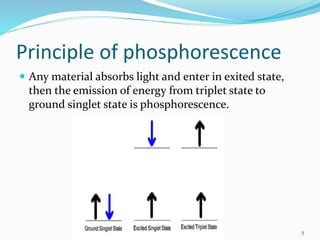
This document discusses the principle and applications of phosphorescence. Phosphorescence occurs when a material absorbs light and enters an excited state, then slowly emits light as it transitions from a triplet excited state to a ground singlet state. Common phosphors use transition metal compounds or rare earth elements as the host material doped with an activator. Phosphors have various applications including in lighting such as fluorescent lamps, glow-in-the-dark toys which use calcium or strontium sulphide phosphors, white LEDs which combine blue LEDs with yellow phosphors, and electroluminescent displays.