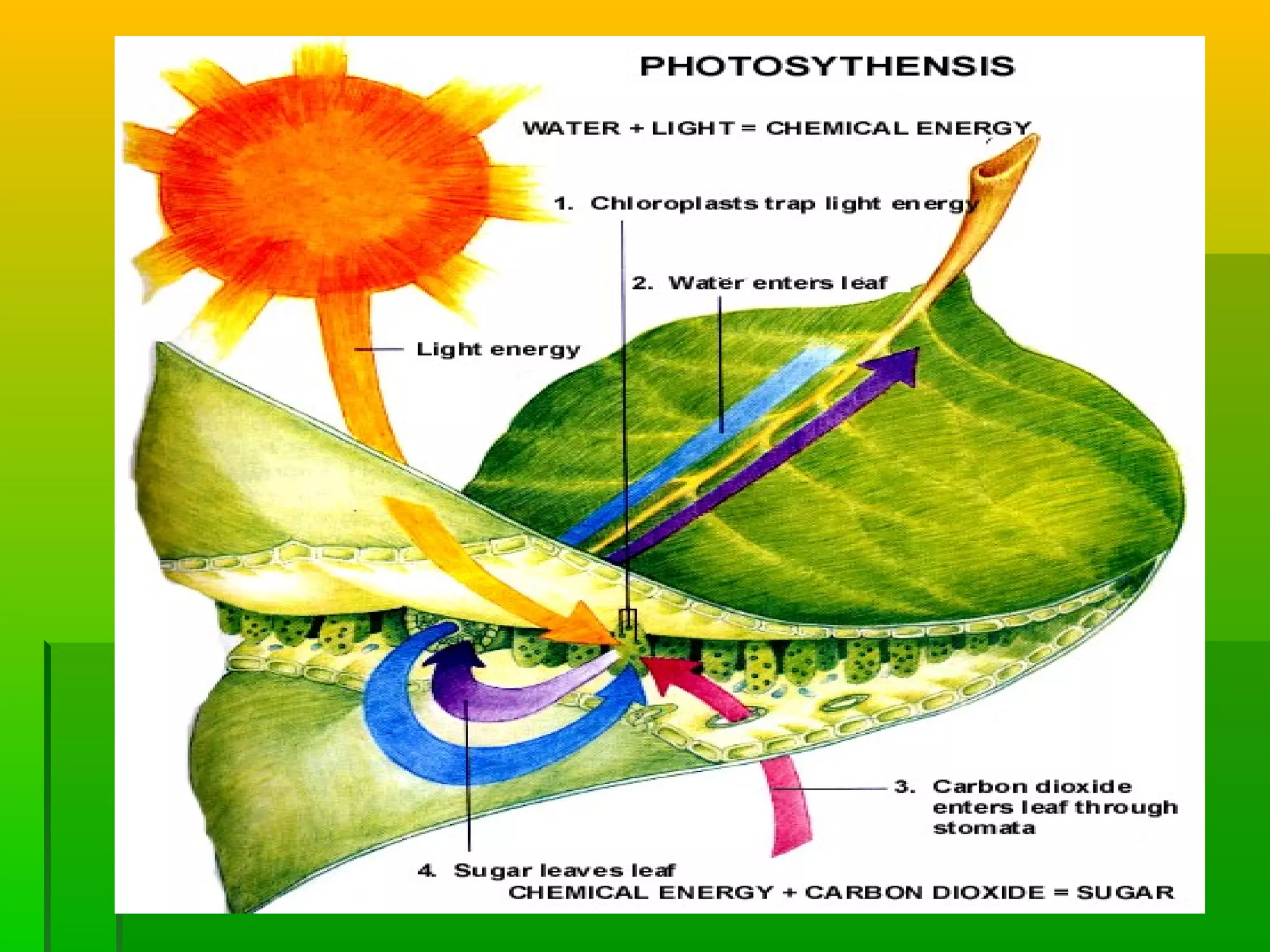
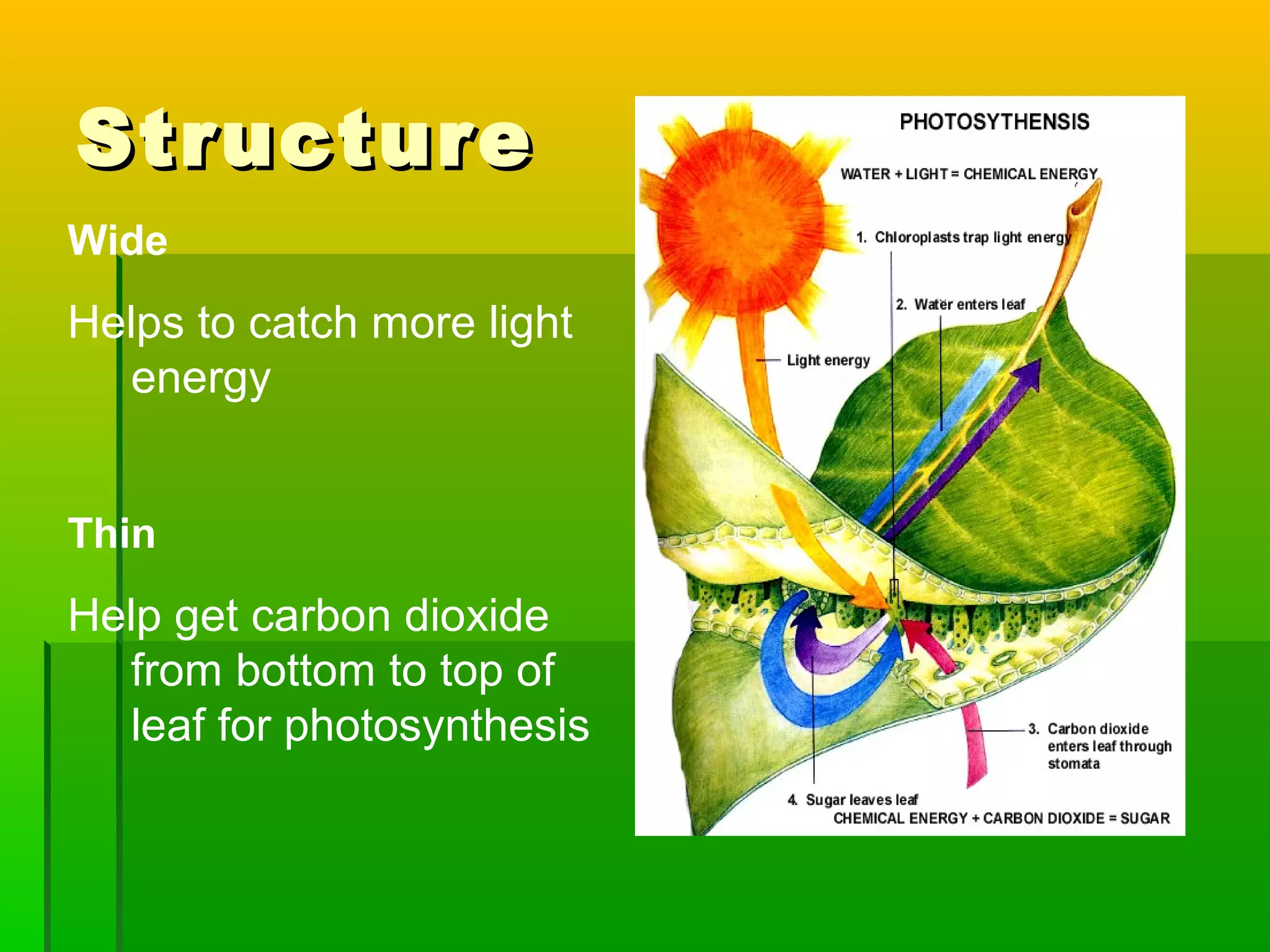
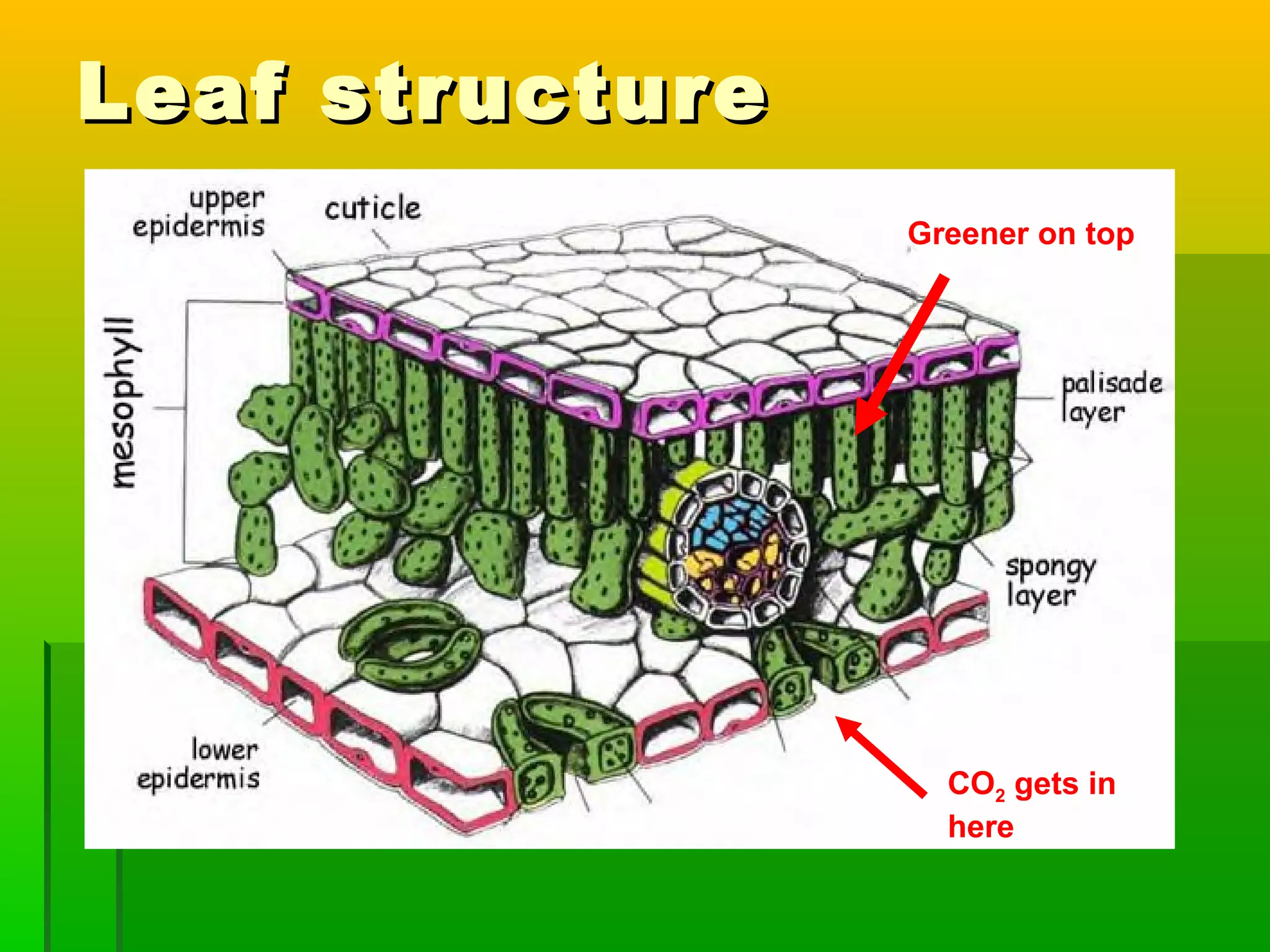
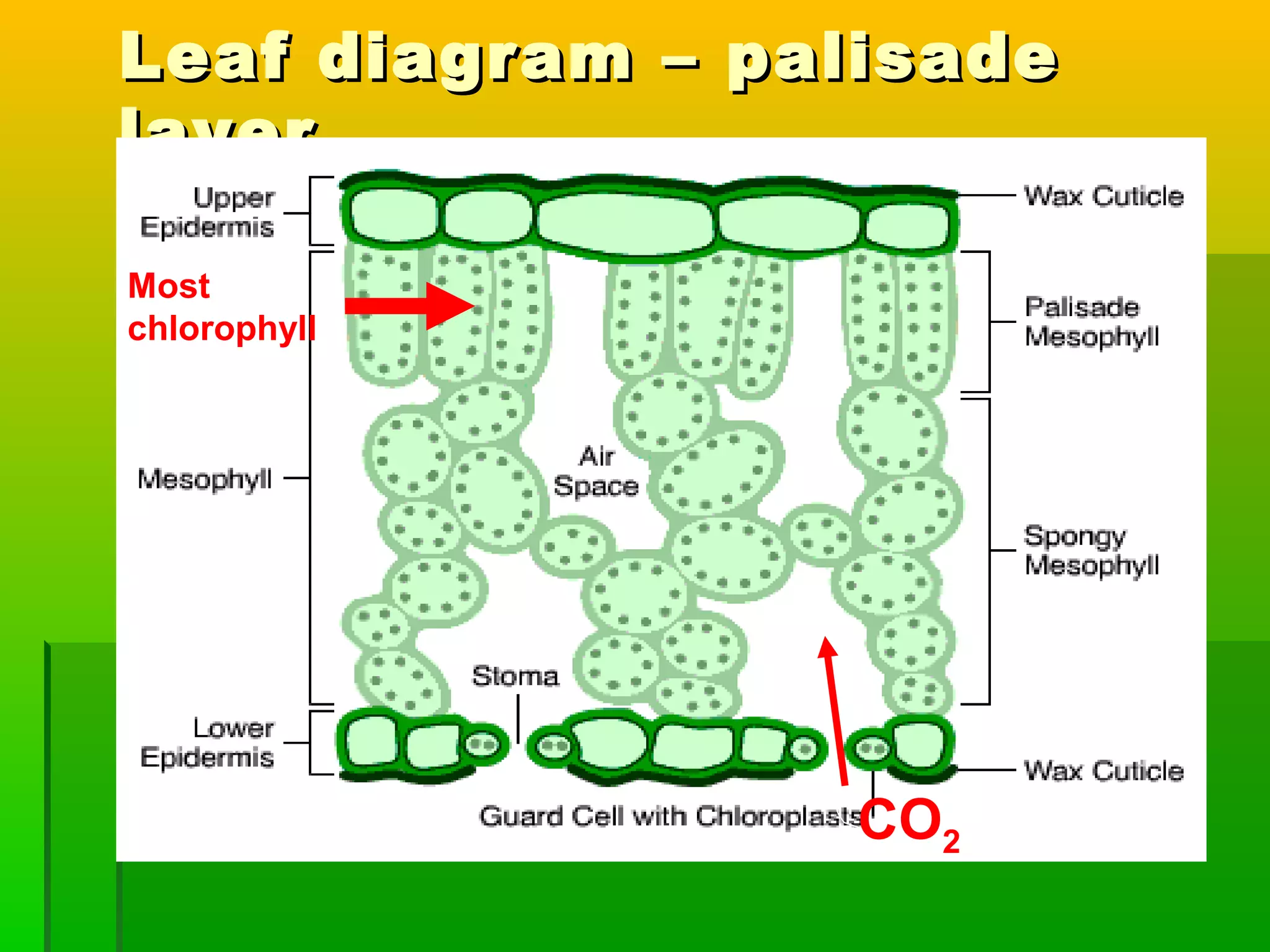
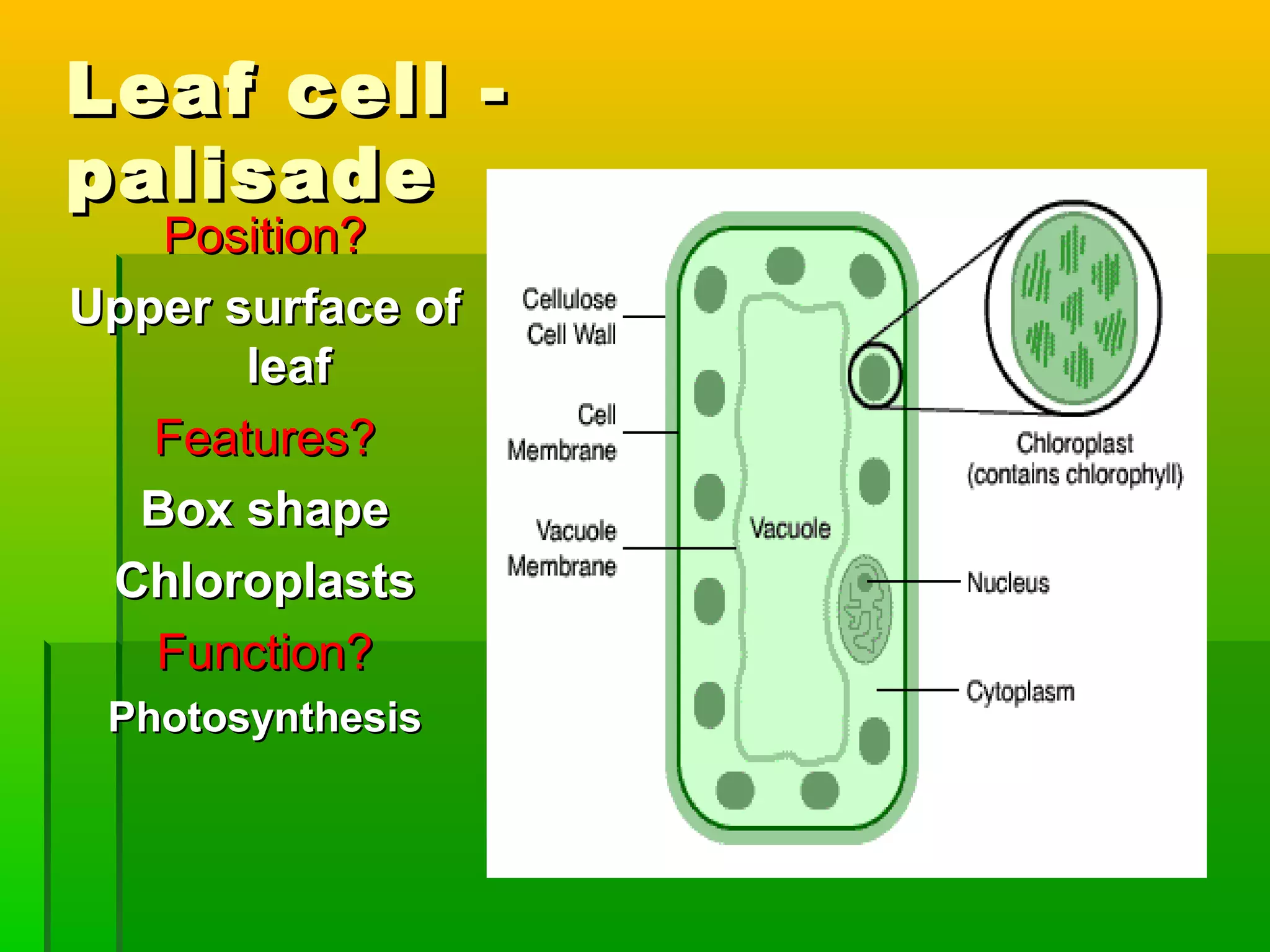
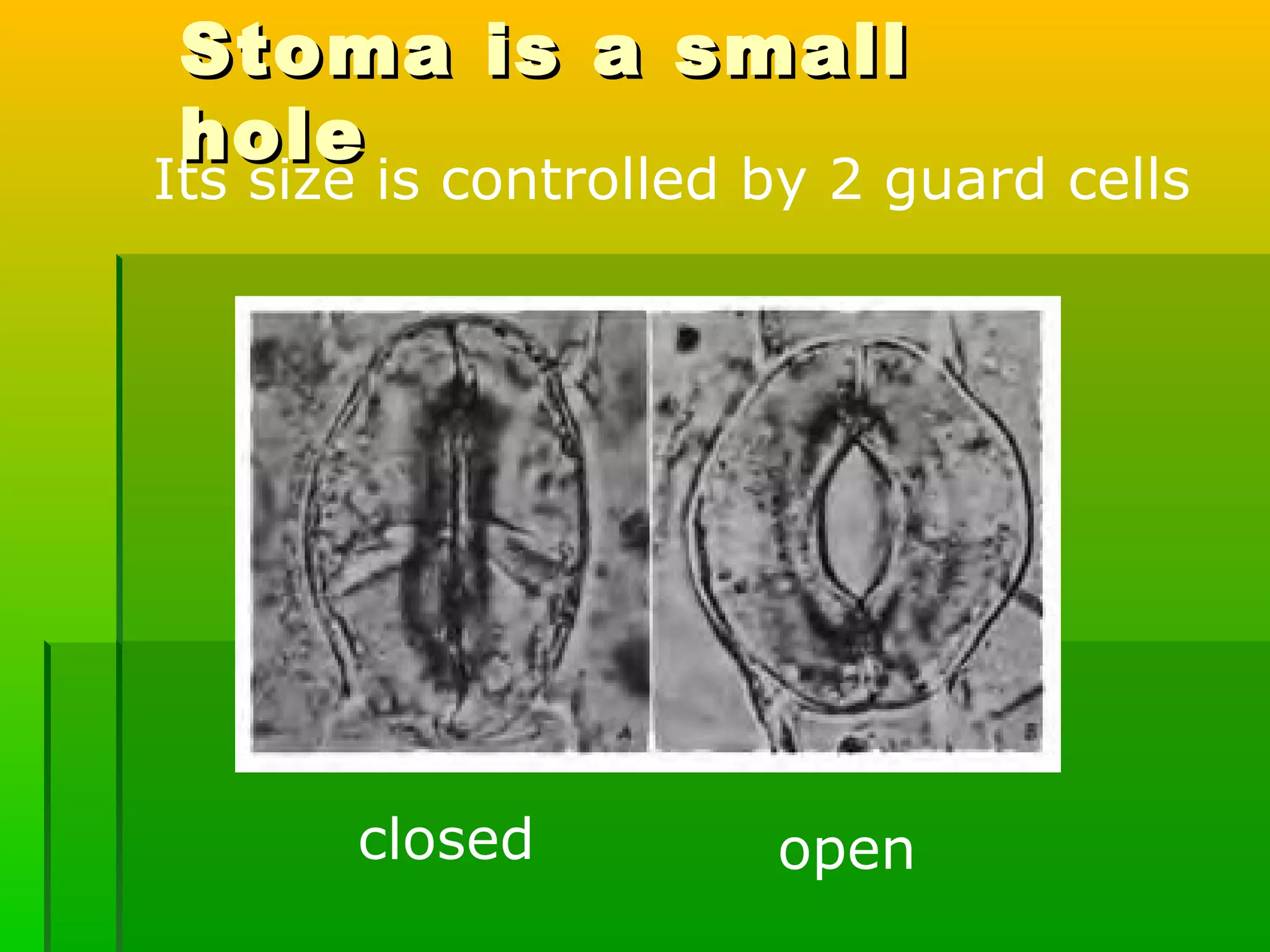
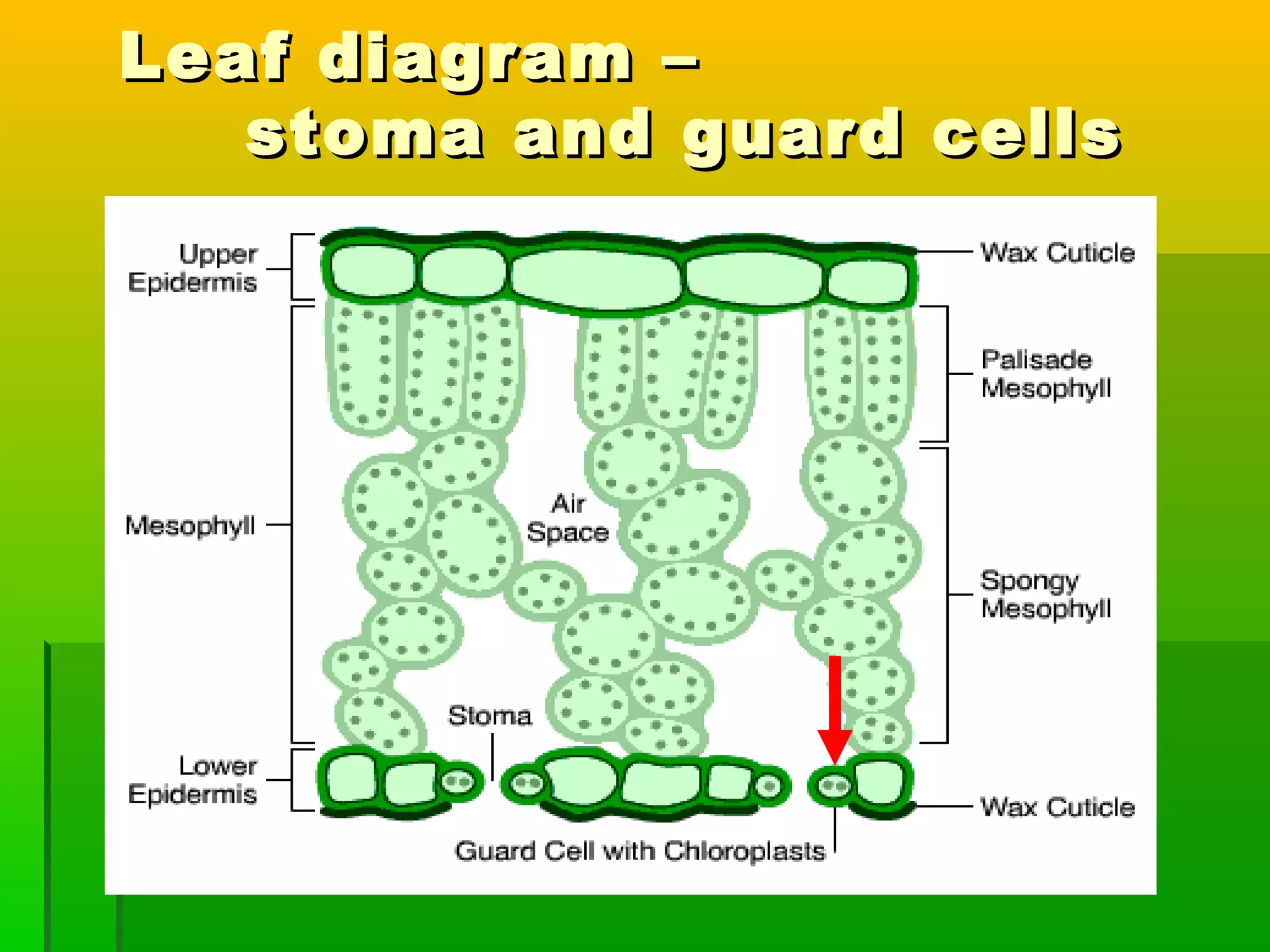
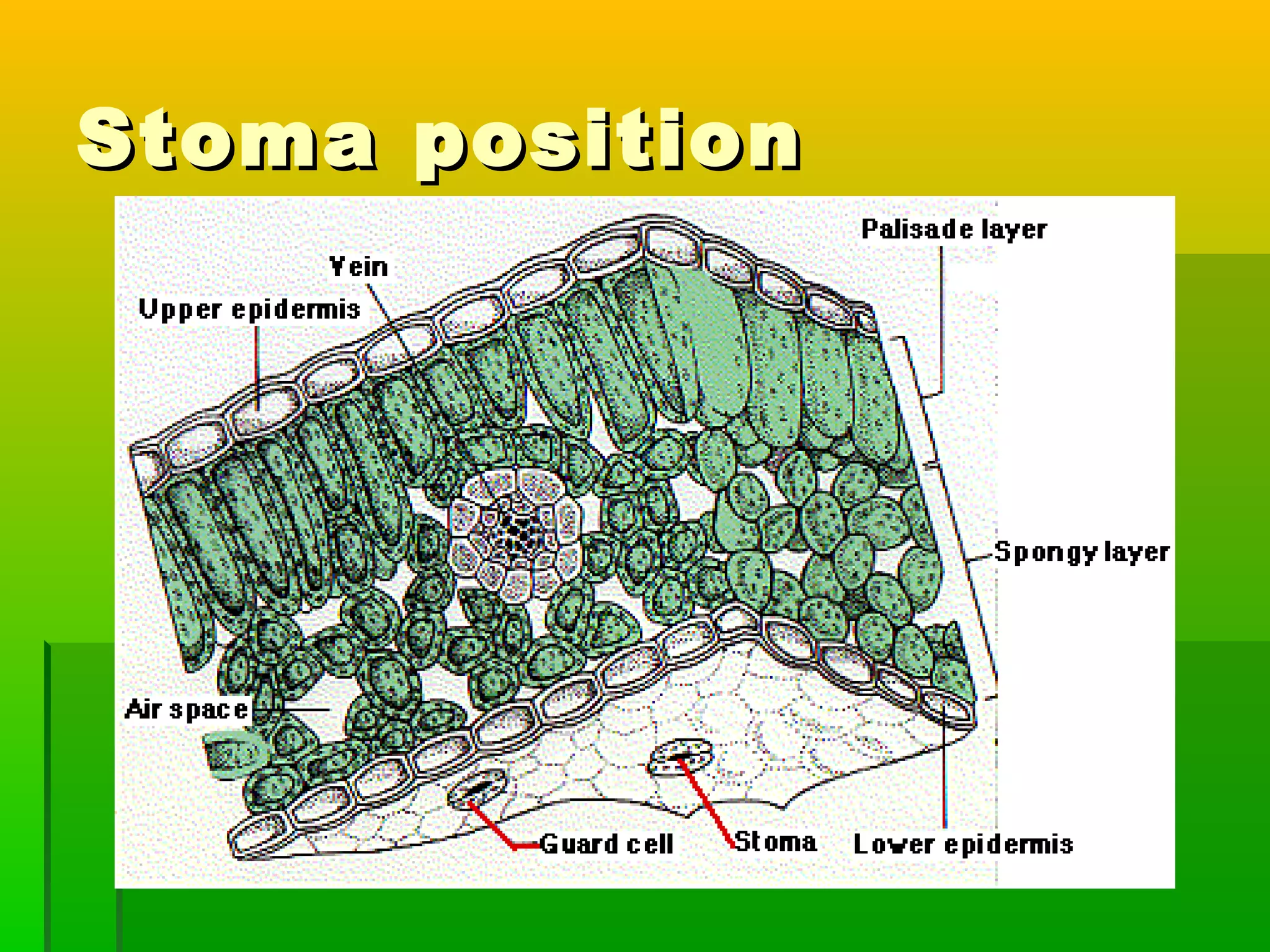
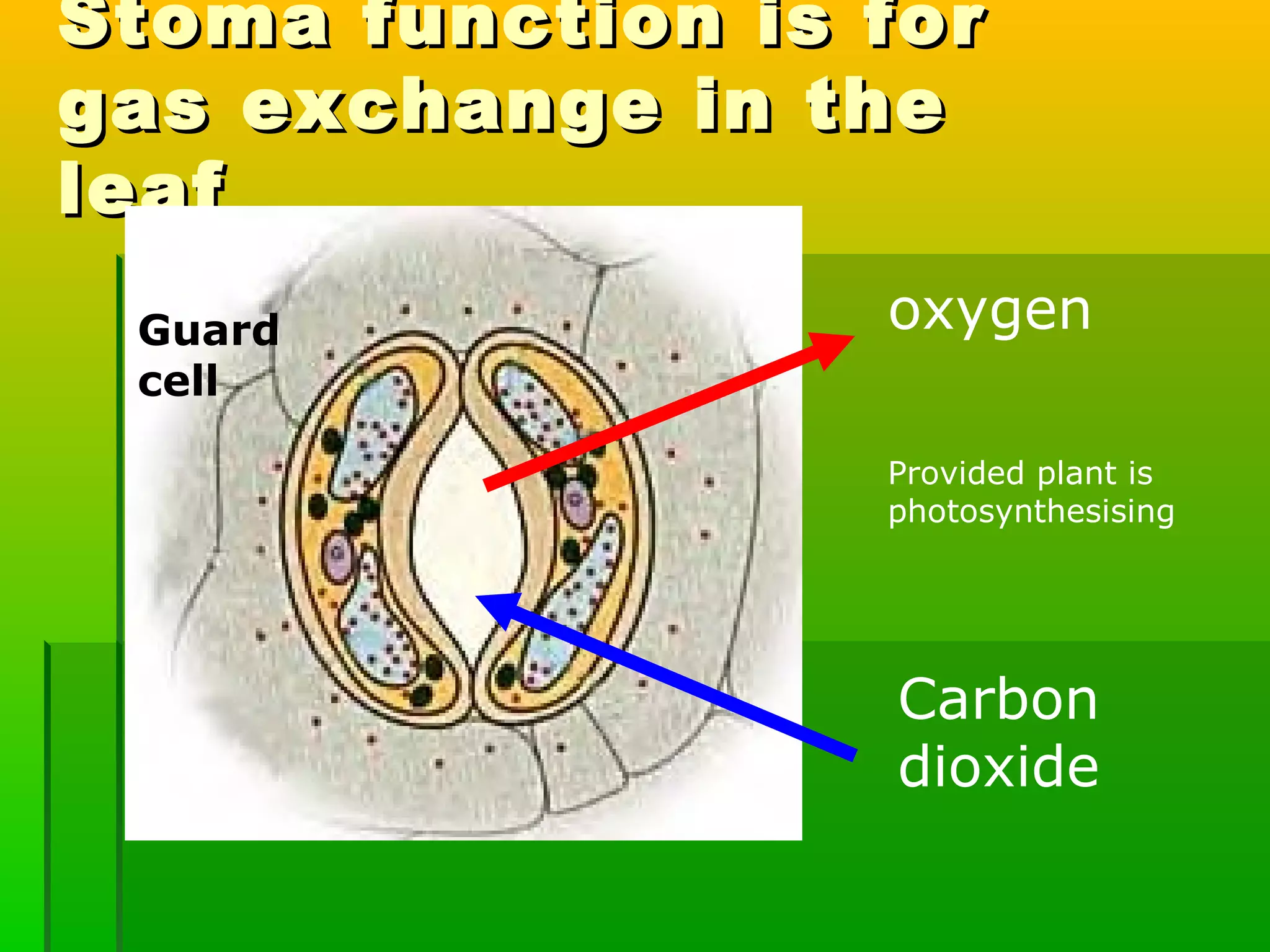
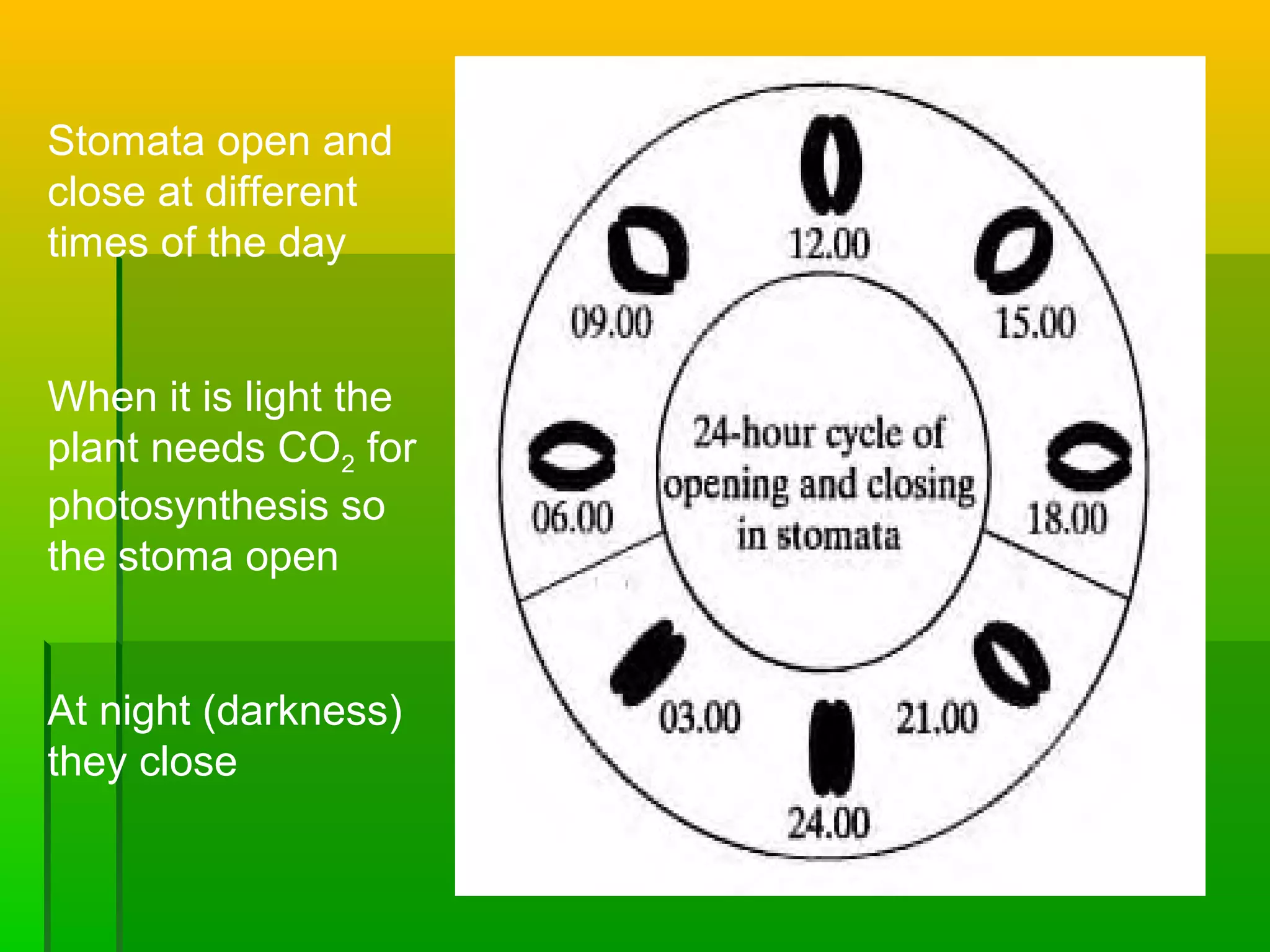
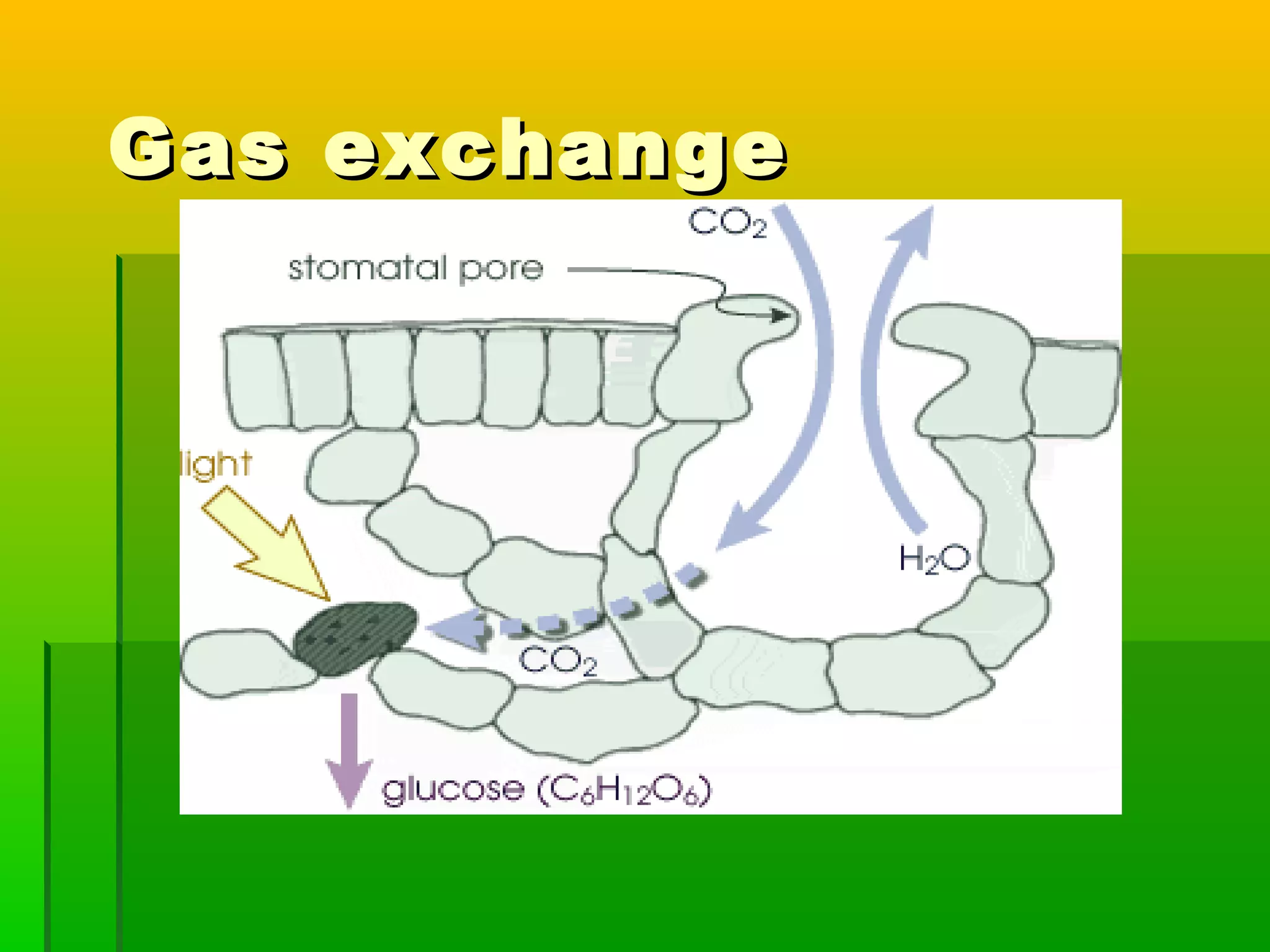
Leaves have a structure and perform functions that allow them to effectively capture light for photosynthesis and exchange gases. Leaves are typically wider at the top to catch more light, and thinner toward the bottom to allow for efficient gas exchange. They contain structures like the palisade layer and stomata that facilitate photosynthesis and the transport of carbon dioxide into the leaf and oxygen out. Stomata, which are small openings with guard cells, are primarily located on the underside of leaves and can open and close to regulate gas exchange as needed throughout the day for photosynthesis.