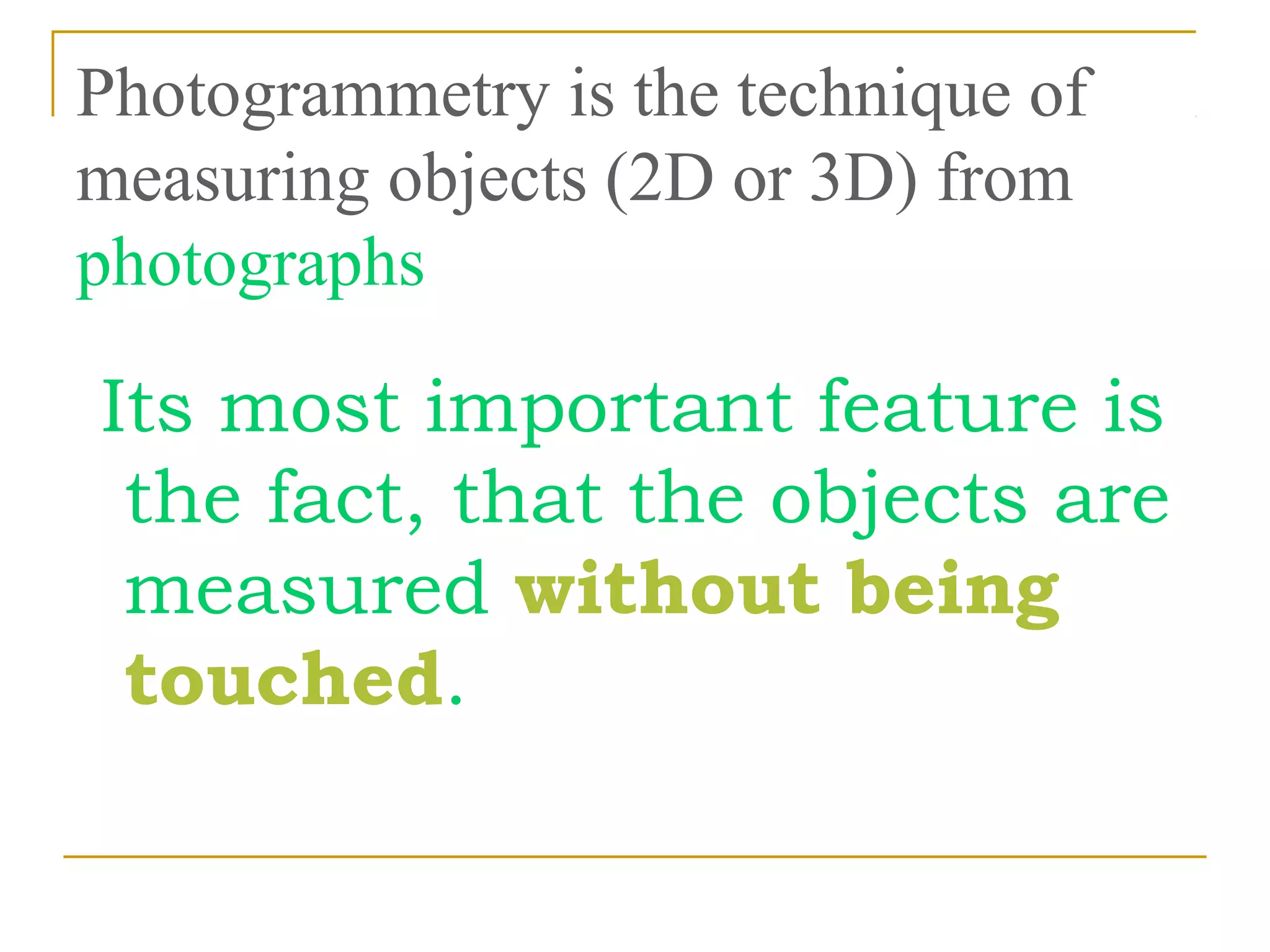
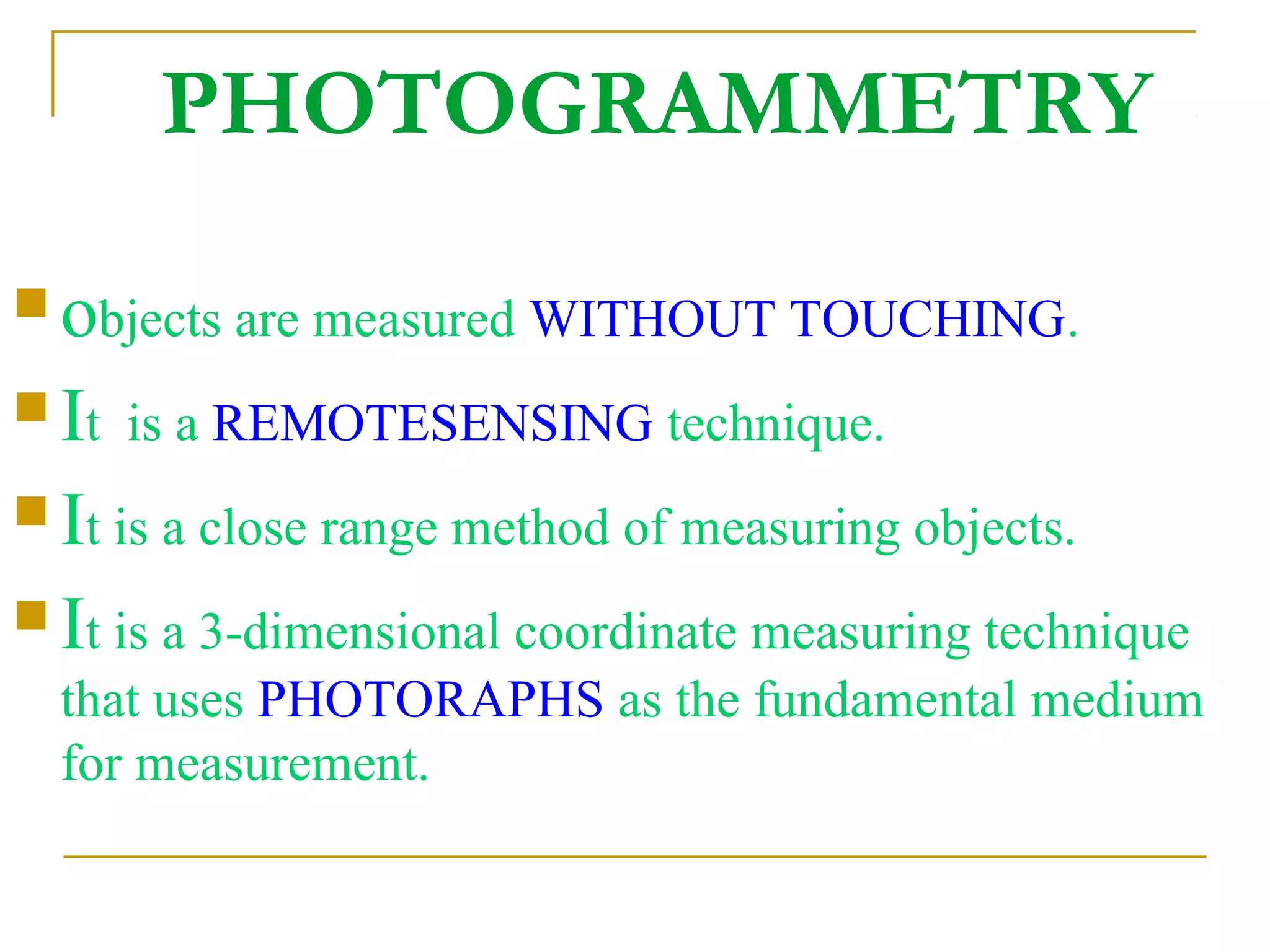
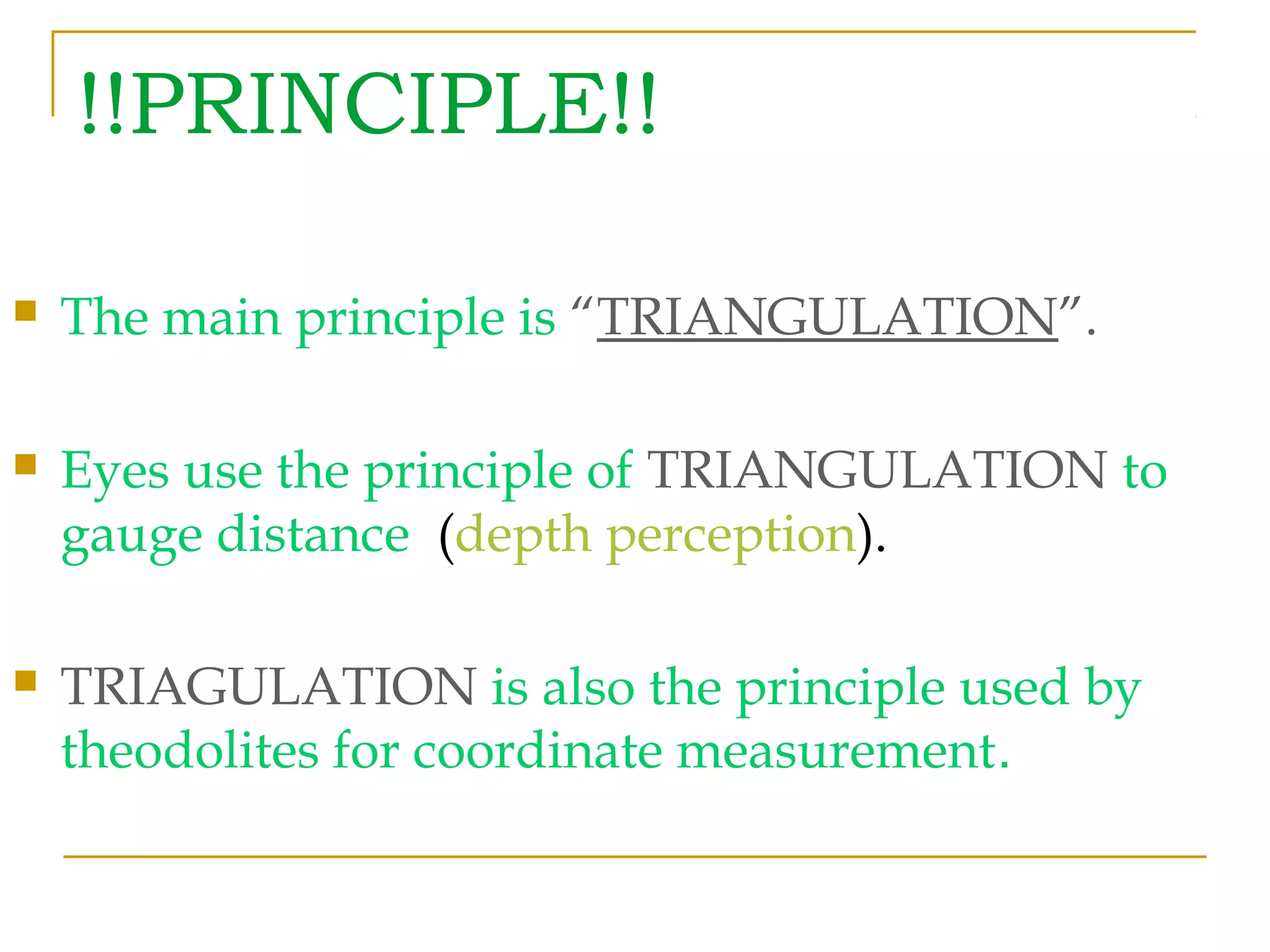
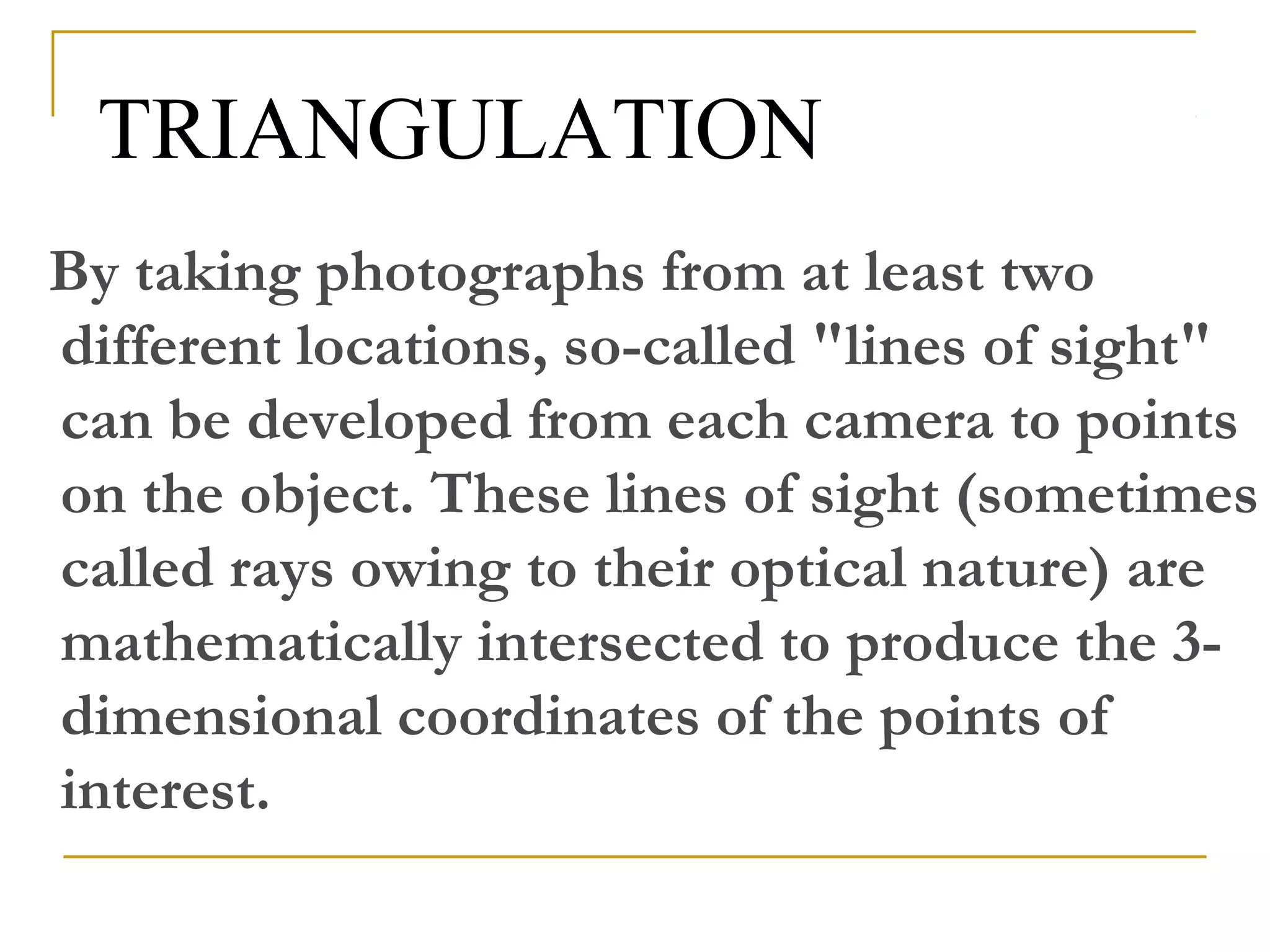
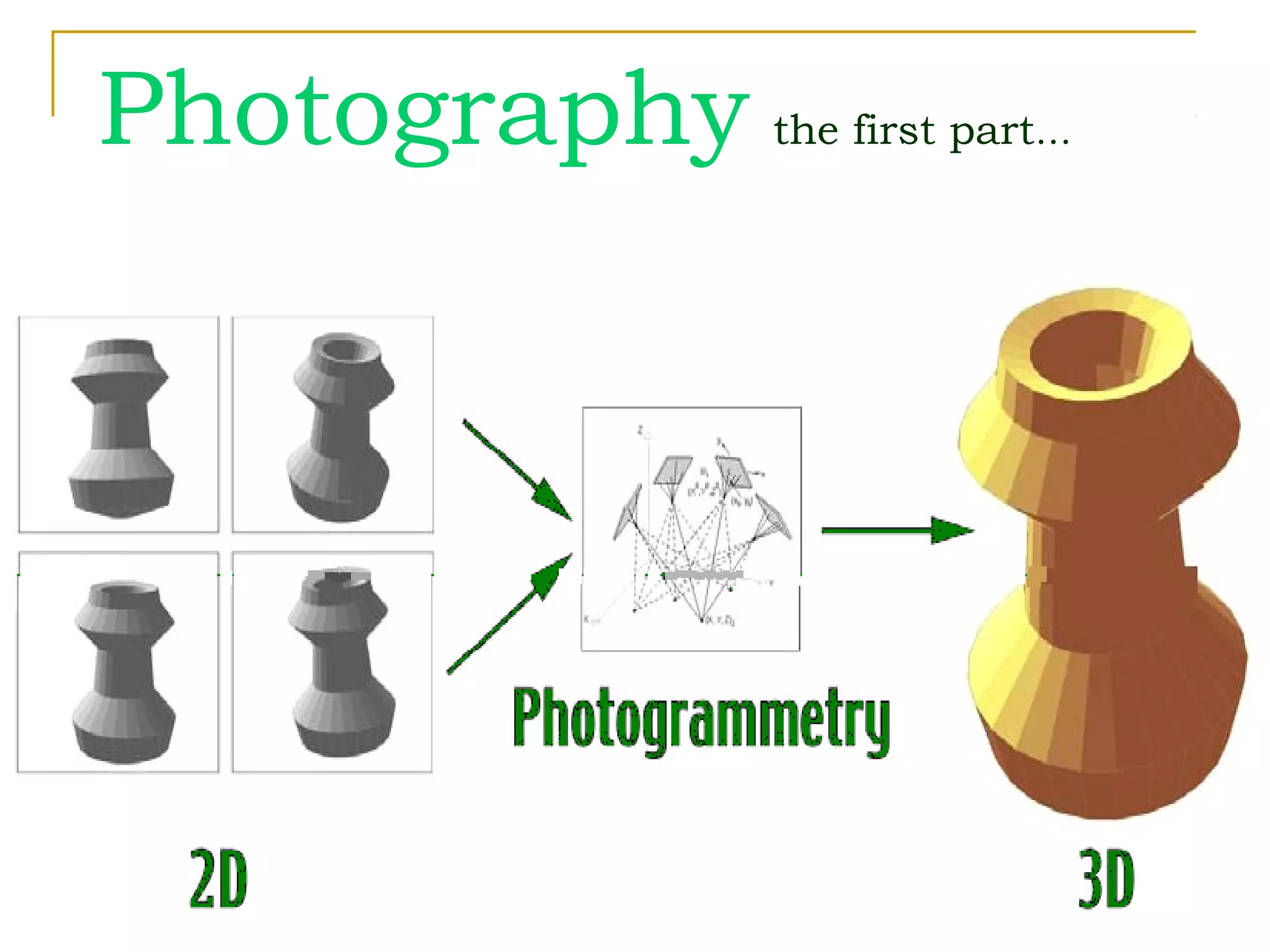
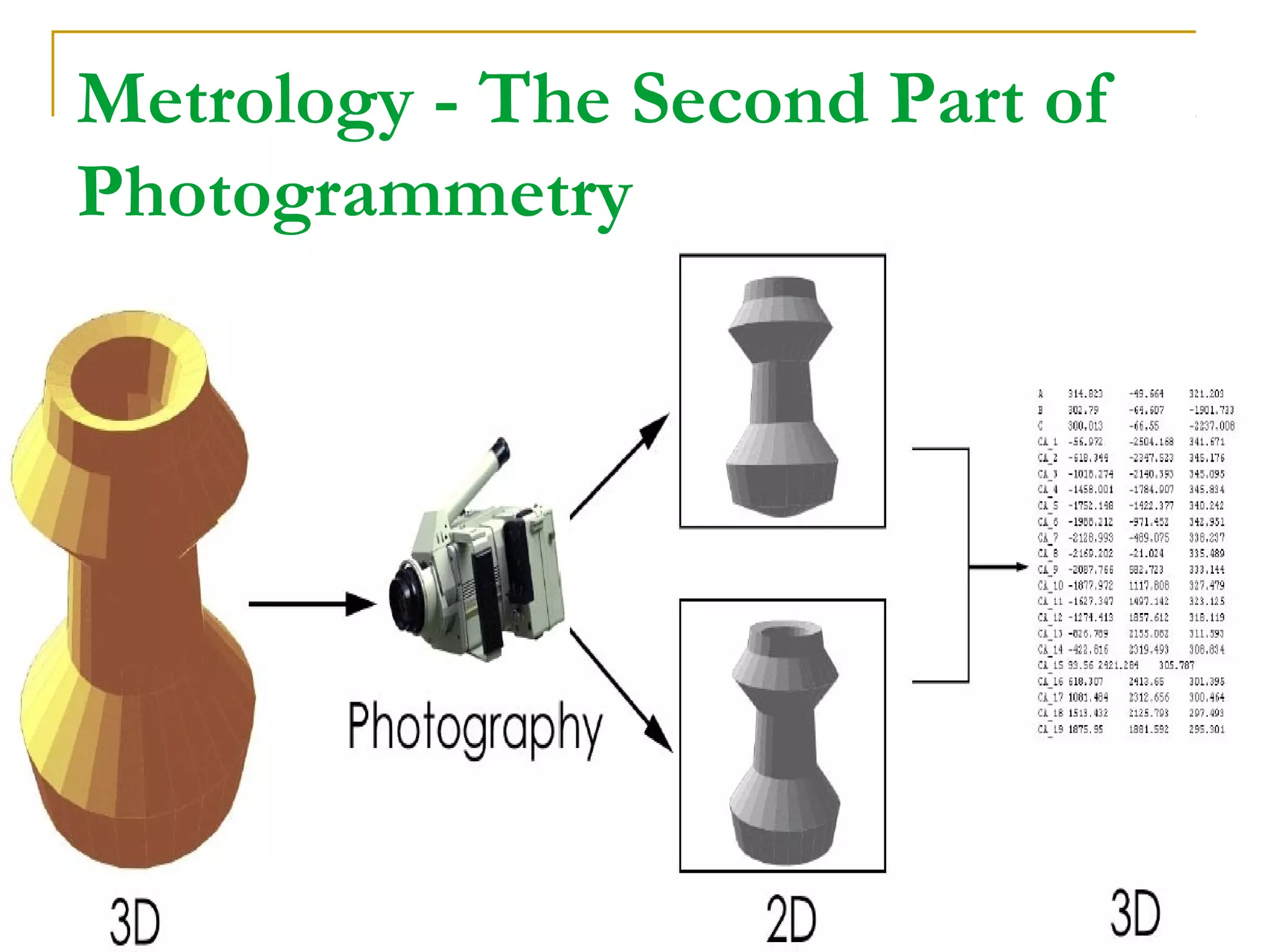
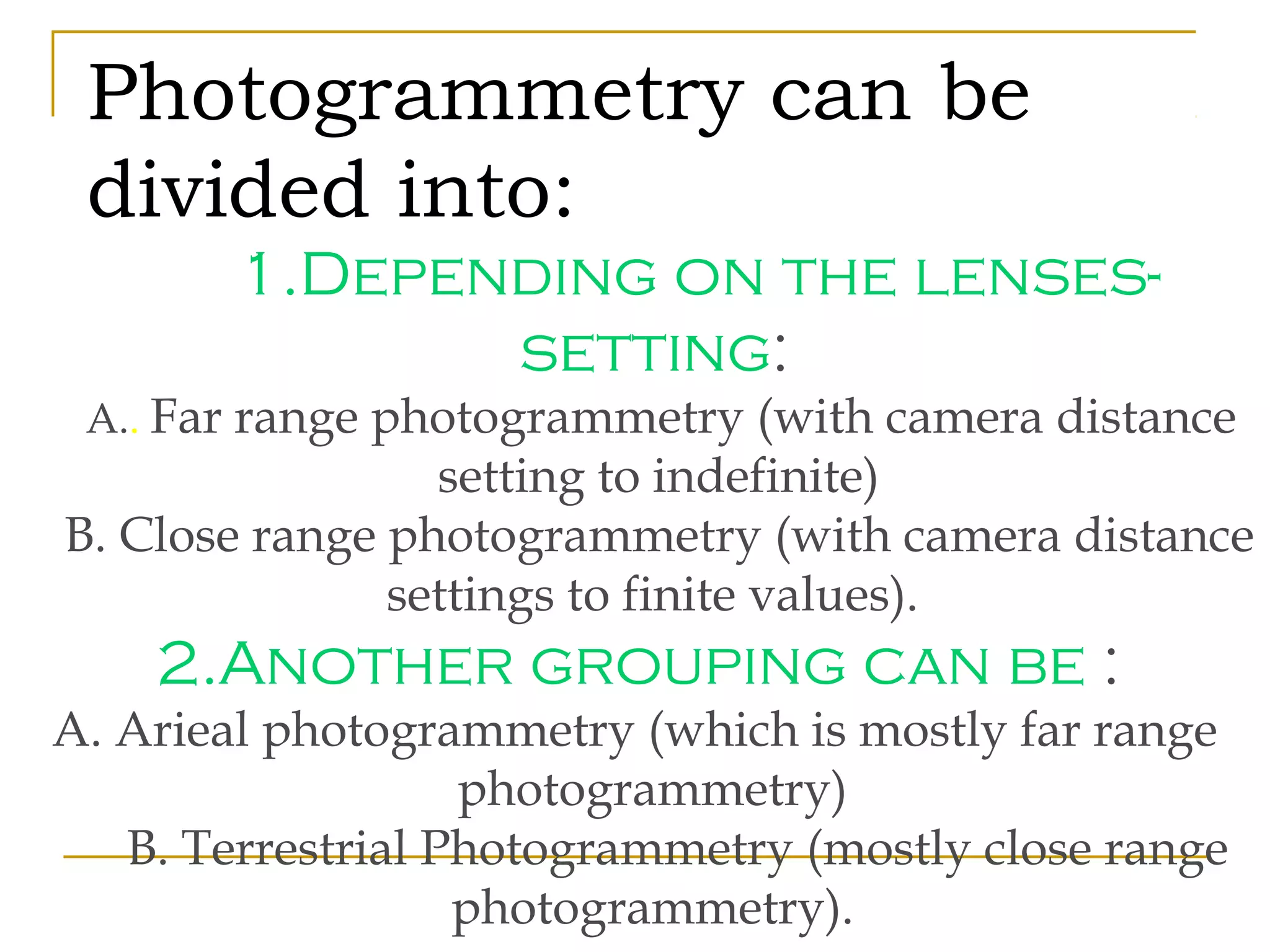
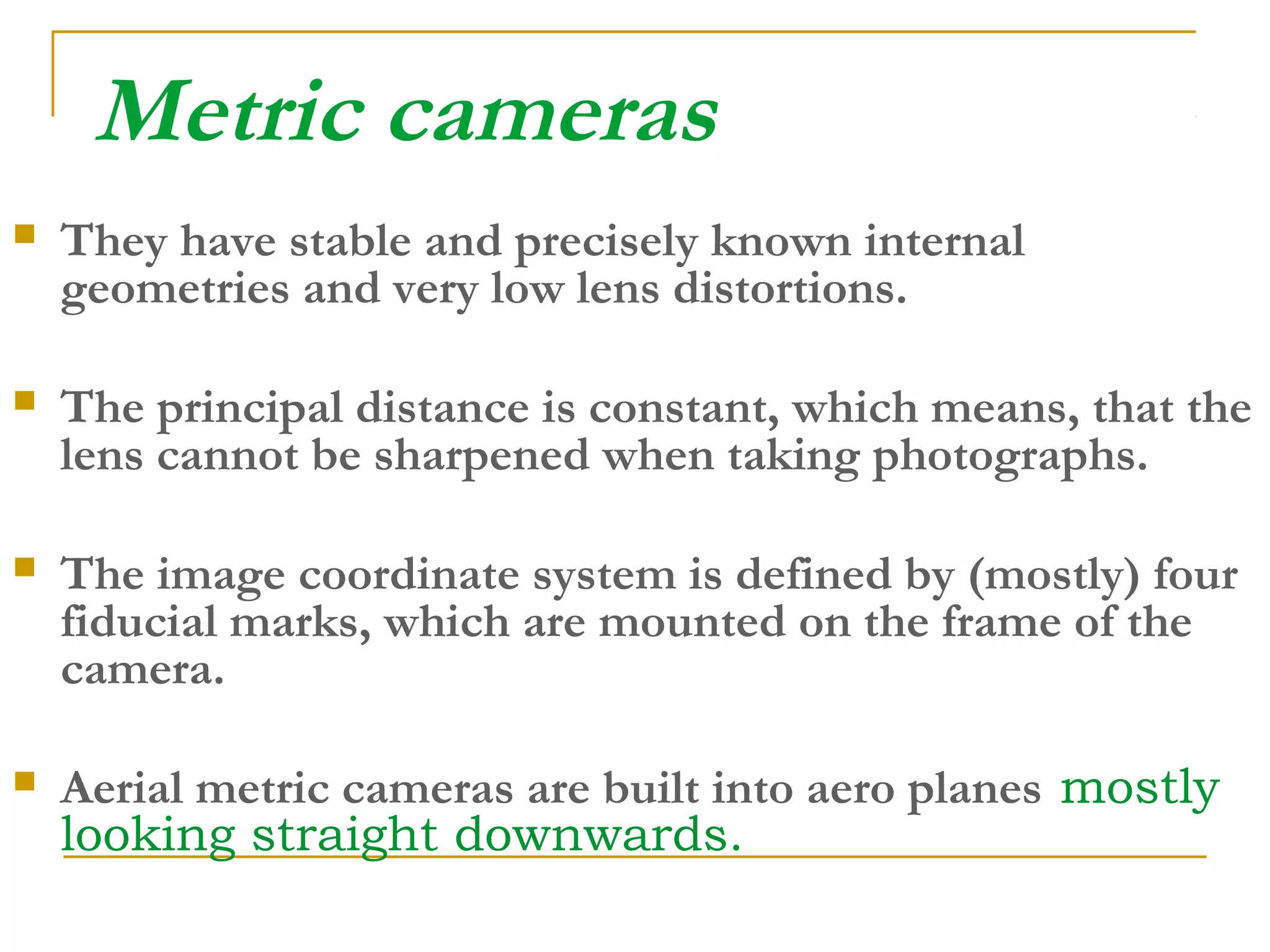
Photogrammetry is a technique for measuring objects using photographs without touching them. It involves taking photographs from different positions and using triangulation to determine the three-dimensional coordinates of points on the objects. The main principle is triangulation, which allows lines of sight from camera positions to be intersected to calculate 3D coordinates. Photogrammetry has been used since the 1850s and has evolved with improvements in computing power to allow digital photogrammetry techniques. It can be used for close-range terrestrial applications or long-range aerial applications.