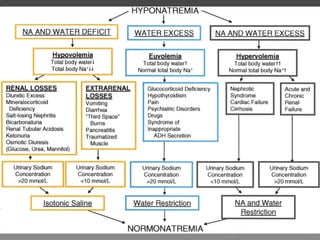
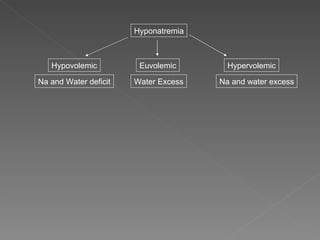
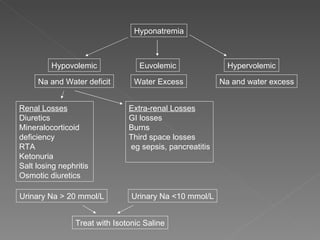
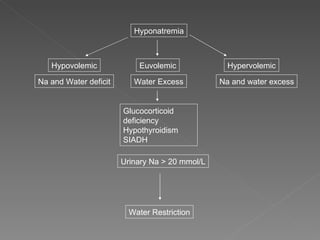
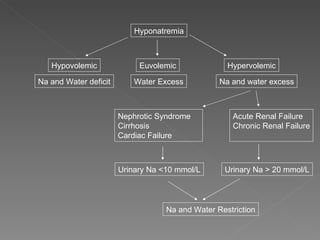
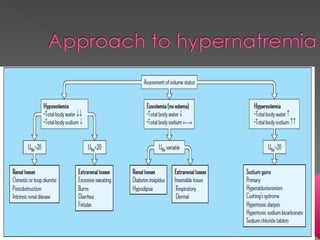
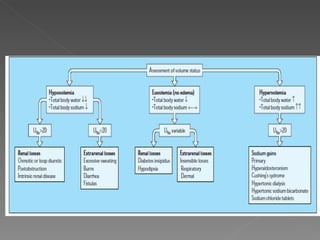
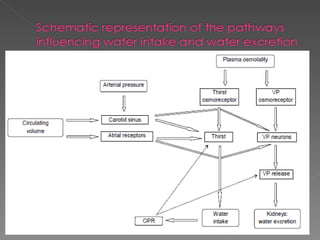
The document discusses sodium homeostasis and the kidney's role in regulating sodium and water balance. The key points are:
- The kidney plays a major role in sodium and water homeostasis by precisely regulating excretion and reabsorption along the nephron. Over 99% of filtered sodium is reabsorbed.
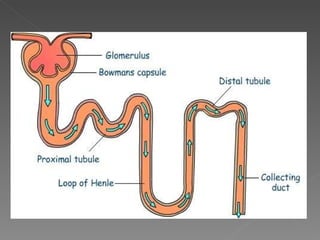
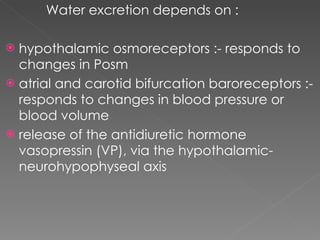
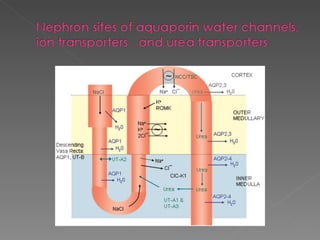
- Various segments of the nephron (proximal tubule, loop of Henle, distal tubule) differentially reabsorb sodium, water, and other solutes under the control of hormones like aldosterone and vasopressin.
- The collecting duct is the final site where the kidney determines how much sodium and water will be excreted in the urine based on solute