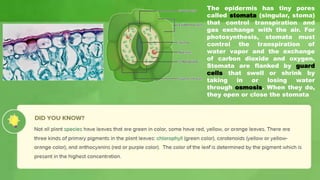
The document discusses photosynthesis and the structures involved in carrying out this process in plants. It describes how chloroplasts, which contain thylakoids, are where photosynthesis occurs within plant cells. Chloroplasts absorb light energy and use it to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and glucose through two stages - the light-dependent reactions in the thylakoids and the light-independent reactions in the chloroplast stroma. The chloroplasts and thylakoids play a key role in harvesting sunlight and producing chemical energy to fuel plant growth and provide food and oxygen.