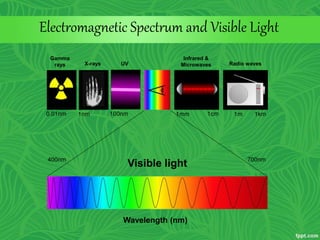
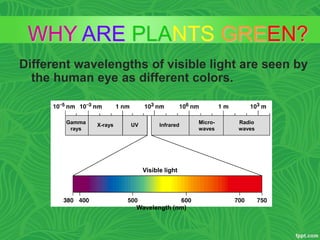
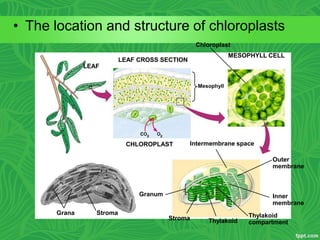
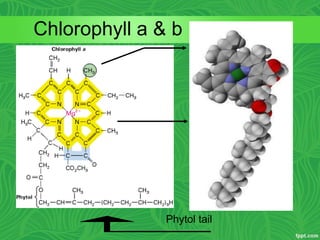
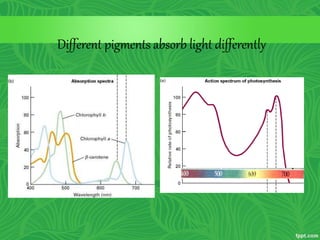
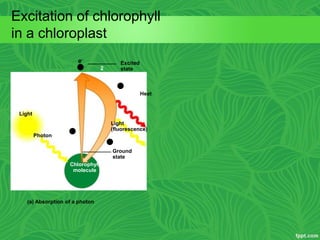
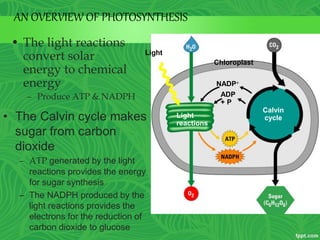
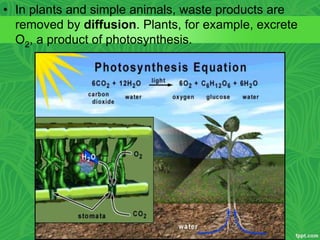
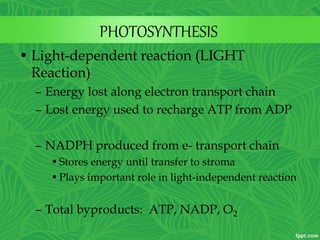
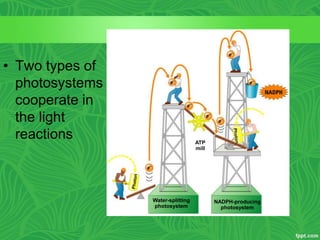
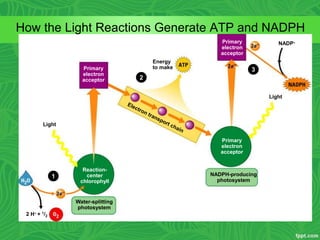
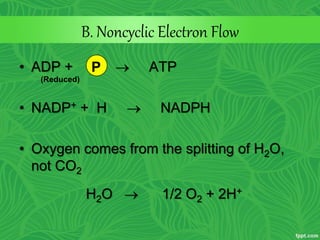
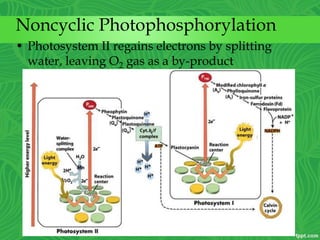
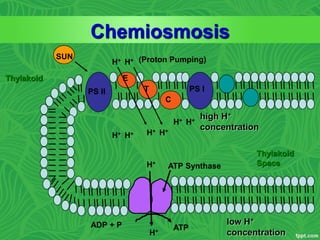
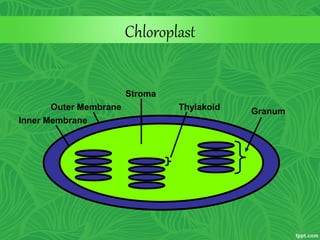
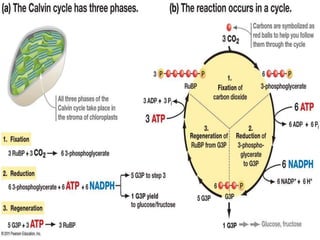
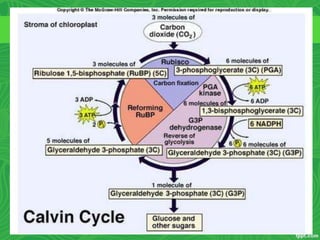
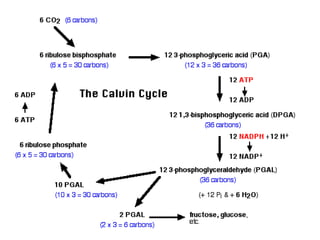
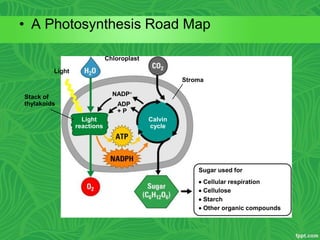
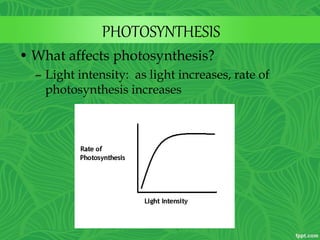
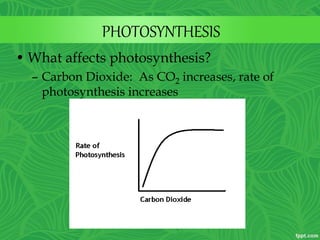
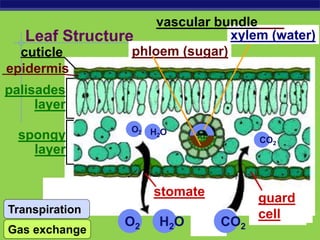
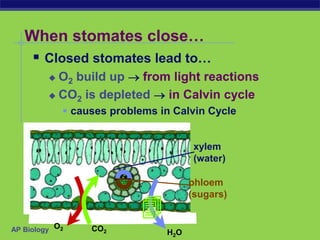
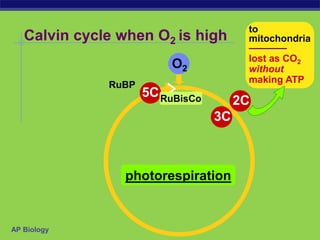
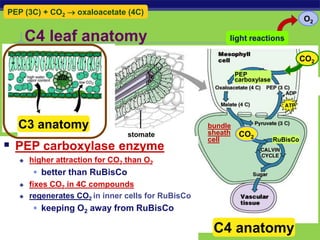
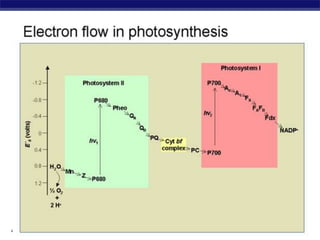
Photosynthesis is a process where autotrophic organisms, primarily plants, convert light energy into chemical energy by transforming carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This process occurs in chloroplasts and involves two main stages: the light-dependent reactions, which generate ATP and NADPH, and the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle), which use these products to synthesize glucose. Factors that affect photosynthesis include light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature, while photorespiration can hinder efficiency under certain conditions.