1. Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development explains how children construct mental models of the world through biological maturation and interaction with their environment, rather than viewing intelligence as fixed.
2. Piaget's theory differs from others in that it focuses on child development and proposes discrete stages marked by qualitative differences, rather than gradual increases in complexity.
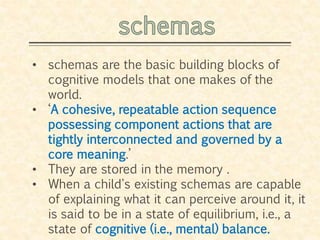
3. Piaget's theory has three basic components: schemas which are mental representations of concepts, and the processes of assimilation, accommodation, and equilibration which drive development forward through adaptation to the environment.