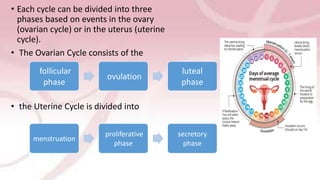
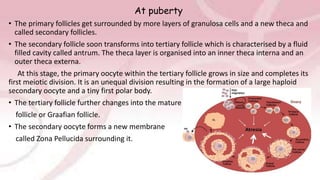
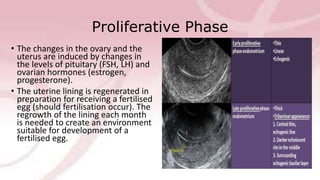
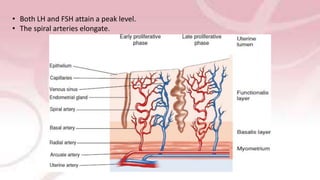
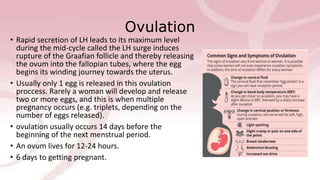
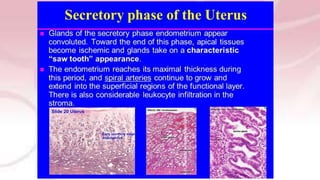
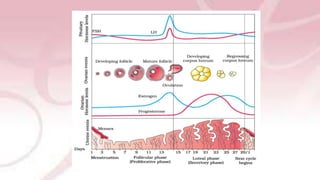
The menstrual cycle involves changes in the ovaries and uterus driven by hormones. It begins at menarche and typically repeats every 21-35 days until menopause. Each cycle can be divided into the follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase. During the follicular phase, FSH stimulates follicle growth and estrogen production. Ovulation occurs when an LH surge causes an egg to be released. In the luteal phase, the corpus luteum produces progesterone to thicken the uterine lining if implantation occurs. If not, progesterone levels drop and menstruation begins, restarting the cycle.