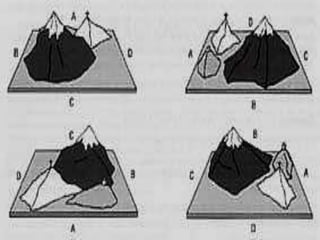
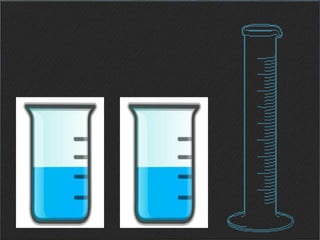
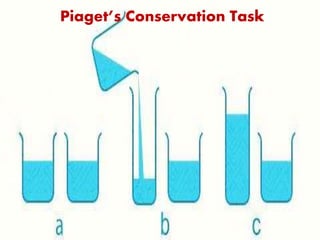
Jean Piaget was a Swiss psychologist who spent decades studying children's cognitive development and is best known for his theory of cognitive development. Some key points of his theory include:
- He identified 4 main stages of cognitive development: sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational.
- He believed that knowledge is constructed by learners through hands-on experiences and interactions with the environment.
- Important concepts in his theory include schemas, assimilation, accommodation, equilibrium, and disequilibrium which describe how children incorporate new information and experiences into their existing understanding of the world.
- His work has had a large influence on constructivist approaches in education which aim to actively engage students in