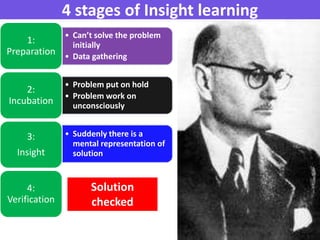
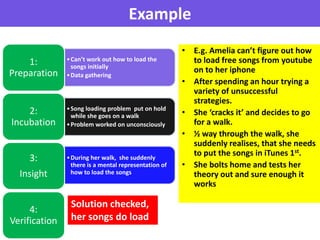
Insight learning, as explored by Kohler, involves a sudden realization of a solution after a period of mentally manipulating aspects of a problem, exemplified through Sultan the chimp's clever use of sticks to obtain food. The process consists of four stages: preparation, incubation, insight, and verification, where an individual initially struggles with a problem, temporarily sets it aside, experiences an 'aha' moment, and then tests the solution. Key points include that solutions are often found correctly on the first attempt, are retained for future problems, and reflect a more cognitive learning process.