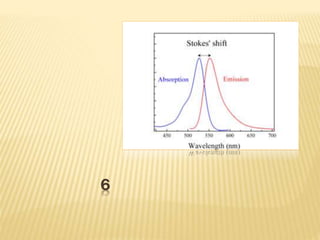
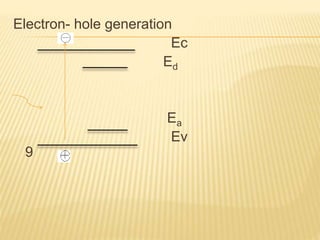
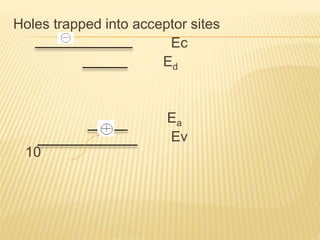
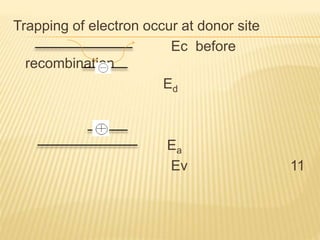
The document discusses luminescence, a phenomenon where materials emit light after absorbing energy, with a focus on photoluminescence which includes fluorescence and phosphorescence. Fluorescence occurs almost instantaneously after excitation, while phosphorescence can result in light emission over minutes to days. Applications include fluorescent lamps and display devices that harness these luminescent properties for improved visual output.