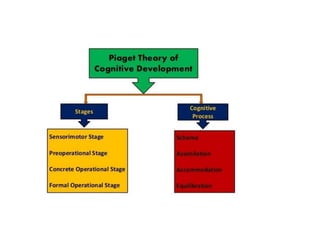
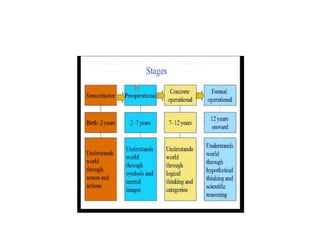
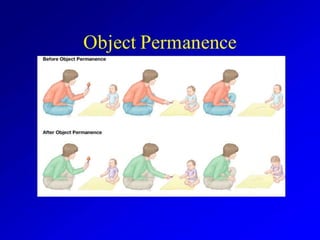
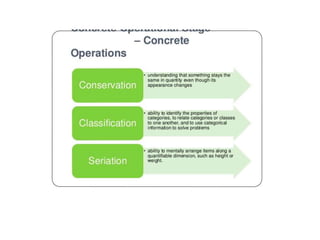
Jean Piaget was a Swiss psychologist known for his work on child development. He placed great importance on children's education. According to Piaget's theory of cognitive development, the sensorimotor stage occurs from birth to age 2, where infants learn about the world through senses and interactions. During this stage, object permanence develops as children understand that objects still exist even when they can't be seen.