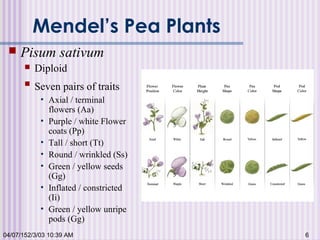
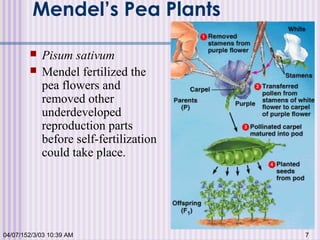
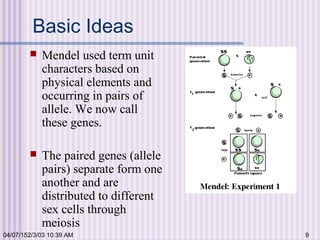
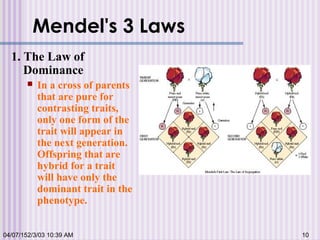
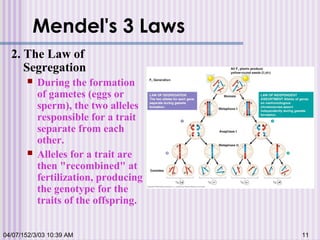
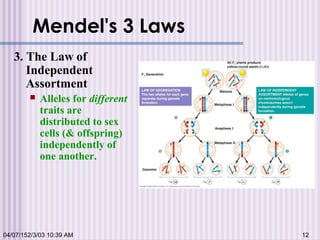
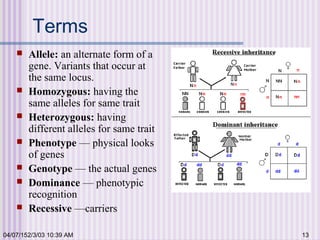
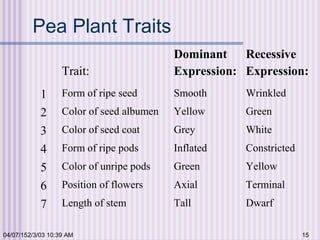
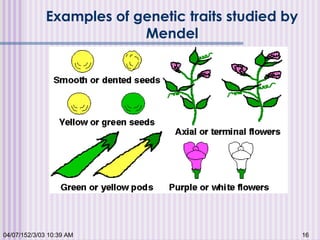
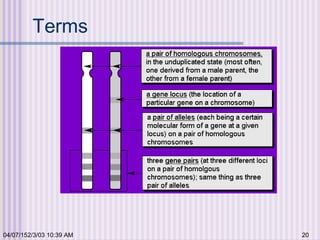
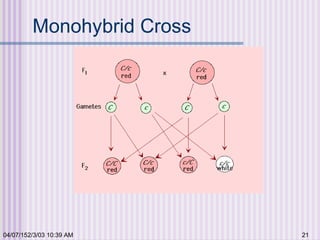
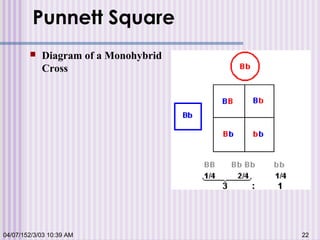
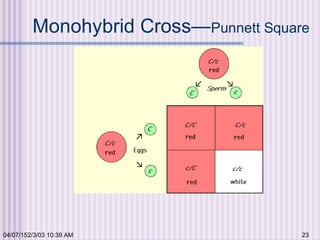
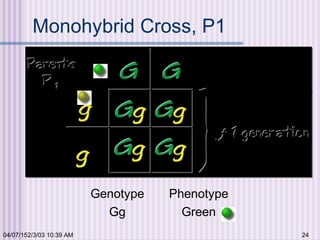
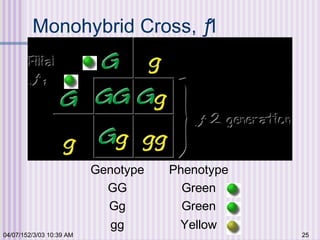
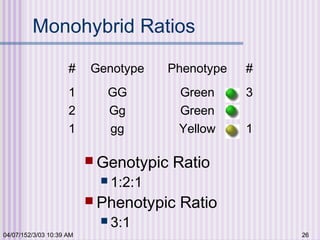
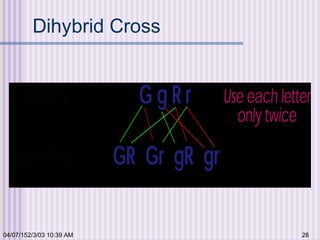
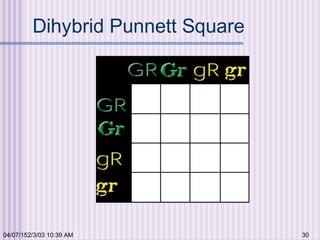
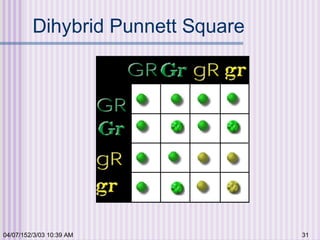
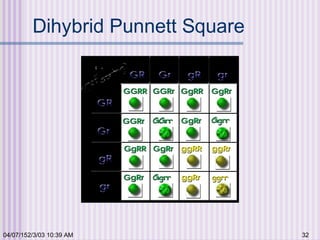
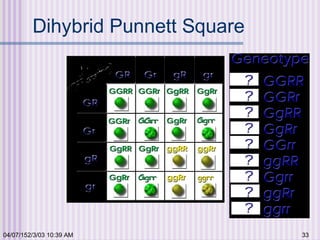
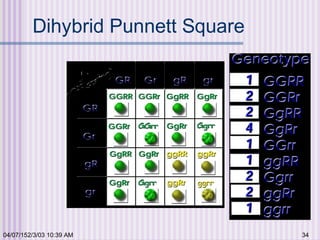
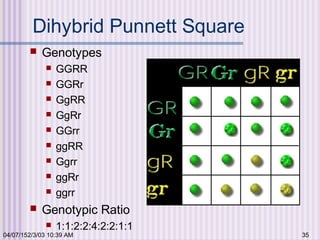
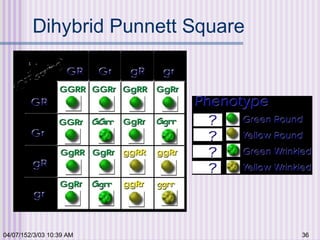
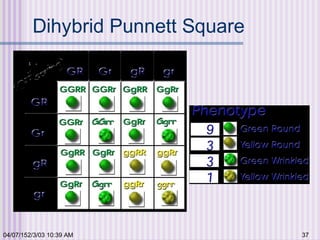
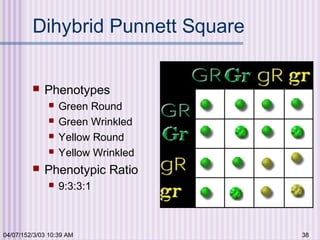
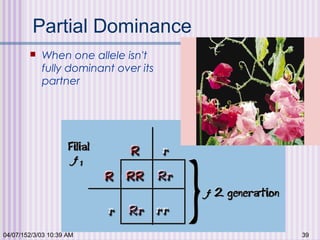
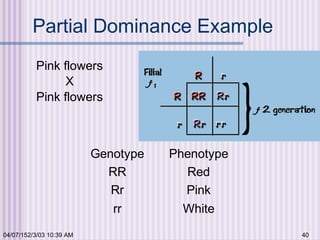
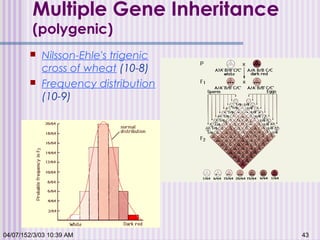
Gregor Mendel conducted experiments with garden peas in the 1850s to study inheritance of traits. He found that traits are passed from parents to offspring in predictable ratios. Some key findings were that traits are controlled by discrete units (now known as genes), alleles can be dominant or recessive, and genes assort independently during reproduction. Mendel's work established the foundations of classical genetics but was not widely recognized until the early 1900s.