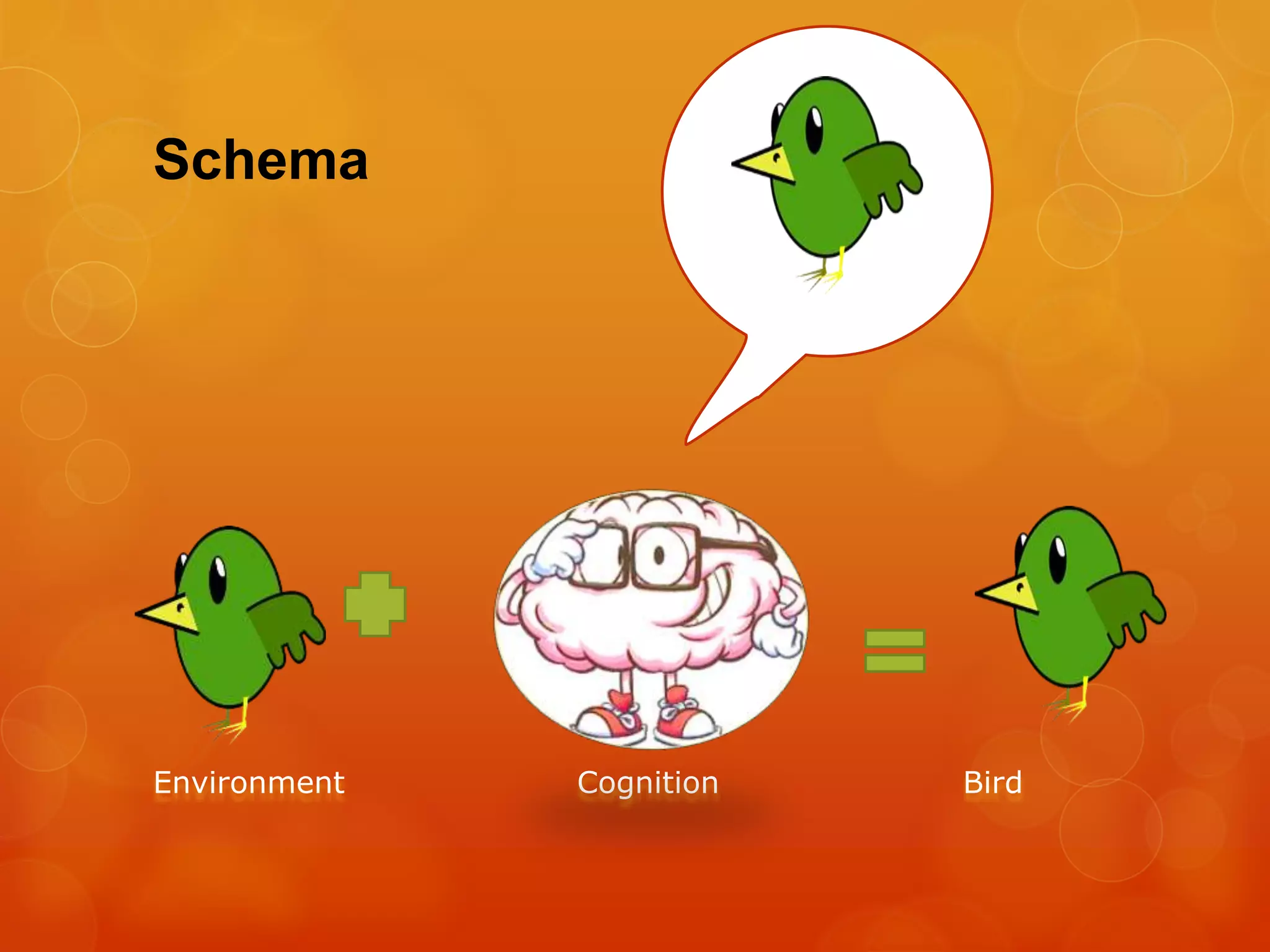
Jean Piaget was a Swiss psychologist who developed a theory of cognitive development in children. He observed his own children from infancy and developed a four stage model: sensorimotor (birth to age 2), preoperational (ages 2 to 7), concrete operational (ages 7 to 11), and formal operational (age 11 and up). In each stage, children develop new cognitive abilities as they interact with the world, such as object permanence, language development, logical thinking, and abstract reasoning. Piaget believed cognitive development was driven by biological maturation and environmental experiences that create challenges for children's understanding.