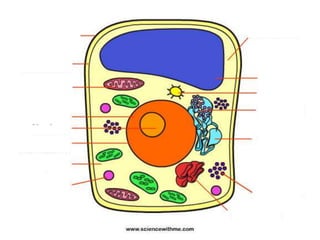
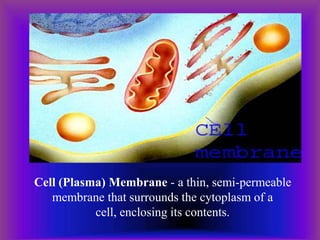
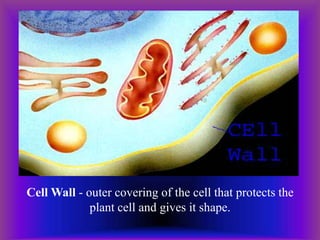
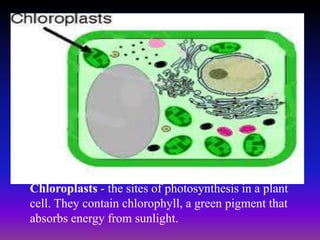
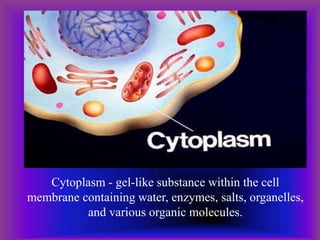
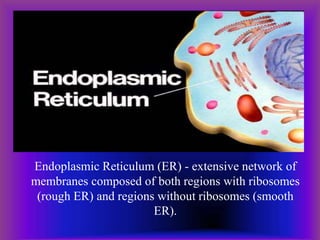
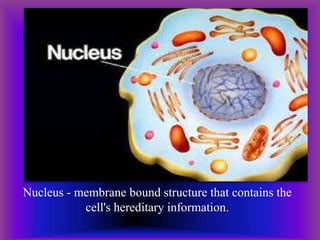
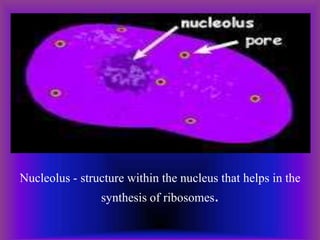
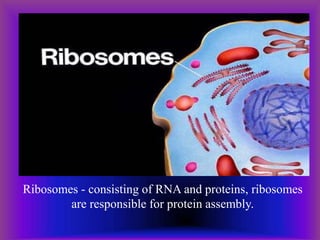
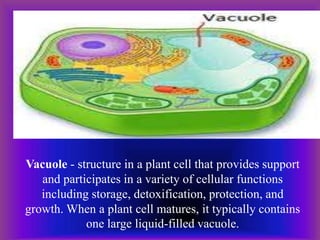
A plant cell contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles and has a cell membrane, cell wall, chloroplasts, cytoplasm, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus, ribosomes, and vacuole. As plants mature, cells become specialized to perform functions like synthesizing and storing organic products or transporting nutrients throughout the plant. Specialized plant cell types include parenchyma cells, collenchyma cells, sclerenchyma cells, water conducting cells, and sieve tube members.