Physiology of Menstrual Cycle.
- 1. PHYSIOLOGY OF THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE 1
- 2. OUTLINE: • Introduction • Definition • Characteristics of Normal Menstruation • The Hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian Axis • Ovarian Cycle • Uterine Cycle • Menstrual Abnormalities • Comfort Measures During Menstruation 2
- 3. INTRODUCTION • Typically, a woman of childbearing age or reproductive age (15-45) should menstruate every 28 days or so unless pregnant or in menopause. • Numerous things can go wrong with the normal menstrual cycle. • The menstrual cycle is essential for the production of ova, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. 3
- 4. DEFINITION • Menstruation is the periodic discharge of blood, mucus and uterine cellular debris at cyclic intervals from menarche to menopause. • A.K.A: Period, Menses, Menstrual bleeding. • Exception: Pregnancy, Lactation, Anovulation, Pharmacological Interventions e.g. contraceptive pills. 4
- 5. CHARACTERISTICS OF N.M 1. Menarche: 10–16 years (Average: 13 years). 2. Duration: 2–7 days. • <2 days – Hypomenorrhea • >7 days – Menorrhagia 3. Amount: 30–80 ml. • Uses 3 napkins/pads per day • <30ml – Hypomenorrhea • >80ml – Menorrhagia 4. Cycle length: 21-35 days (Average: 28 days). 5
- 6. CHARACTERISTICS OF N.M CONT. 5. Normal menstrual blood doesn’t coagulate as a result of secretion of fibrinolysin enzyme (plasmin) secreted by the endometrium. 6. Menstrual molimina refers to mild symptoms of 7-10 days before menstruation relieved once menstruation occurs exaggerated condition called Premenstrual Syndrome. 6
- 7. NOTE: • Menopause: 45 – 55 years (Average: 51 years). • Factors such as hereditary, diet and overall health can accelerate or delay menarche. • Irregular menstrual cycle is when the cycle length is <21 days or >35 days. 7
- 8. CHARACTERISTICS OF N.M CONT. 8
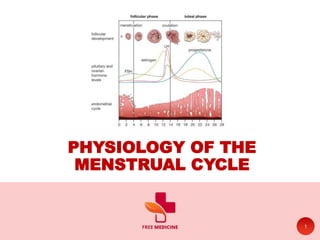
- 9. THE HYPOTHALAMIC- PITUITARY-OVARIAN AXIS • The phases of the MC and ovulation are regulated by interaction between hypothalamus, anterior pituitary and ovaries. • The interaction involves hormones. ENDOCRINE GLAND HORMONES Hypothalamus Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Anterior Pituitary Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Hormone (LH). Ovaries Estrogen and Progesterone 9
- 11. PHASES OF MENSTRUAL CYCLE • There are two main components of the menstrual cycle, the changes that happens in the ovaries (Ovarian Cycle) and the variations that take place in the uterus (Uterine Cycle). • The ovarian cycle is divided into three phases; Follicular, Ovulatory and Luteal. • The uterine cycle into three phases; Menstrual, Proliferative and Secretory. 11
- 13. 13 A. FOLLICULAR PHASE B. OVULATOTY PHASE C. LUTEAL PHASE OVARIAN CYCLE
- 14. A. FOLLICULAR PHASE • Follicular phase begins with menses on first day of the menstrual cycle and ends with ovulation( Day 1 to Day 14 of 28-days cycle) . • At the beginning of menstrual cycle, GnRH (pulsatile manner) ➤ FSH and LH. FSH is responsible for the recruitment and growth of several primordial follicle. • Only one follicle on one of the ovaries reaches maturity (Graafian follicle) which secretes estrogen. 14
- 15. A. FOLLICULAR PHASE CONT. • Increase in estrogen level causes: 1. Negative feedback on the pituitary to stop FSH 2. The uterine lining (endometrium) to grow thicker 15
- 16. B. OVULATORY PHASE • The estrogen peak stimulates secretion of LH, leading to the LH peak which leads to the follicle to burst open, releasing the mature ovum, a process called ovulation. • The remaining Graafian follicle forms Corpus luteum. • Ovulation occurs on day 14 of a 28-day cycle. • High estrogen also suppress FSH secretion so no further follicles grow. 16
- 17. C. LUTEAL PHASE • After ovulation, LH levels remain elevated and cause the remnants of the follicle to develop into a yellow body called the corpus luteum. • In addition to producing estrogen, the corpus luteum secretes a hormone called progesterone. • When progesterone reaches a high level it inhibits the secretion of LH leads to degeneration of the corpus luteum (If fertilization does not take place). 17
- 18. C. LUTEAL PHASE CONT. • Degeneration of corpus luteum leads decrease in estrogen and progesterone level and separation of the endometrium (menstruation). • Decrease in estrogen and progesterone level stimulates the hypothalamus to secrete more GnRH, a new cycle is started. • If fertilization and implantation occurs, placenta secretes human chorionic gonadotropin hormone (hCG) which stimulates and maintain the corpus luteum. hCG leads to positive urine pregnancy test. 18
- 19. 19 A. MENSTRUAK PHASE B. PROLIFERATIVE PHASE C. SECRETOTY PHASE UTERINE CYCLE
- 20. A. MENSTRUAL PHASE • First day of the menstrual cycle is marked by the onset of menstruation (period). • During the menstrual phase of the uterine cycle, the uterine lining is shed because of low levels of progesterone and estrogen. • At the same time, a follicle is beginning to develop and starts producing. • The menstrual phase ends when the menstrual period stops on approximately day 5. 20
- 21. B. PROLIFERATIVE PHASE • When estrogen levels are high enough, the endometrium begins to regenerate. • Estrogen stimulates blood vessels to develop. The blood vessels in turn bring nutrients and oxygen to the uterine lining, and it begins to grow and become thicker. • The proliferative phase ends with ovulation on day 14. 21
- 22. C. SECRETORY PHASE • After ovulation, the corpus luteum begins to produce progesterone. • This hormone causes the uterine lining to become rich in nutrients in preparation for pregnancy. • Estrogen levels also remain high so that the lining is maintained. • If pregnancy doesn’t occur, the corpus luteum gradually degenerates, and the woman enters the ischemic phase of the menstrual cycle. 22
- 23. C. SECRETORY PHASE • Ischemic Phase - on days 27 and 28, estrogen and progesterone levels fall because the corpus luteum is no longer producing them. • Without these hormones to maintain the blood vessel network, the uterine lining becomes ischemic. • When the lining start slough, the woman has come full cycle and is once again at day 1 of the menstrual cycle. 23
- 24. 24
- 25. OTHER PHYSIOLOGICAL CHANGE A. CERVICAL MUCUS CHANGE B. BASAL BODY TEMPERATURE 25
- 26. A. CERVICAL MUCUS CHANGES • Changes in cervical mucus takes place over the course of the menstrual cycle. • Some women use these characteristics to help determine when ovulation is likely to happen. • During the menstrual phase the cervix doesn’t produce mucus. • As the proliferative phase begins, the cervix begins to produce a tacky, crumbly type of mucus that is yellow or white. 26
- 27. A. CERVICAL MUCUS CHANGES • As the time of ovulation becomes near, the mucus becomes progressively clear, thin and lubricative, with the properties of raw egg white. • At the peak of fertility(i.e., during ovulation), the mucus has a distensible, stretchable called spinbarkheit. • After ovulation the mucus becomes scanty, thick, and opaque. 27
- 28. 28
- 29. B. BASAL BODY TEMPERATURE • Basal body temperature (BBT or BTP) is the lowest body temperature attained during rest (usually during sleep). • It is usually estimated by a temperature measurement immediately after awakening and before any physical activity has been undertaken. • Monitoring BBTs is one way of estimating the day of ovulation 29
- 30. 30
- 31. MENSTRUAL ABNORMALITIES • Anovulation • Dysmenorrhea • Hypomenorrhea • Metrorrhagia • Oligomenorrhea • Amenorrhea • Polymenorrhea 31
- 32. MENSTRUAL ABNORMALITIES • Amenorrhea (no periods) is the absence of uterine bleeding for more than 6 months in non- menopausal women. • Dysmenorrhea (painful periods) is the painful menstruation, typically involving cramps. • Hypomenorrhea is the regular menstruation occurring at normal intervals, but with minimal blood loss. • Menorrhagia/Hypermenorrhea is the regular menstruation occurring at normal intervals, but with heavy blood loss. 32
- 33. MENSTRUAL ABNORMALITIES • Menometrorrhagia is the uterine bleeding occurring at irregular intervals, with heavy (>80mL) or prolonged (>7days) menstrual flow. • Oligomenorrhea is the uterine bleeding occurring at intervals of 35 days or longer (every five weeks or more). • Polymenorrhea is the uterine bleeding occurring at intervals of 21 days or less (every three weeks or less). • Postmenopausal bleeding is the uterine bleeding that occurs after menopause. 33
- 34. MENSTRUAL ABNORMALITIES • Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) is the physical and psychological symptoms that occur before the start of a period. • Primary amenorrhea is absence for uterine bleeding ever starting (at puberty). • Secondary amenorrhea is absence of uterine for more than 3 months after menarche. 34
- 35. CARE AND COMFORT MEASURES Menstrual hygiene: 1. Sanitary pads and tampons: • Wash hands before and after giving self- perineal care. • Washing or wiping the perineum should be always done from front to back. • Reduce use of tampons by substituting sanitary pads especially at night. • Use tampon only for heavy menstrual flow. 35
- 36. CARE AND COMFORT MEASURES Menstrual hygiene: 2. Vaginal spray and douching: • Spray should be used externally only not with pads. • Should not be applied with broken irritated or itched skin. • Douching washes away the natural mucus and upsets the vaginal ecology, thus make it liable to infection. 36
- 37. REFERENCES 1. Dutta, D.C. and Hiralal Konar (2016). DC Dutta’s textbook of gynecology : including contraception. New Delhi: Jaypee 2. Hall, J. (2015). Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology. Elsevier. 3. Wikipedia Contributors (2019). Menstrual cycle. [online] Wikipedia. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Menstrual_Cycle. 4. All Image from google.com/images 37
- 38. THANK YOU By Free Medicine 38