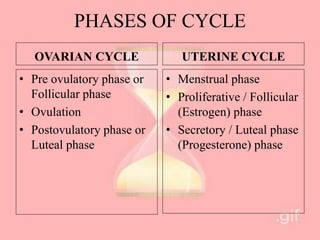
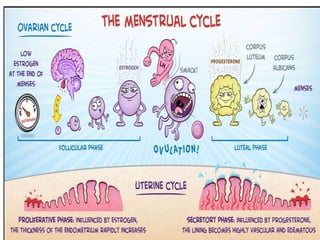
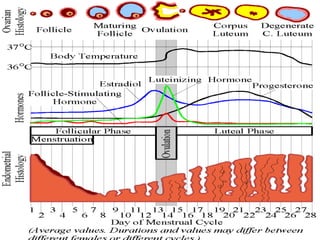
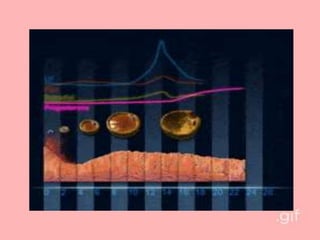
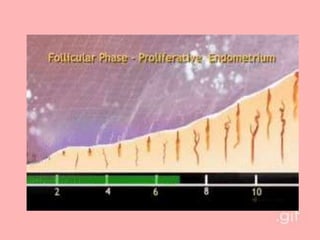
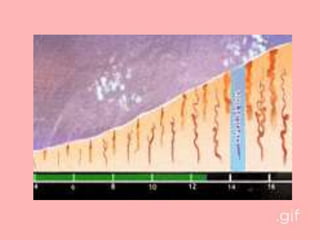
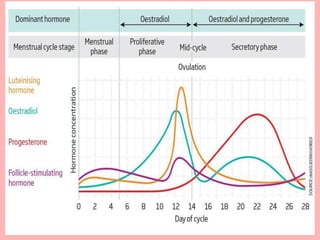
The document provides an overview of the menstrual cycle, detailing its phases, hormonal regulation, and physiological changes in females during reproductive years. Key components of the cycle include menarche, menopause, the duration of the cycle, and average blood loss. It also discusses the hormonal interplay involving gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), estrogen, and progesterone throughout different phases of the cycle.