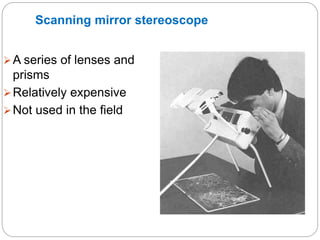
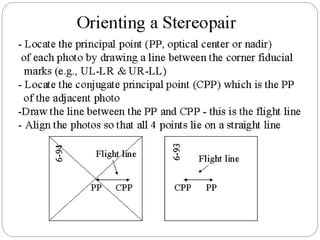
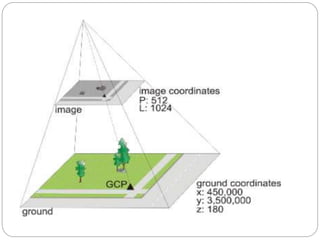
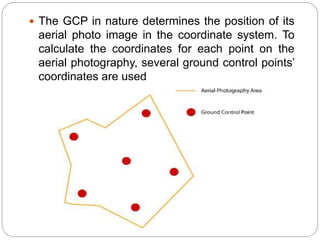
This presentation discusses stereoscopy and stereoscopes. It defines stereoscopy as using binocular vision to achieve 3D effects by viewing an object from two camera positions. Stereo pairs of photographs allow stereoscopic viewing in the overlapping portions. Various types of stereoscopes are described, including lens, mirror, scanning, and zoom stereoscopes. Lens stereoscopes are simplest and least expensive. Ground control points are also discussed as features with known coordinates that establish the relationship between an image and the ground, allowing georeferencing of aerial photographs.




![Types of Stereoscopes:
[A] Mirror
stereoscope
Photos can be placed
separately for viewing
Used in the field?
• Consist of four mirror makes an angle 45 deg with plane of photo
• Two larger Wing mirror, two eyepiece mirror](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typesofstereoscope-200408074402/85/Types-of-stereoscope-5-320.jpg)