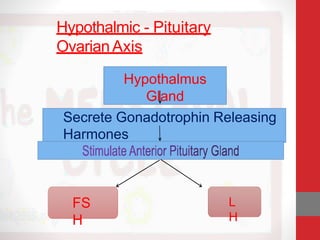
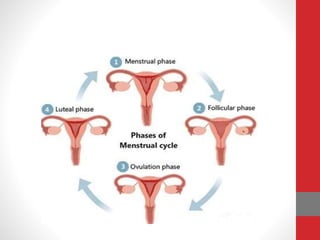
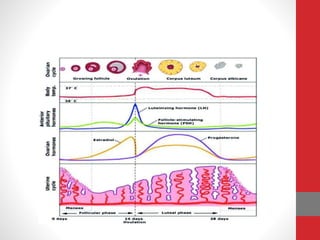
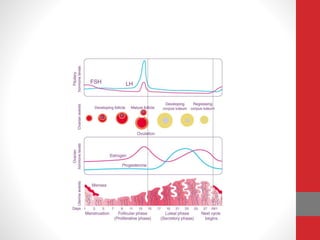
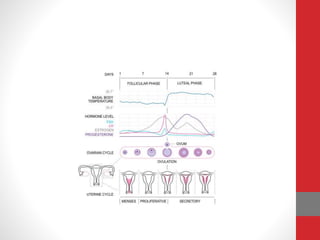
The document summarizes the physiology of the human menstrual cycle. It describes the four phases - menstrual, follicular, ovulatory, and luteal. Key events include menarche beginning the cycle around age 14 and menopause ending it around age 50. The ovarian cycle involves follicle maturation and ovulation in response to hormones. The uterine cycle involves changes to the endometrium also in response to hormones that prepare it for potential pregnancy.