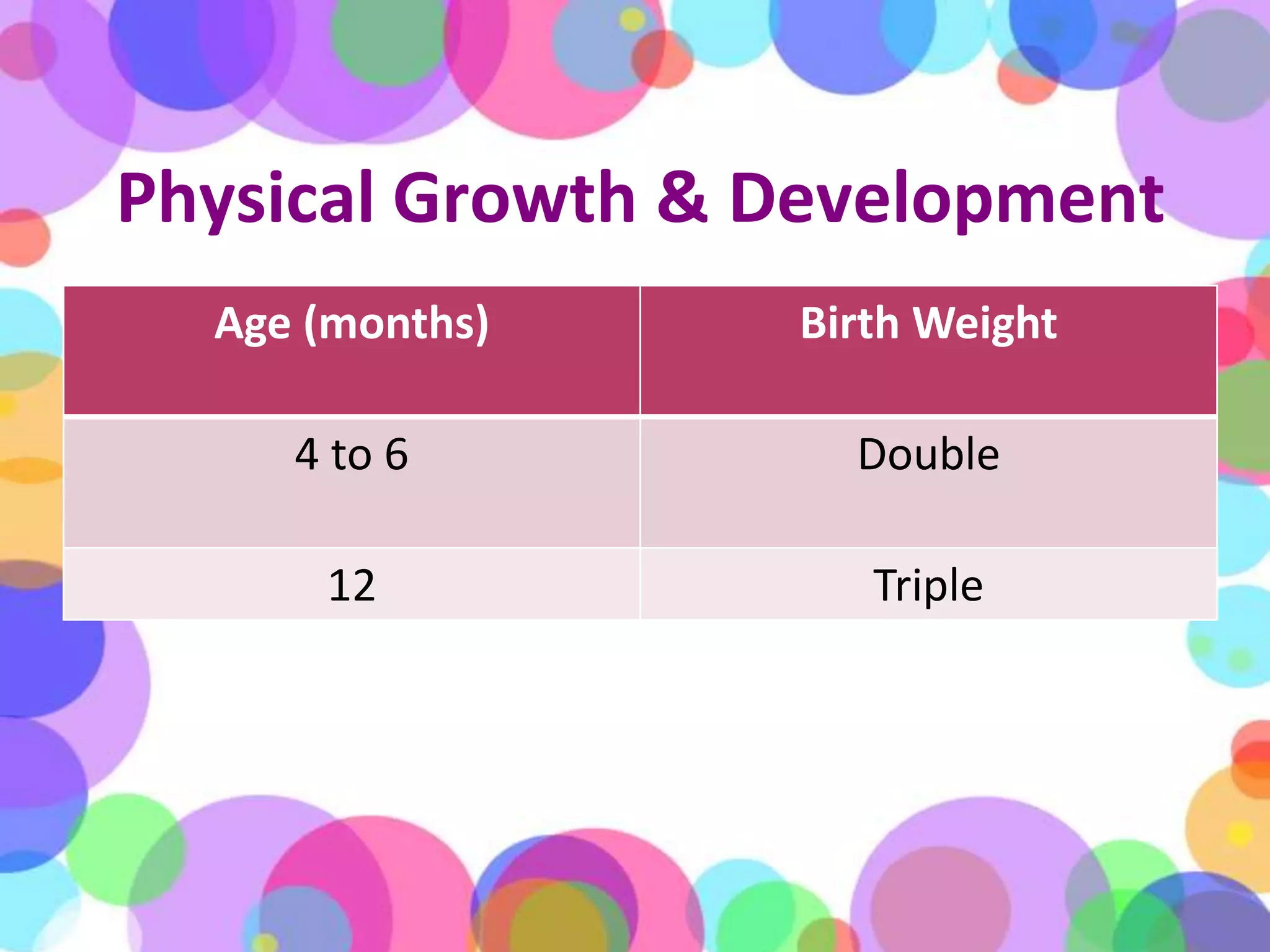
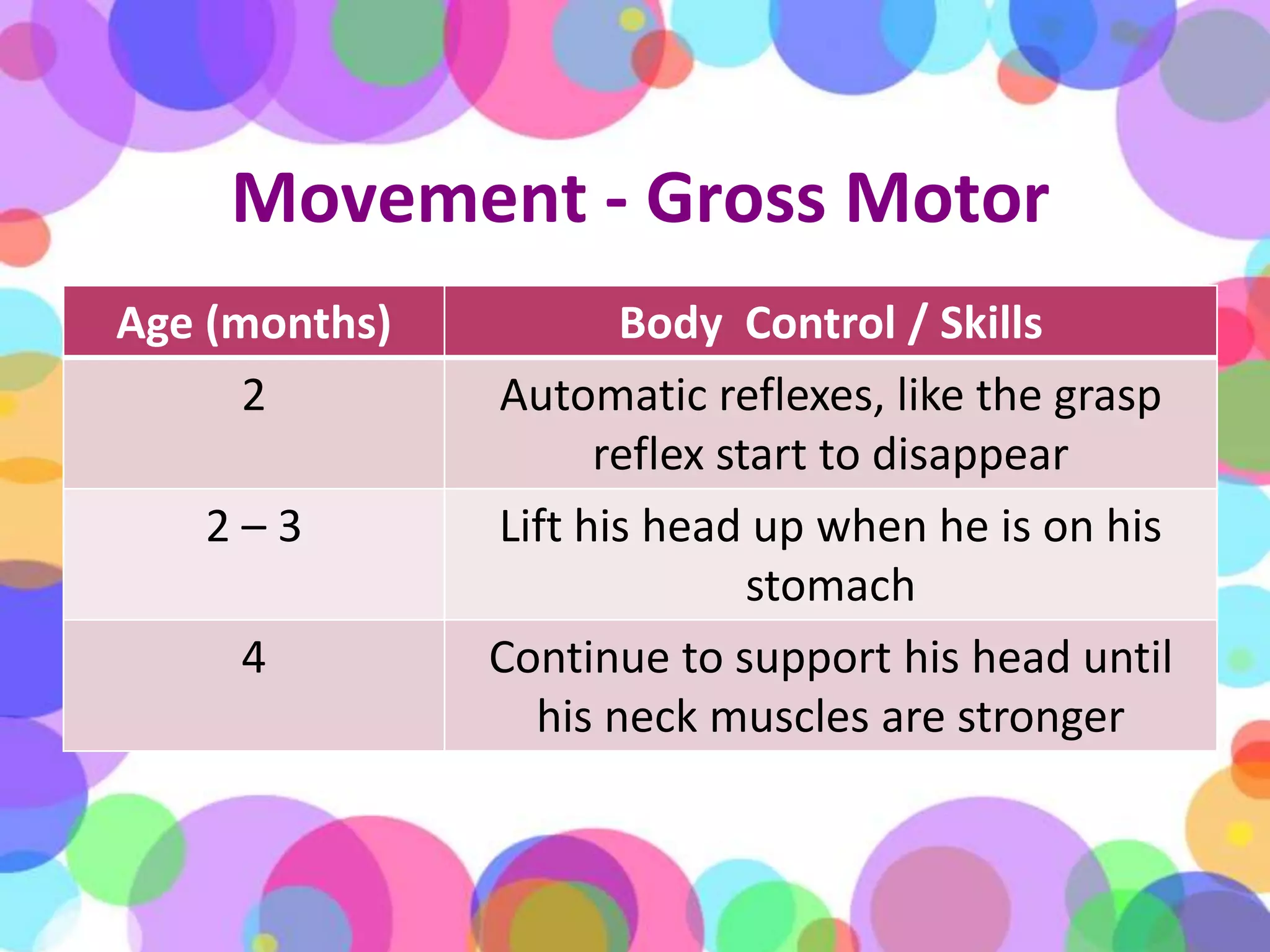
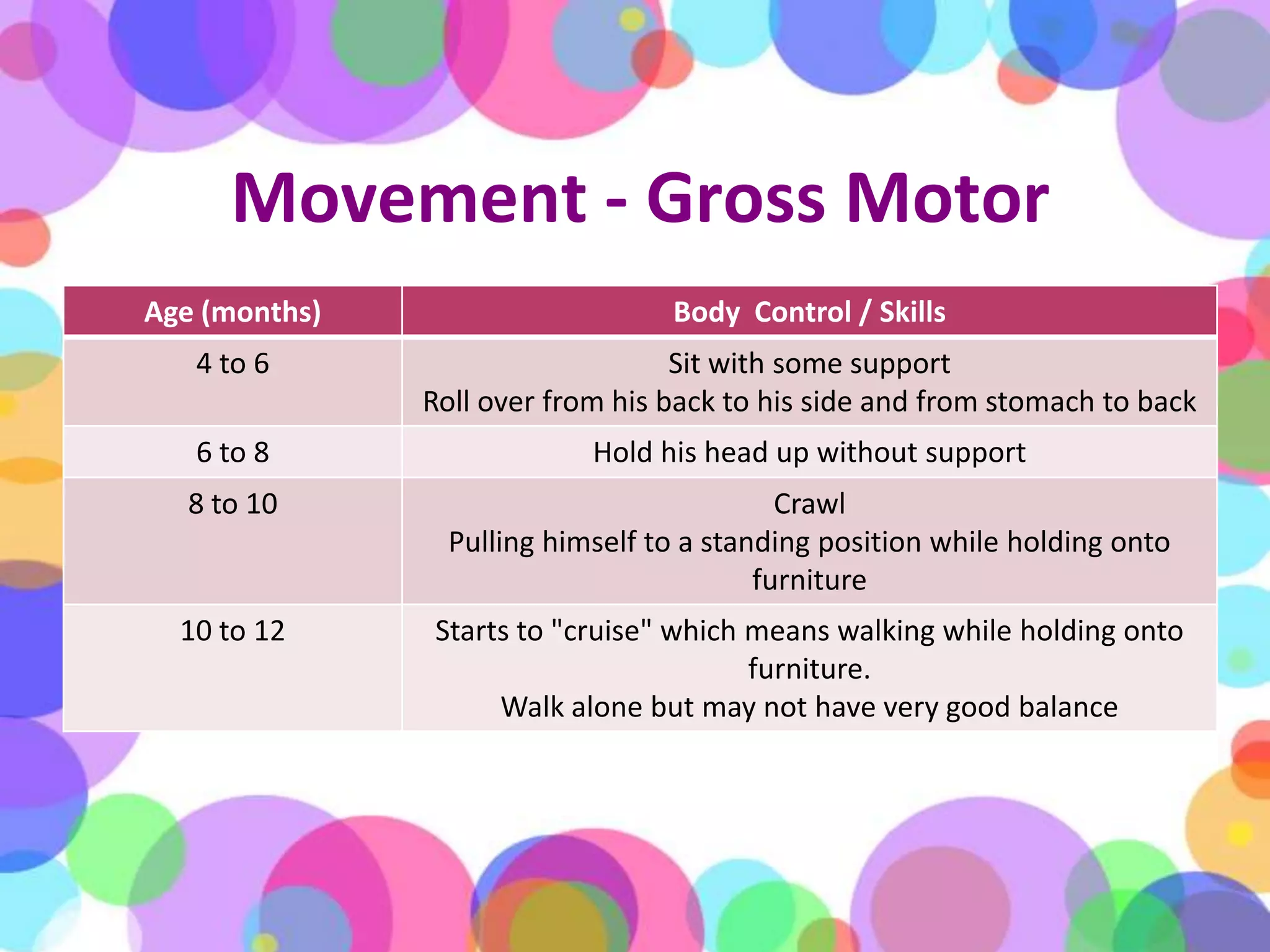
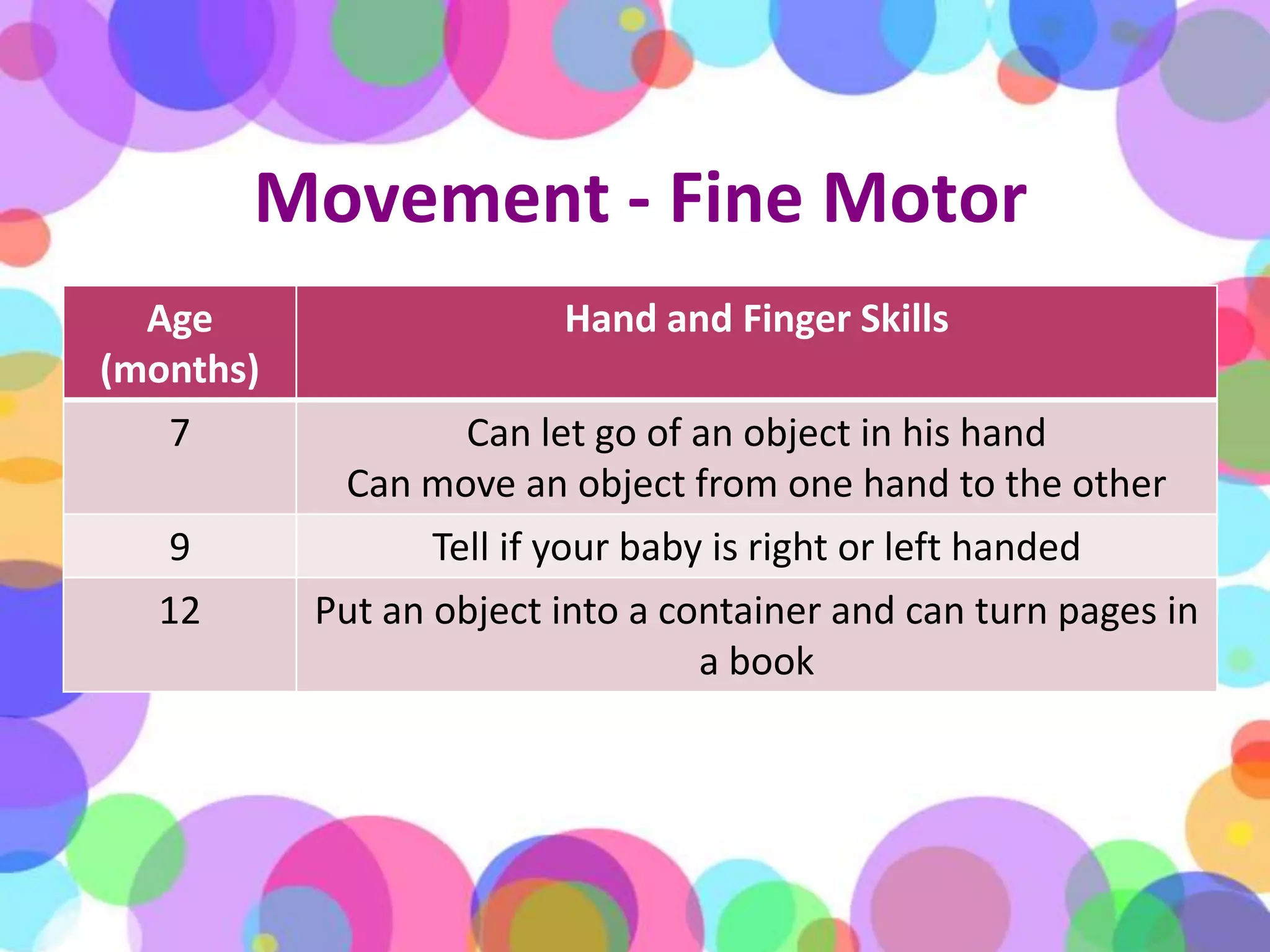
During the first year of life, infants experience significant physical, cognitive, linguistic, and emotional growth and development. Caregivers monitor an infant's physical growth through regular checkups and maintaining a growth chart. Infants develop motor skills and learn to grasp objects and sit up on their own. Establishing routines for sleeping, eating, and playtime is important for development. Infants begin to understand language and may say their first words by the end of the year. Their brains grow rapidly, so interaction and reading are encouraged over excessive TV time. Caregivers should ensure infant safety by maintaining a secure environment, using approved car seats correctly, and preventing hazards like choking, burns, and falls. When infants are sick or hospitalized