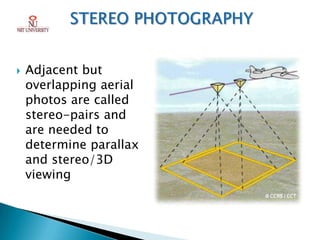
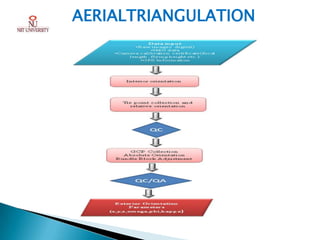
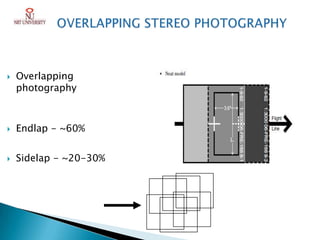
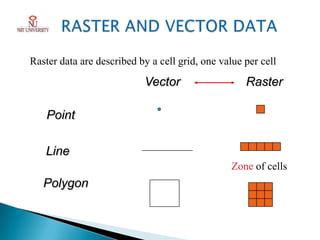
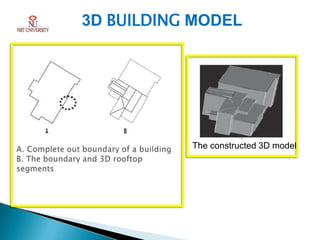
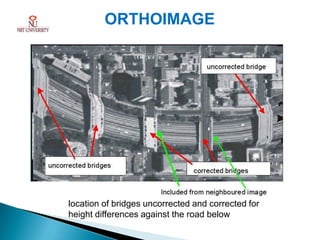
Photogrammetry is the technique of obtaining reliable spatial information about physical objects through analyzing photographs. It involves taking overlapping aerial photographs from an elevated position and processing them using software to extract 3D spatial data and produce accurate maps, models and measurements. The key outputs of photogrammetry include digital elevation models (DEMs), digital terrain models (DTMs), contour maps, orthophotos and 3D city models. Photogrammetry provides precise, cost-effective representations of geographic features and terrain.