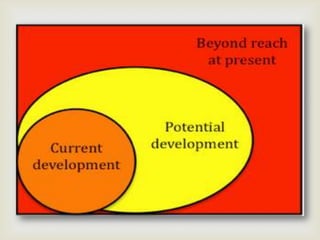
The document discusses Lev Vygotsky's theories on cognitive development, emphasizing the active role of children as knowledge seekers and the interaction between children and their environment. Key concepts include self-regulation, the zone of proximal development, and scaffolding, which highlight the importance of guidance from teachers and peers in the learning process. Vygotsky also posits that language is crucial for the development of thought and consciousness.